

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIG-21-006 | ||
| Search for CP violation in $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H and $\mathrm{t}$H production in multilepton channels at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| March 2022 | ||
| Abstract: We measure the CP structure of the Yukawa interaction between the Higgs boson (H) and one or two top quarks in a data sample enriched in the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H and $\mathrm{t}$H associated production, using 138 fb$^{-1}$ of data collected in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV by the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC, and targeting events where the H decays via H $\to$ WW or H $\to\tau\tau$ and top quarks decay either leptonically or hadronically. We apply machine learning techniques to final states characterized by the presence of at least two leptons to enhance the separation of CP-even from CP-odd scenarios. Two-dimensional confidence regions are set on the ratios $\kappa_{t}$ and $\tilde{\kappa_{t}}$ of the couplings of CP-even and CP-odd Lagrangian terms, respectively, to the SM expectation for the top-Higgs Yukawa coupling. Fractionary CP-odd contributions are not observed; the corresponding $f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}$ parameter is determined to be $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| = $ 0.59 with an interval of (0.24, 0.81) at 68% confidence level. The results are combined with previously published analyses covering the H $\to\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}$ and H $\to\gamma\gamma$ decay modes, yielding two- and one-dimensional confidence regions on $\kappa_{t}$ and $\tilde{\kappa_{t}}$, while $f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}$ is determined to be $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| = $ 0.28 with an interval of $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| < $ 0.55 at 68% confidence level. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, Submitted to JHEP. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
Figure 1:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{\bar{t}} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
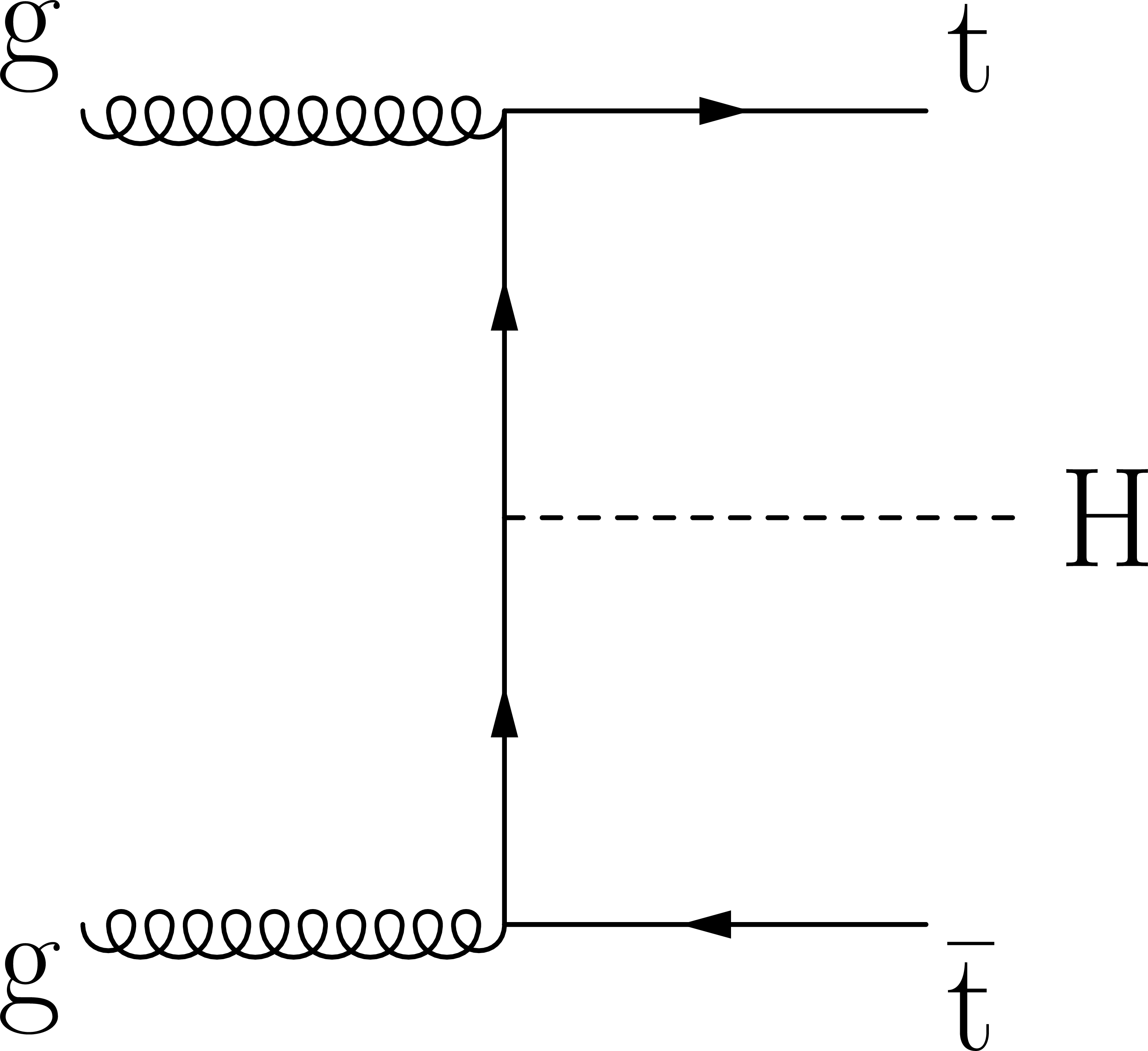
Figure 1-a:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{\bar{t}} $H production processes. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{\bar{t}} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
Figure 2:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} $-channel $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |
png pdf |
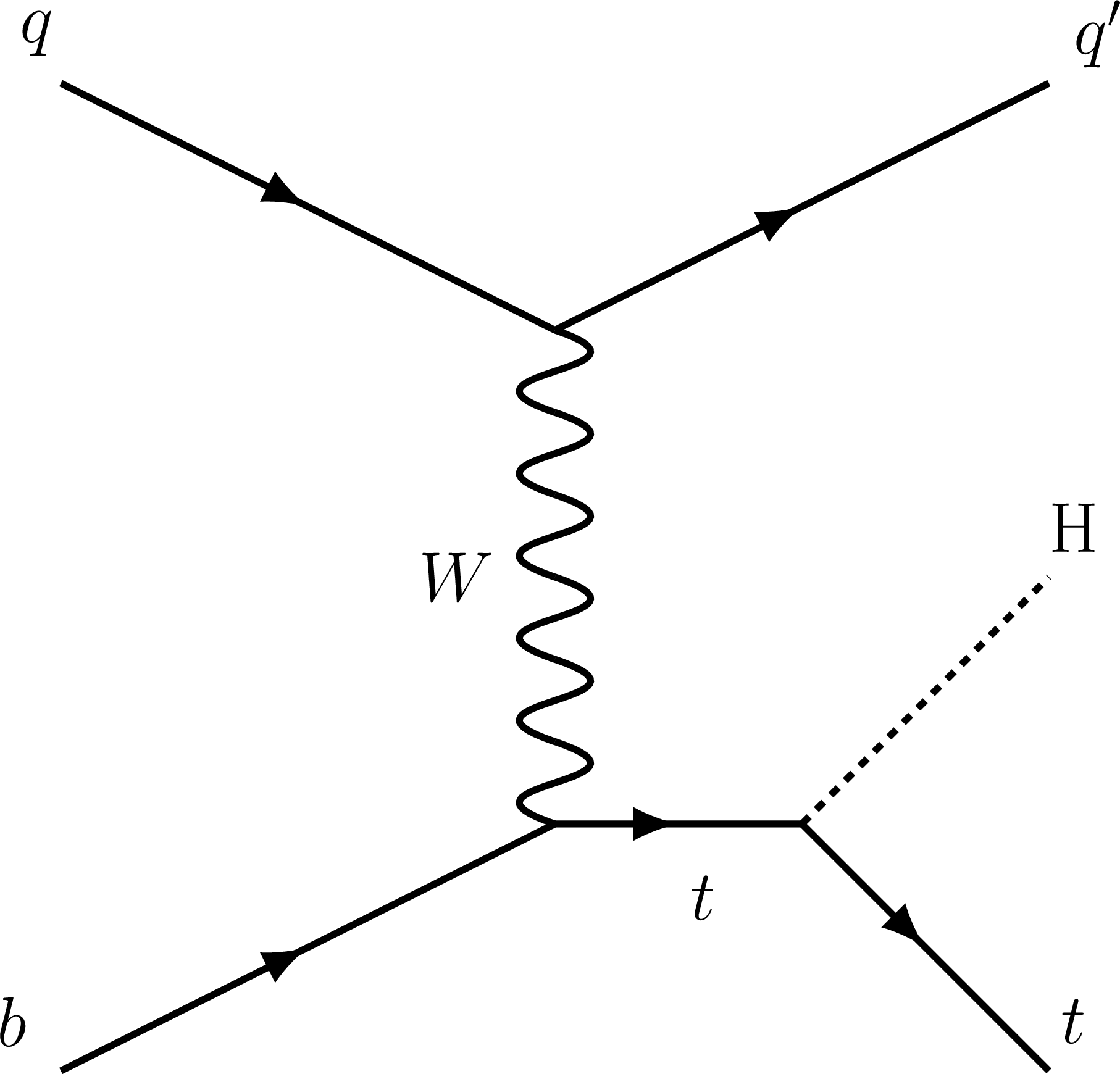
Figure 2-a:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} $-channel $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |
png pdf |
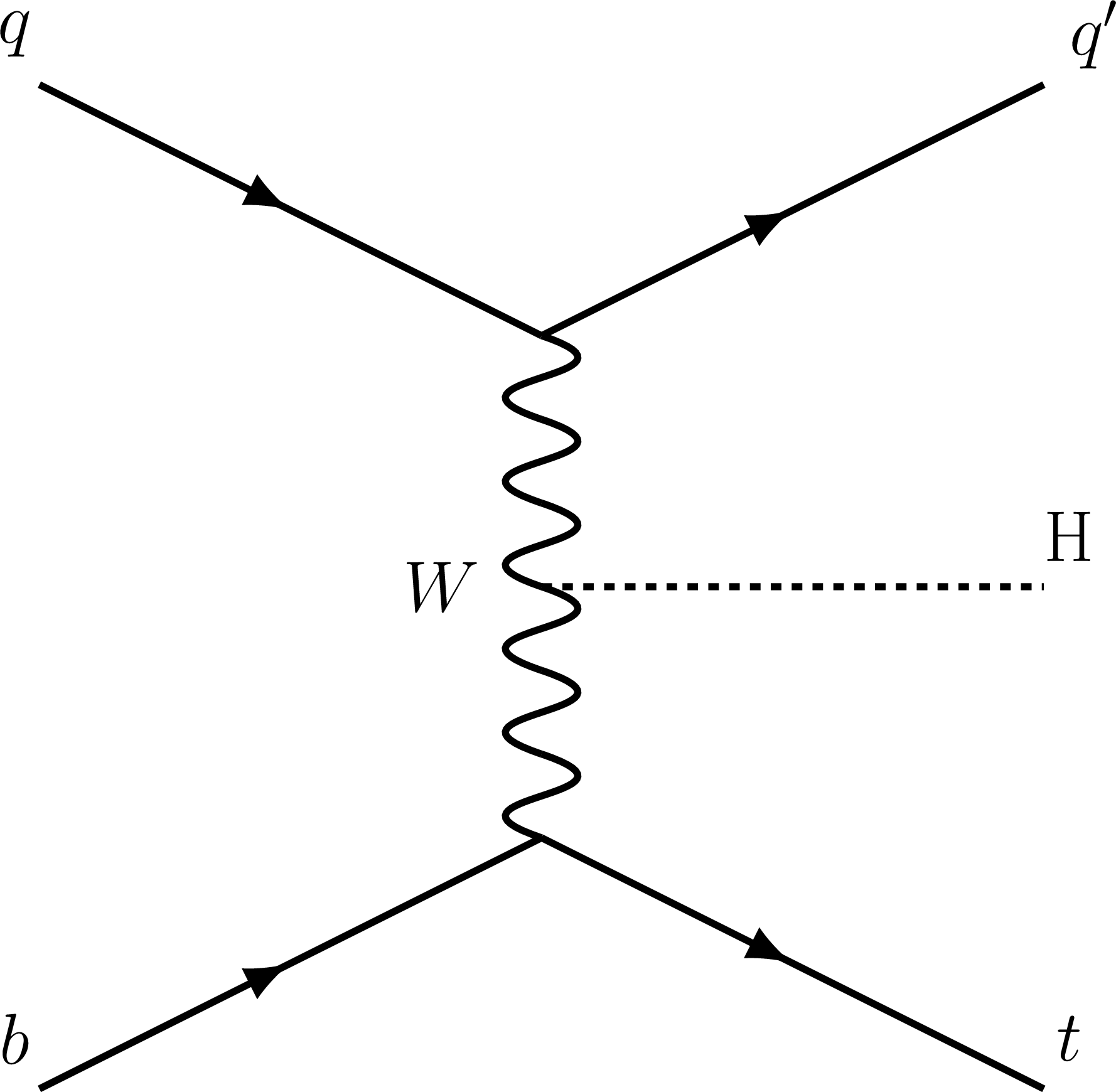
Figure 2-b:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} $-channel $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
Figure 3:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{W} $-associated $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |
png pdf |
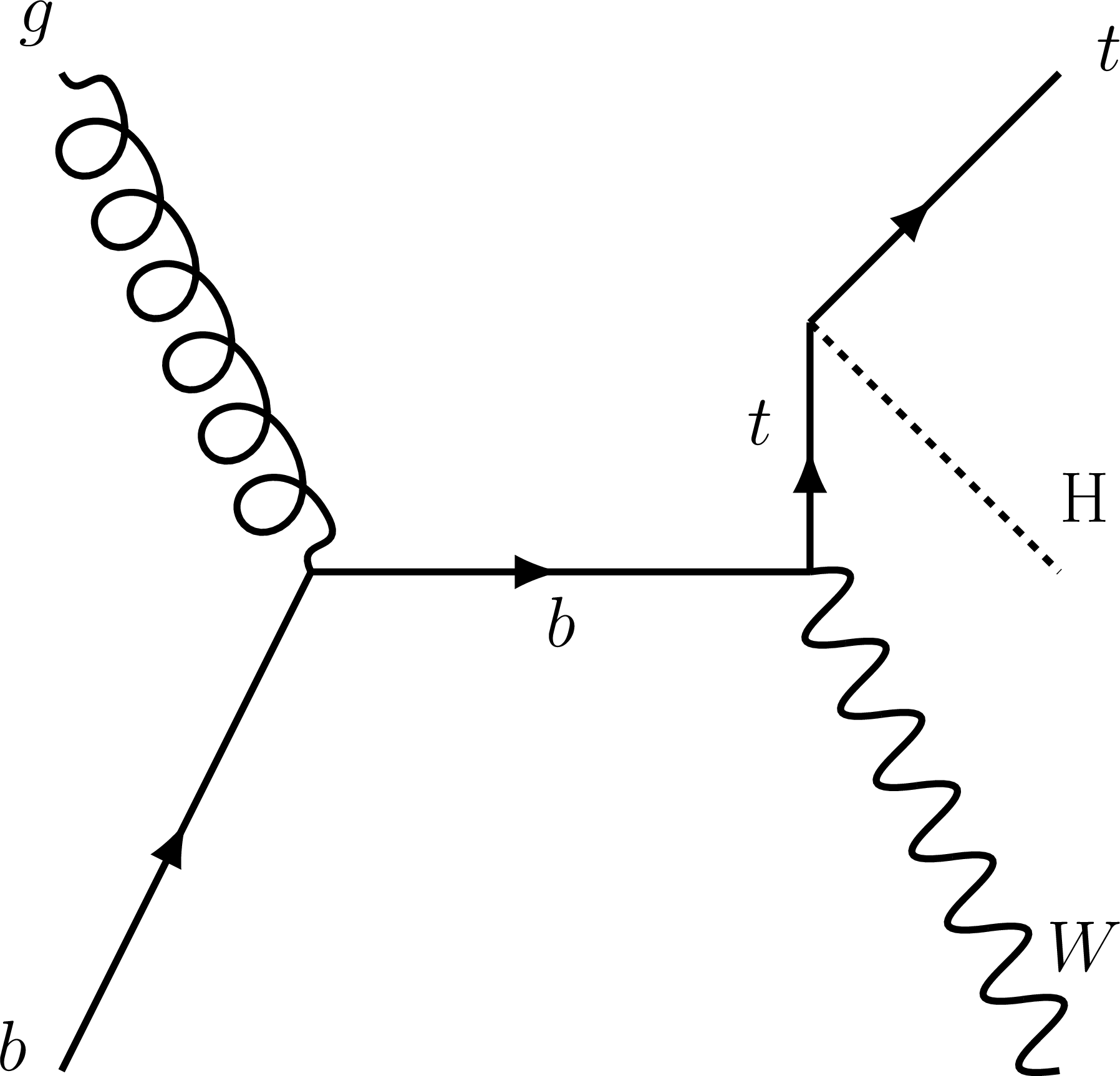
Figure 3-a:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{W} $-associated $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Representative Feynman diagrams for the $\mathrm{t} \mathrm{W} $-associated $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
Figure 4:
Representative Feynman diagram for the s-channel $\mathrm{t} $H production processes. |

png pdf |
Figure 5:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |

png pdf |
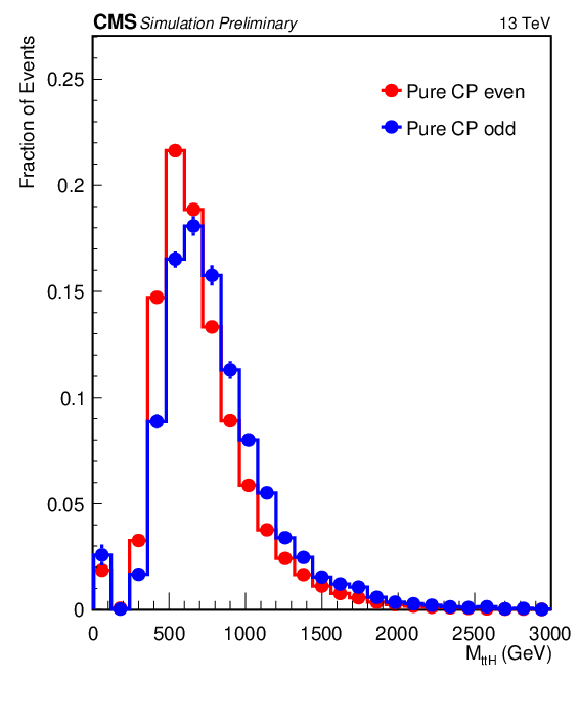
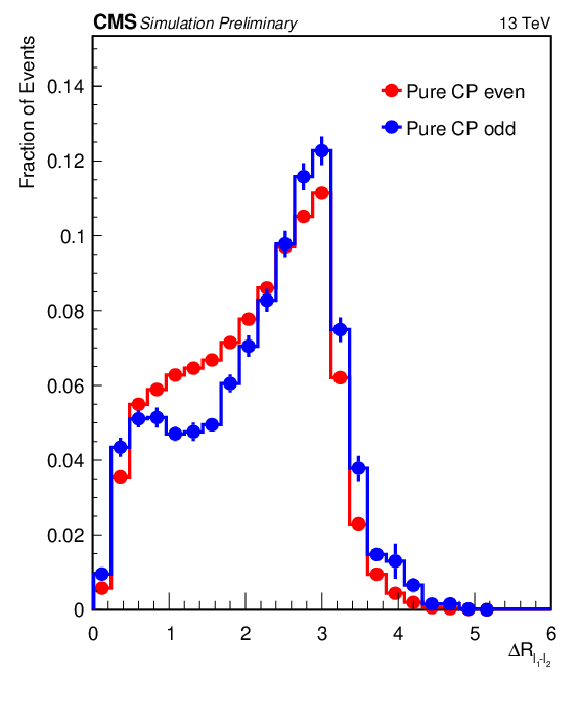
Figure 5-a:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |

png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
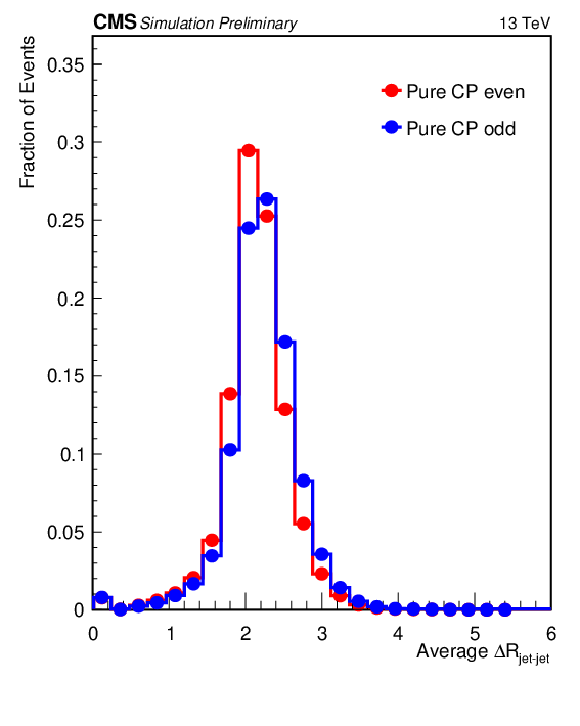
png pdf |
Figure 5-c:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
png pdf |
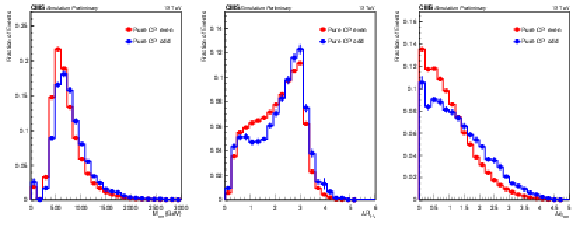
Figure 6:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
png pdf |
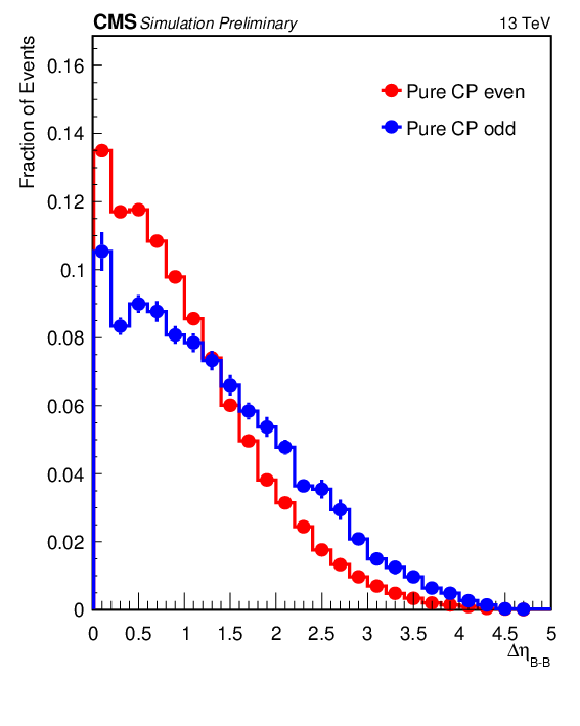
Figure 6-c:
Most important input variables to the XGBoost used for CP discrimination in 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ channel. The vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainty originating from the limited amount of simulated events. When not visible, the bars are smaller than the marker size. |
png pdf |
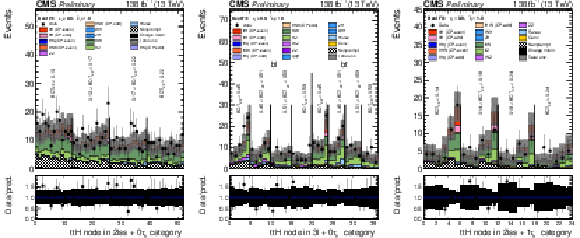
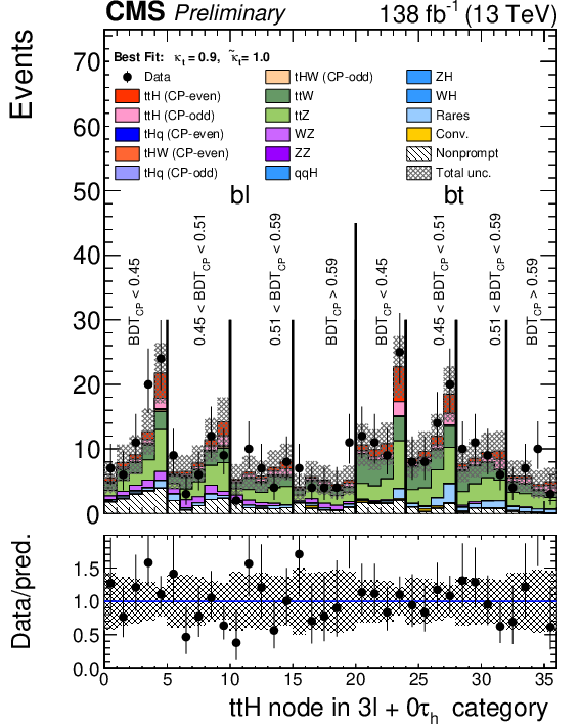
Figure 7:
Postfit plots of the discriminating variables in the SR used as input to the fit in each of the categories: 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (left) 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (centre) and 2$ \ell $SS+1$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (right). The blue line shows the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP odd contribution normalized to the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H SM cross section; the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP even contribution is shown in red and is stacked with the backgrounds. |
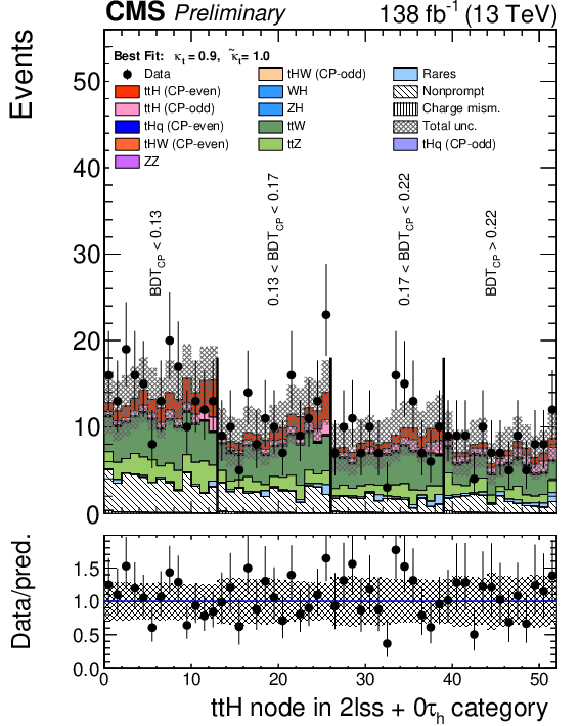
png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
Postfit plots of the discriminating variables in the SR used as input to the fit in each of the categories: 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (left) 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (centre) and 2$ \ell $SS+1$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (right). The blue line shows the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP odd contribution normalized to the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H SM cross section; the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP even contribution is shown in red and is stacked with the backgrounds. |
png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
Postfit plots of the discriminating variables in the SR used as input to the fit in each of the categories: 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (left) 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (centre) and 2$ \ell $SS+1$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (right). The blue line shows the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP odd contribution normalized to the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H SM cross section; the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP even contribution is shown in red and is stacked with the backgrounds. |
png pdf |
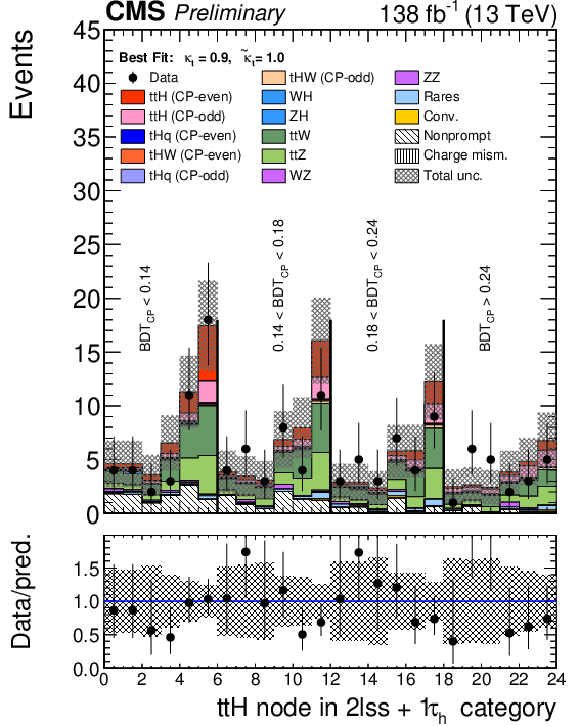
Figure 7-c:
Postfit plots of the discriminating variables in the SR used as input to the fit in each of the categories: 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (left) 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (centre) and 2$ \ell $SS+1$\tau _\mathrm {h}$ (right). The blue line shows the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP odd contribution normalized to the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H SM cross section; the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H CP even contribution is shown in red and is stacked with the backgrounds. |
png pdf |
Figure 8:
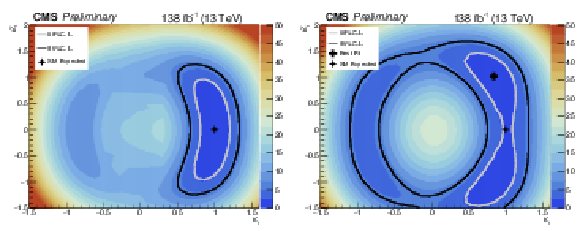
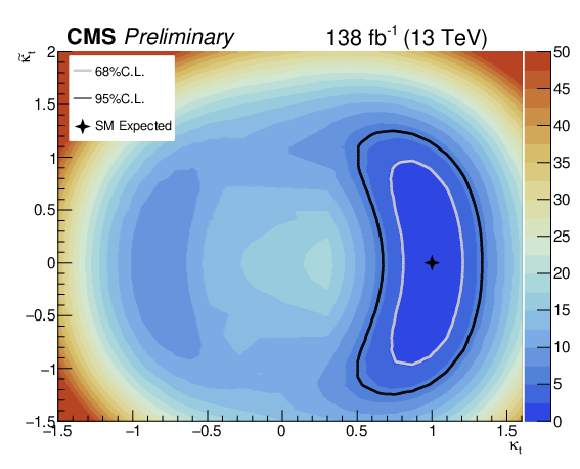
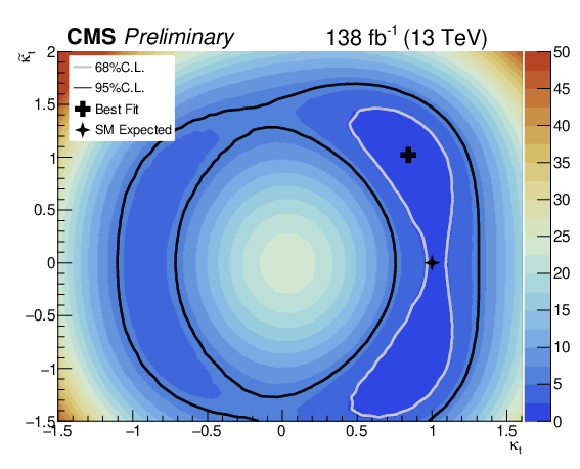
Likelihood scan as a function of $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Left plot shows the expected limits, while right plot shows the observed ones. Black diamond shows the best value for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$ given by the fit. Black cross shows the expected SM values for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Both 68 and 95% CL limits are shown. |
png pdf |
Figure 8-a:
Likelihood scan as a function of $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Left plot shows the expected limits, while right plot shows the observed ones. Black diamond shows the best value for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$ given by the fit. Black cross shows the expected SM values for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Both 68 and 95% CL limits are shown. |
png pdf |
Figure 8-b:
Likelihood scan as a function of $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Left plot shows the expected limits, while right plot shows the observed ones. Black diamond shows the best value for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$ given by the fit. Black cross shows the expected SM values for $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Both 68 and 95% CL limits are shown. |
png pdf |
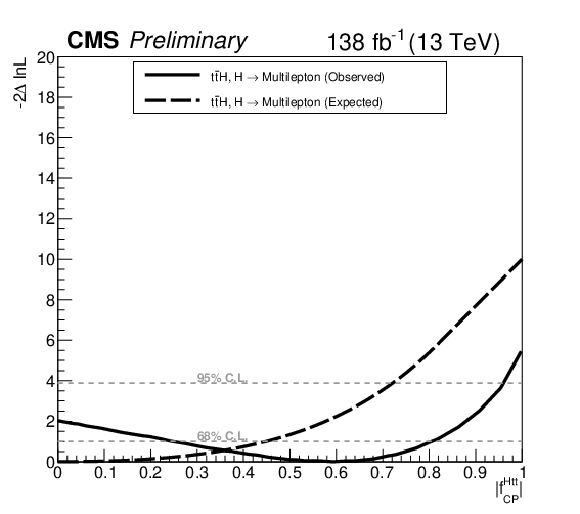
Figure 9:
Likelihood scan as a function of $f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}$ for multilepton final estates. The solid (dashed) line shows the observed (expected) scan. |
png pdf |
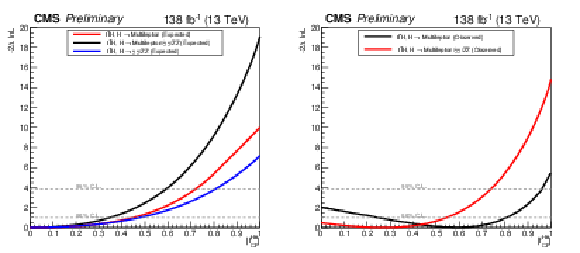
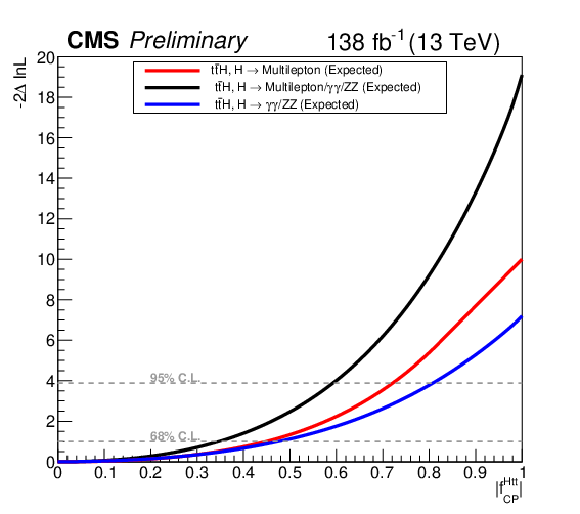
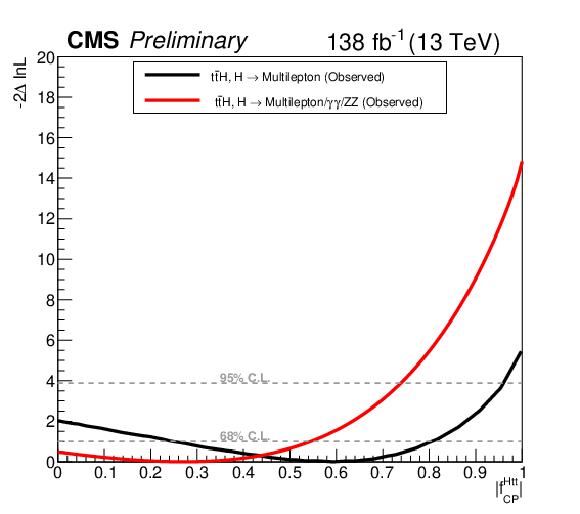
Figure 10:
Likelihood scan as a function of $f^{\text{Htt}}_{CP}$. Left plot shows the expected Likelihood scan for multilepton final states, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states, and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. Right plot shows the observed Likelihood scan for multilepton final states and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. |
png pdf |
Figure 10-a:
Likelihood scan as a function of $f^{\text{Htt}}_{CP}$. Left plot shows the expected Likelihood scan for multilepton final states, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states, and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. Right plot shows the observed Likelihood scan for multilepton final states and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. |
png pdf |
Figure 10-b:
Likelihood scan as a function of $f^{\text{Htt}}_{CP}$. Left plot shows the expected Likelihood scan for multilepton final states, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states, and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. Right plot shows the observed Likelihood scan for multilepton final states and the combination of multilepton, H $ \to \gamma \gamma $, and H $ \to $ ZZ final states. |
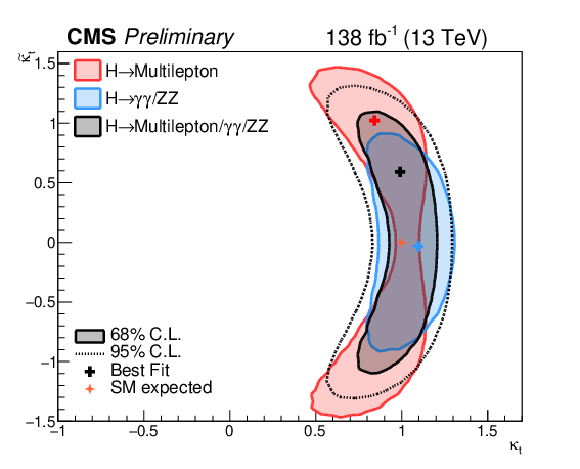
png pdf |
Figure 11:
Likelihood scan as a function of $ {\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $ {\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. Two-dimensional confidence intervals at 68% CL are shown for multilepton final states, the combination of H $ \to \gamma \gamma $ and H $ \to $ ZZ, and the combination of the three channels. |
| Tables | |
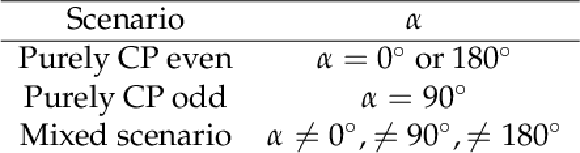
png pdf |
Table 1:
Possible CP scenarios |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Standard model cross sections for the $\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H and $\mathrm{t}$H signals as well as for the most relevant background processes. The cross sections are quoted for pp collisions at $\sqrt {s} = $ 13 TeV. The quoted value for DY production includes a generator-level requirement of $m_{\mathrm{Z} /\gamma ^*} > $ 50 GeV. |

png pdf |
Table 3:
Event selections applied in the 2$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$, 2$ \ell $SS+1$\tau _\mathrm {h}$, 3$ \ell $SS+0$\tau _\mathrm {h}$. |
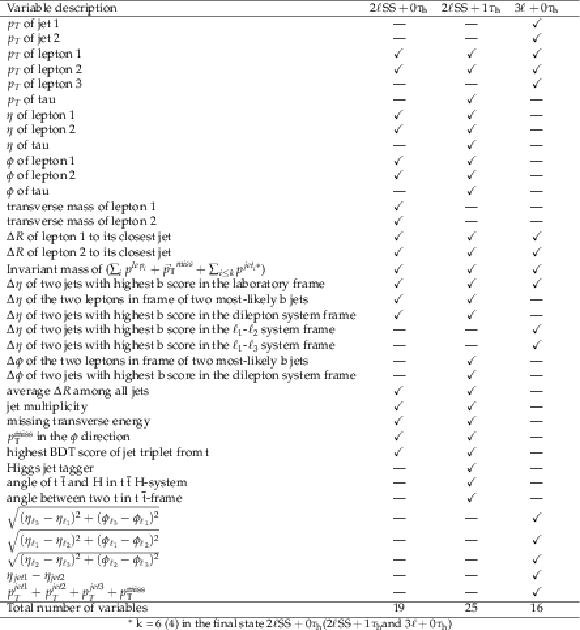
png pdf |
Table 4:
Input features for the three BDTs. A check mark v) indicates the variable is used in a given final state, wherease a long dash (--) indicates the variable is not used in that final state. |
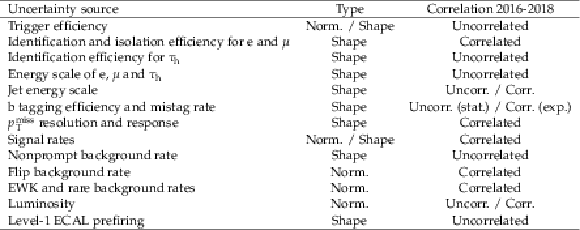
png pdf |
Table 5:
Summary of the main uncertainty sources, their type and the correlations across the three data-taking periods. |
png pdf |
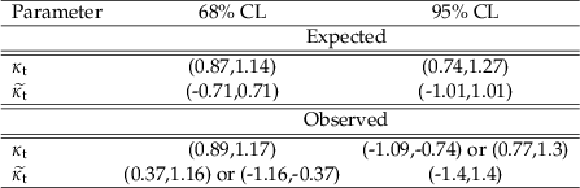
Table 6:
One-dimensional confidence intervals at 68 and 95% CL for ${\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and ${\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. The upper part of the table shows the expected limits while the lower part shows the observed limits |
png pdf |
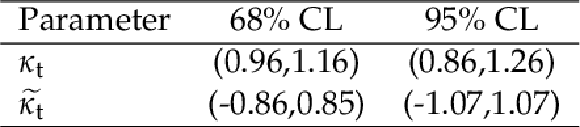
Table 7:
One-dimensional confidence intervals at 68 and 95% CL for ${\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}$ and ${\tilde{\kappa _{\mathrm{t}}}}$. |
| Summary |
| A measurement of the CP structure of the Yukawa coupling between the Higgs boson (H) and top quarks at tree level, when H is produced in association with one ($\mathrm{t}$H) or two ($\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}$H) top quarks, is presented. The measurement is based on data collected in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV by the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$^{-1}$. The analysis targets events where the H decays via H $\to\mathrm{W}\mathrm{W}$ or H $\to\tau\tau$ and the top quark(s) decay either leptonically or hadronically. Separation of CP-even from CP-odd scenarios is achieved by applying machine learning techniques to final states characterized by the presence of at least two leptons. Two-dimensional confidence regions are set on the ratios ${\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $\tilde{\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ of the couplings of CP-even and CP-odd Lagrangian terms, respectively, to the SM expectation for the top-Higgs Yukawa coupling: one-dimensional confidence intervals are also set, constraining ${\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ to be within $(-1.09, -0.74)$ or $(0.77, 1.30)$ and $\tilde{\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ to be within ($-$1.4, 1.4) at 95% confidence level (CL). No fractional contribution is observed, and the corresponding $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}|$ parameter is determined to be $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| = $ 0.59 with an interval of $(0.24, 0.81)$ at 68% CL. The results are combined with previously published analyses covering the H $\to\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}$ and H $\to\gamma\gamma$ decay modes. Two- and one-dimensional confidence regions are set on ${\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ and $\tilde{\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$, constraining ${\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ to be within (0.86, 1.26) and $\tilde{\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}}$ to be within ($-$1.07, 1.07) at 95% CL. Fractional contribution is also investigated in the combination, yielding a best fit of $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| = $ 0.28 and an interval of $|f_{CP}^{\text{Htt}}| < $ 0.55 at 68% CL. The results are compatible with predictions for the standard model H. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1 | 1207.7214 |
| 2 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 3 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonances decaying to a pair of Higgs bosons in the $ \mathrm{b\overline{b}q\overline{q}'}\ell\nu $ final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 10 (2019) 125 | 1904.04193 |
| 4 | CMS Collaboration | A measurement of the Higgs boson mass in the diphoton decay channel | PLB 805 (2020) 135425 | |
| 5 | CMS Collaboration | Precise determination of the mass of the Higgs boson and tests of compatibility of its couplings with the standard model predictions using proton collisions at 7 and 8 TeV | EPJC 75 (2015) 212 | CMS-HIG-14-009 1412.8662 |
| 6 | CMS Collaboration | Combined measurements of Higgs boson couplings in proton--proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}=$ 13 TeV | EPJC 79 (2019) 421 | CMS-HIG-17-031 1809.10733 |
| 7 | ATLAS, CDF, CMS, and DO Collaborations | First combination of Tevatron and LHC measurements of the top-quark mass | 1403.4427 | |
| 8 | B. A. Dobrescu and C. T. Hill | Electroweak symmetry breaking via top condensation seesaw | PRL 81 (1998) 2634 | hep-ph/9712319 |
| 9 | R. S. Chivukula, B. A. Dobrescu, H. Georgi, and C. T. Hill | Top Quark Seesaw Theory of Electroweak Symmetry Breaking | PRD 59 (1999) 075003 | hep-ph/9809470 |
| 10 | D. Delepine, J. M. Gerard, and R. Gonzalez Felipe | Is the standard Higgs scalar elementary? | PLB 372 (1996) 271 | hep-ph/9512339 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Search for the associated production of the Higgs boson with a top-quark pair | JHEP 09 (2014) 087 | CMS-HIG-13-029 1408.1682 |
| 12 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the Standard Model Higgs boson produced in association with top quarks and decaying into $ \mathrm{b\bar{b}} $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 75 (2015) 349 | 1503.05066 |
| 13 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the Standard Model Higgs boson decaying into $ \mathrm{b\bar{b}} $ produced in association with top quarks decaying hadronically in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 05 (2016) 160 | 1604.03812 |
| 14 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the associated production of the Higgs boson with a top quark pair in multilepton final states with the ATLAS detector | PLB 749 (2015) 519 | 1506.05988 |
| 15 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for $ \mathrm{H} \to \gamma\gamma $ produced in association with top quarks and constraints on the Yukawa coupling between the top quark and the Higgs boson using data taken at 7 TeV and 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 740 (2015) 222 | 1409.3122 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of properties of the Higgs boson decaying into the four-lepton final state in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2017) 047 | CMS-HIG-16-041 1706.09936 |
| 17 | ATLAS Collaboration | Evidence for the associated production of the Higgs boson and a top quark pair with the ATLAS detector | PRD 97 (2018) 072003 | 1712.08891 |
| 18 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the standard model Higgs boson produced in association with top quarks and decaying into a $ b\bar{b} $ pair in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 97 (2018) 072016 | 1712.08895 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for associated production of a Higgs boson with a top quark pair in final states with electrons, muons, and hadronically decaying $ \tau $ leptons at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 08 (2018) 066 | CMS-HIG-17-018 1803.05485 |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | Search for $ \mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}} $H production in the all-jet final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 06 (2018) 101 | CMS-HIG-17-022 1803.06986 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of Higgs boson properties in the diphoton decay channel in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2018) 185 | CMS-HIG-16-040 1804.02716 |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Search for $ \mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}\mathrm{H} $ production in the $ \mathrm{H}\to \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ decay channel with leptonic $ \mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}} $ decays in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 03 (2019) 026 | CMS-HIG-17-026 1804.03682 |
| 23 | ATLAS Collaboration | $ CP $ Properties of Higgs Boson Interactions with Top Quarks in the $ t\bar{t}H $ and $ tH $ Processes Using $ H \rightarrow \gamma\gamma $ with the ATLAS Detector | PRL 125 (2020) 061802 | 2004.04545 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of $ \mathrm{t\bar{t}}H $ Production and the CP Structure of the Yukawa Interaction between the Higgs Boson and Top Quark in the Diphoton Decay Channel | PRL 125 (2020) 061801 | CMS-HIG-19-013 2003.10866 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the Higgs boson production rate in association with top quarks in final states with electrons, muons, and hadronically decaying tau leptons at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-HIG-19-008 2011.03652 |
|
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of $ \mathrm{t\overline{t}} $H production | PRL 120 (2018) 231801 | CMS-HIG-17-035 1804.02610 |
| 27 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of Higgs boson production in association with a top quark pair at the LHC with the ATLAS detector | PLB 784 (2018) 173 | 1806.00425 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Search for the associated production of a Higgs boson with a single top quark in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2016) 177 | CMS-HIG-14-027 1509.08159 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Search for associated production of a Higgs boson and a single top quark in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRD 99 (2019) 092005 | CMS-HIG-18-009 1811.09696 |
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | On the mass and spin-parity of the Higgs boson candidate via its decays to Z boson pairs | PRL 110 (2013) 081803 | CMS-HIG-12-041 1212.6639 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the properties of a Higgs boson in the four-lepton final state | PRD 89 (2014) 092007 | CMS-HIG-13-002 1312.5353 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on the spin-parity and anomalous HVV couplings of the Higgs boson in proton collisions at 7 and 8 TeV | PRD 92 (2015) 012004 | CMS-HIG-14-018 1411.3441 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Limits on the Higgs boson lifetime and width from its decay to four charged leptons | PRD 92 (2015) 072010 | CMS-HIG-14-036 1507.06656 |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | Combined search for anomalous pseudoscalar HVV couplings in VH(H $ \to b \bar b $) production and H $ \to $ VV decay | PLB 759 (2016) 672 | CMS-HIG-14-035 1602.04305 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous Higgs boson couplings using production and decay information in the four-lepton final state | PLB 775 (2017) 1 | CMS-HIG-17-011 1707.00541 |
| 36 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous HVV couplings from the production of Higgs bosons decaying to $ \tau $ lepton pairs | PRD 100 (2019) 112002 | CMS-HIG-17-034 1903.06973 |
| 37 | ATLAS Collaboration | Evidence for the spin-0 nature of the Higgs boson using ATLAS data | PLB 726 (2013) 120 | 1307.1432 |
| 38 | ATLAS Collaboration | Study of the spin and parity of the Higgs boson in diboson decays with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 75 (2015) 476 | 1506.05669 |
| 39 | ATLAS Collaboration | Test of CP Invariance in vector-boson fusion production of the Higgs boson using the Optimal Observable method in the ditau decay channel with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 76 (2016) 658 | 1602.04516 |
| 40 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of inclusive and differential cross sections in the $ H \rightarrow ZZ^* \rightarrow 4\ell $ decay channel in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 10 (2017) 132 | 1708.02810 |
| 41 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the Higgs boson coupling properties in the $ H\rightarrow ZZ^{*} \rightarrow 4\ell $ decay channel at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 03 (2018) 095 | 1712.02304 |
| 42 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurements of Higgs boson properties in the diphoton decay channel with 36 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 98 (2018) 052005 | 1802.04146 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous Higgs boson couplings to vector bosons and fermions in its production and decay using the four-lepton final state | CMS-HIG-19-009 2104.12152 |
|
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of the Higgs boson width and anomalous HVV couplings from on-shell and off-shell production in the four-lepton final state | PRD 99 (2019) 112003 | CMS-HIG-18-002 1901.00174 |
| 45 | C. Zhang and S. Willenbrock | Effective-field-theory approach to top-quark production and decay | PRD 83 (2011) 034006 | 1008.3869 |
| 46 | R. Harnik et al. | Measuring CP Violation in $ h \to \tau^+ \tau^- $ at Colliders | PRD 88 (2013) 076009 | 1308.1094 |
| 47 | T. Ghosh, R. Godbole, and X. Tata | Determining the spacetime structure of bottom-quark couplings to spin-zero particles | PRD 100 (2019) 015026 | 1904.09895 |
| 48 | A. V. Gritsan, R. Rontsch, M. Schulze, and M. Xiao | Constraining anomalous Higgs boson couplings to the heavy flavor fermions using matrix element techniques | PRD 94 (2016) 055023 | 1606.03107 |
| 49 | CMS Collaboration | Analysis of the CP structure of the Yukawa coupling between the Higgs boson and $ \tau $ leptons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-HIG-20-006 2110.04836 |
|
| 50 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group Collaboration | Handbook of LHC Higgs Cross Sections: 4. Deciphering the Nature of the Higgs Sector | 1610.07922 | |
| 51 | F. Maltoni, G. Ridolfi, and M. Ubiali | b-initiated processes at the LHC: a reappraisal | JHEP 07 (2012) 022 | 1203.6393 |
| 52 | K. Kondo | Dynamical likelihood method for reconstruction of events with missing momentum. 1: method and toy models | J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 57 (1988) 4126 | |
| 53 | K. Kondo | Dynamical likelihood method for reconstruction of events with missing momentum. 2: mass spectra for $ 2 \to 2 $ processes | J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 60 (1991) 836 | |
| 54 | F. Demartin, F. Maltoni, K. Mawatari, and M. Zaro | Higgs production in association with a single top quark at the LHC | EPJC 75 (2015) 267 | 1504.00611 |
| 55 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 56 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 57 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 58 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 59 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 | CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 60 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | CPC 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 61 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA 8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 62 | CMS Collaboration | Investigations of the impact of the parton shower tuning in PYTHIA 8 in the modelling of $ \mathrm{t\bar{t}} $ at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 and 13 TeV | CMS-PAS-TOP-16-021 | CMS-PAS-TOP-16-021 |
| 63 | CMS Collaboration | Event generator tunes obtained from underlying event and multiparton scattering measurements | EPJC 76 (2016) 155 | CMS-GEN-14-001 1512.00815 |
| 64 | J. Alwall et al. | Comparative study of various algorithms for the merging of parton showers and matrix elements in hadronic collisions | EPJC 53 (2008) 473 | 0706.2569 |
| 65 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 66 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 67 | P. Artoisenet, R. Frederix, O. Mattelaer, and R. Rietkerk | Automatic spin-entangled decays of heavy resonances in Monte Carlo simulations | JHEP 03 (2013) 015 | 1212.3460 |
| 68 | J. S. Gainer et al. | Exploring theory space with Monte Carlo reweighting | JHEP 10 (2014) 078 | 1404.7129 |
| 69 | O. Mattelaer | On the maximal use of Monte Carlo samples: re-weighting events at NLO accuracy | EPJC 76 (2016) 674 | 1607.00763 |
| 70 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4--a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 71 | J. Allison et al. | Recent developments in Geant4 | NIMA 835 (2016) 186 | |
| 72 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of inclusive $ \mathrm{W} $ and $ \mathrm{Z} $ cross sections in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2011) 080 | CMS-EWK-10-002 1012.2466 |
| 73 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 74 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P05011 | CMS-BTV-16-002 1712.07158 |
| 75 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_{\tau} $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P10005 | CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 76 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 77 | F. Demartin et al. | tWH associated production at the LHC | EPJC 77 (2017) 34 | 1607.05862 |
| 78 | R. Frederix and I. Tsinikos | Subleading EW corrections and spin-correlation effects in $ t\bar{t}W $ multi-lepton signatures | EPJC 80 (2020) 803 | 2004.09552 |
| 79 | J. A. Dror, M. Farina, E. Salvioni, and J. Serra | Strong tW Scattering at the LHC | JHEP 01 (2016) 071 | 1511.03674 |
| 80 | M. Czakon and A. Mitov | Top++: a program for the calculation of the top-pair cross section at hadron colliders | CPC 185 (2014) 2930 | 1112.5675 |
| 81 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Vector boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2011) 018 | 1105.0020 |
| 82 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ {k_{\mathrm{T}}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 83 | E. Bols et al. | Jet Flavour Classification Using DeepJet | JINST 15 (2020) P12012 | 2008.10519 |
| 84 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the DeepJet b tagging algorithm using 41.9/fb of data from proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV with Phase 1 CMS detector | CDS | |
| 85 | T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, and J. Friedman | The elements of statistical learning | Springer-Verlag, second edition, 2013 , ISBN 978-0-387-84858-7 | |
| 86 | L. Breiman, J. Friedman, R. Olshen, and C. Stone | Classification and regression trees | Wadsworth, 1984 ISBN 978-0412048418 | |
| 87 | J. Brehmer, K. Cranmer, G. Louppe, and J. Pavez | Constraining effective field theories with machine learning | PRL 121 (2018) 111801 | 1805.00013 |
| 88 | T. Chen and C. Guestrin | XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system | CoRR abs/1603.02754 (2016) | 1603.02754 |
| 89 | R. J. Barlow and C. Beeston | Fitting using finite Monte Carlo samples | CPC 77 (1993) 219 | |
| 90 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group Collaboration | Handbook of LHC Higgs Cross Sections: 3. Higgs Properties | 1307.1347 | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|