

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-HIG-23-011 ; CERN-EP-2025-007 | ||
| Search for $ \gamma $H production and constraints on the Yukawa couplings of light quarks to the Higgs boson | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 8 February 2024 | ||
| Phys. Rev. D 112 (2025) 112001 | ||
| Abstract: A search for $ \gamma $H production is performed with data from the CMS experiment at the LHC corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $ at a proton-proton center-of-mass collision energy of 13 TeV. The analysis focuses on the topology of a boosted Higgs boson recoiling against a high-energy photon. The final states of $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ are analyzed. This study examines effective $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z}\gamma $ and $ \mathrm{H}\gamma\gamma $ anomalous couplings within the context of an effective field theory. In this approach, the production cross section is constrained to be $ \sigma_{\gamma \mathrm{H}} < $ 16.4 fb at 95% confidence level (CL). Simultaneous constraints on four anomalous couplings involving $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z}\gamma $ and $ \mathrm{H}\gamma\gamma $ are provided. Additionally, the production rate for $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ is examined to assess potential enhancements in the Yukawa couplings between light quarks and the Higgs boson. Assuming the standard model values for the Yukawa couplings of the bottom and top quarks, the following simultaneous constraints are obtained: $ \kappa_\mathrm{u}=( $ 0.0 $ \pm $ 1.5 $)\times $ 10$^{3} $, $ \kappa_\mathrm{d}=( $ 0.0 $ ^{+6.7}_{-6.8} )\times $ 10$^2$, $ \kappa_\mathrm{s}= $ 0 $ ^{+30}_{-32} $, and $ \kappa_\mathrm{c}= $ 0.0 $ ^{+2.3}_{-2.8} $. This rules out the hypothesis that up- or down-type quarks in the first or second generation have the same Yukawa couplings as those in the third generation, with a CL greater than 95%. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2502.05665 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
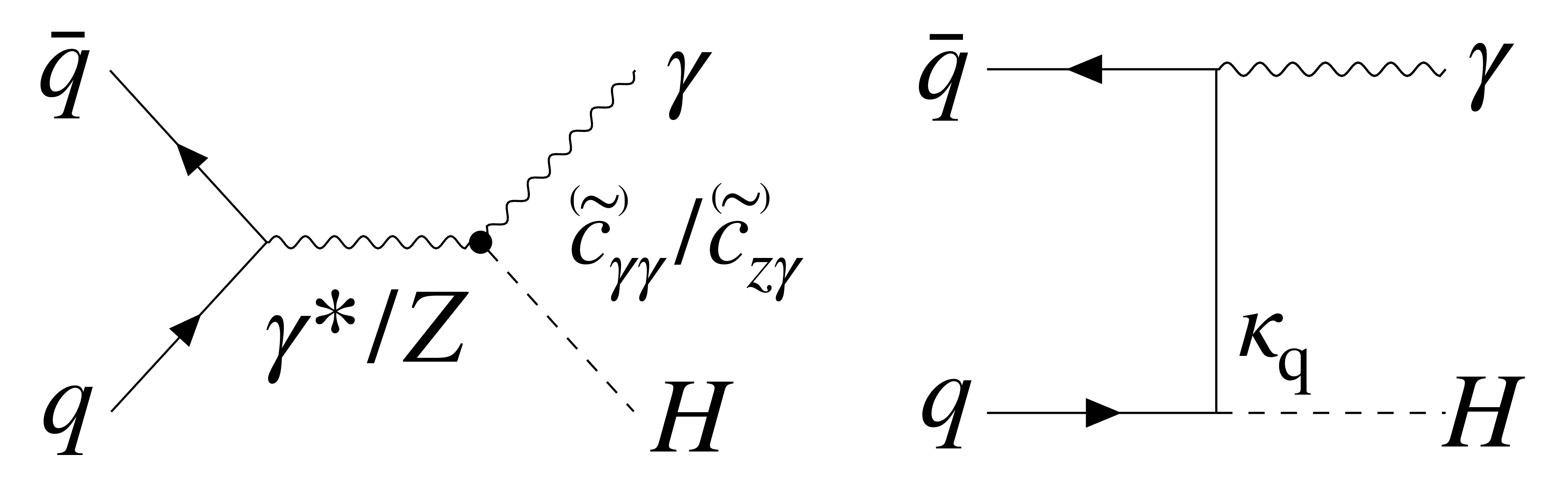
png pdf |
Figure 1:
Examples of Feynman diagrams illustrating $ \gamma $H production at the LHC, highlighting the relevant couplings as discussed in the text. On the left, production occurs via an effective loop-generated $ \mathrm{H}\gamma\gamma $ or $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z}\gamma $ interaction, denoted by a dot, which is the primary focus of this paper. On the right, production proceeds through H boson production in $ \mathrm{q}\overline{\mathrm{q}} $ annihilation with photon radiation. |
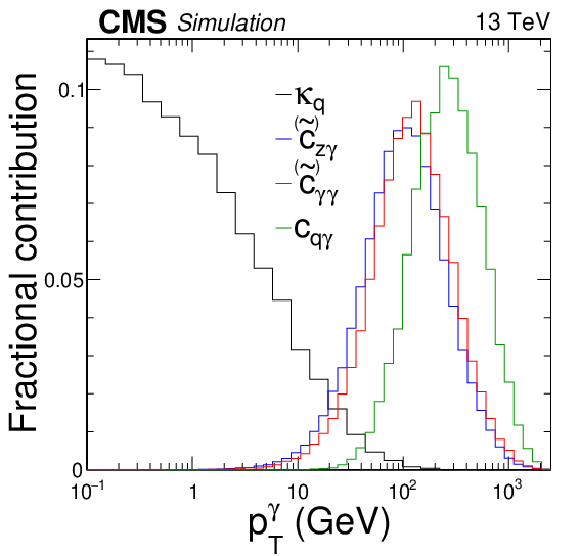
png pdf |
Figure 2:
The spectrum of the photon transverse momentum in $ \gamma $H production, as generated by the leading-order diagrams shown in Figs. 1 and 3. The four distributions correspond to production resulting from couplings $ \kappa_\mathrm{q} $, $ c_{z\gamma} $ ($ \widetilde{c}_{z\gamma} $), $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $ ($ \widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma} $), and $ c_{\mathrm{q}\gamma} $. |
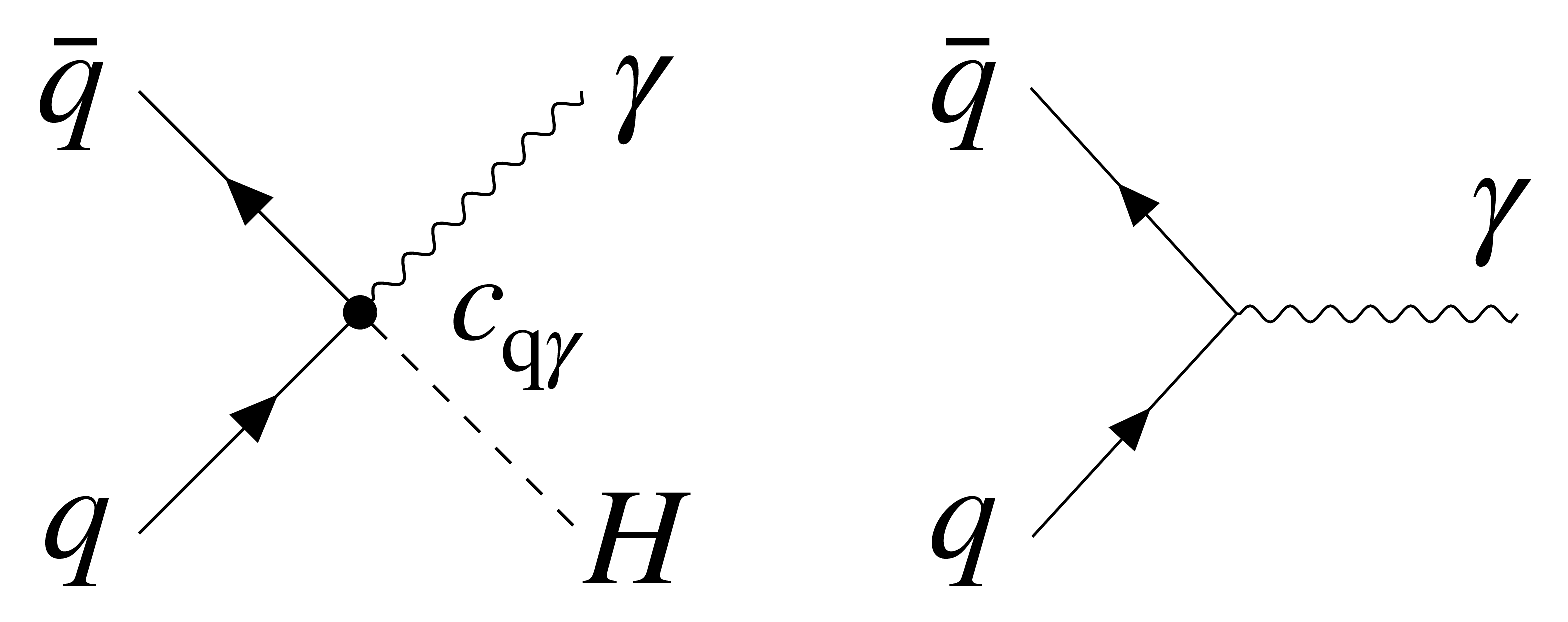
png pdf |
Figure 3:
Feynman diagrams describing the $ \mathrm{q}\overline{\mathrm{q}} $ annihilation with production of $ \gamma $H through a point-like EFT operator (left) and with photon production (right). |
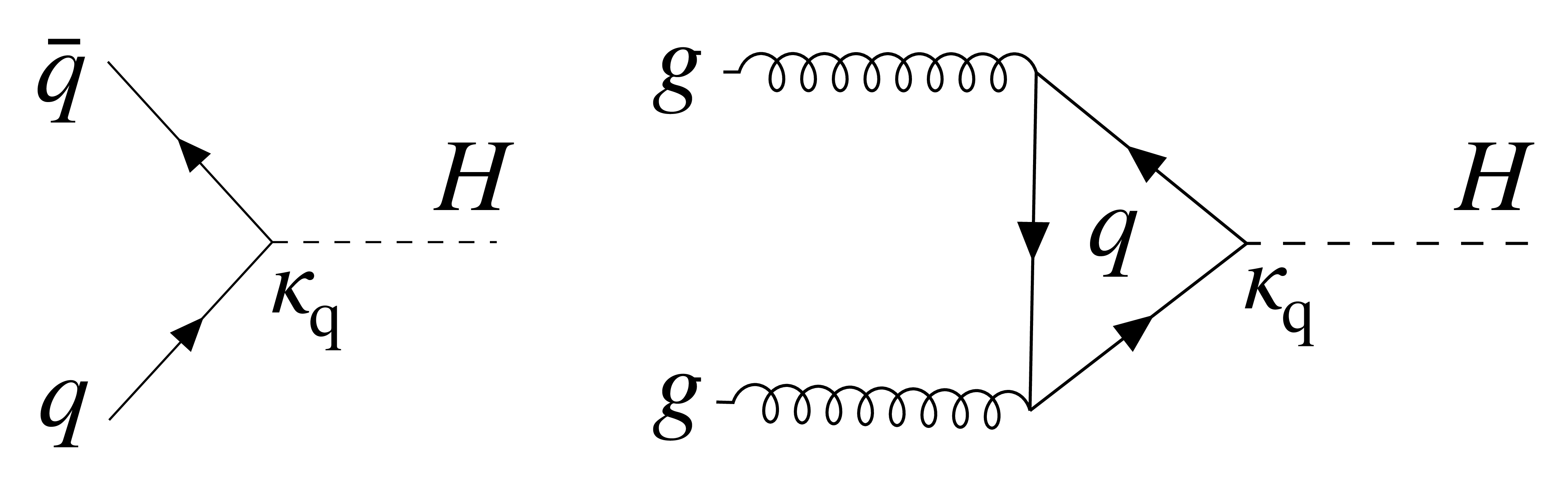
png pdf |
Figure 4:
Feynman diagrams describing the H boson production at LHC through direct $ \mathrm{q}\overline{\mathrm{q}} $ annihilation (left) and gluon fusion production (right). |
png pdf |
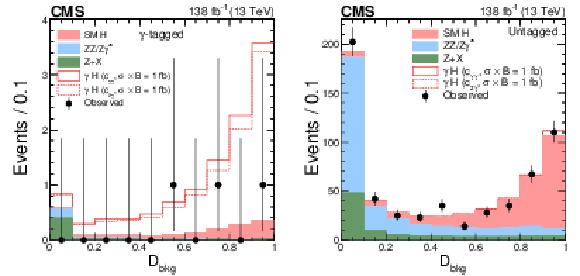
Figure 5:
Distributions of events for the $ {\mathcal{D}}_{\text{bkg}} $ observable in the $ \gamma $-tagged (left) and Untagged (right) categories of the $ \mathrm{H}\to 4\ell $ candidate events. Observed events (black markers) and expected background estimates (solid histograms) from MC simulation (ZZ/Z$ \gamma^* $) or control samples in data ($ \mathrm{Z}+\mathrm{X} $) are shown. The $ \gamma $H signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{4\ell}= $ 1 fb for either the $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $ (solid) and $ c_{z\gamma} $ (dashed) coupling hypothesis. |
png pdf |
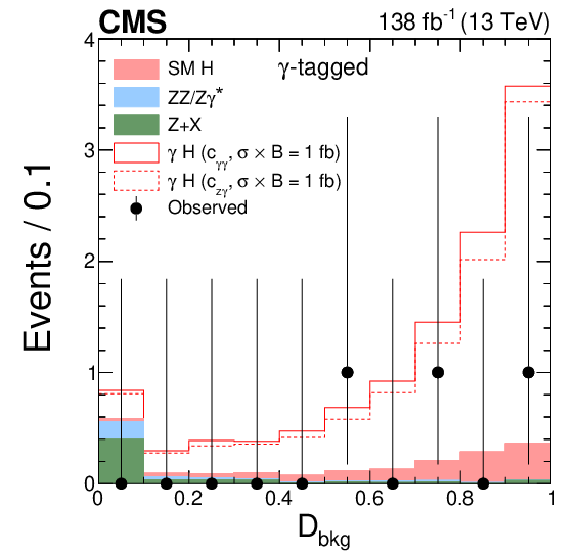
Figure 5-a:
Distributions of events for the $ {\mathcal{D}}_{\text{bkg}} $ observable in the $ \gamma $-tagged (left) and Untagged (right) categories of the $ \mathrm{H}\to 4\ell $ candidate events. Observed events (black markers) and expected background estimates (solid histograms) from MC simulation (ZZ/Z$ \gamma^* $) or control samples in data ($ \mathrm{Z}+\mathrm{X} $) are shown. The $ \gamma $H signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{4\ell}= $ 1 fb for either the $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $ (solid) and $ c_{z\gamma} $ (dashed) coupling hypothesis. |
png pdf |
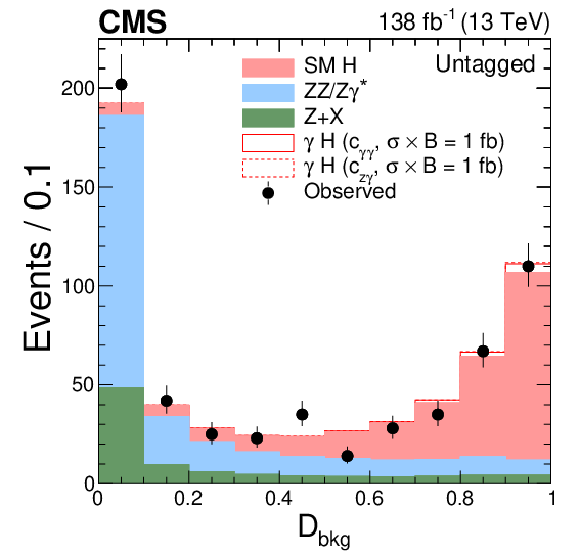
Figure 5-b:
Distributions of events for the $ {\mathcal{D}}_{\text{bkg}} $ observable in the $ \gamma $-tagged (left) and Untagged (right) categories of the $ \mathrm{H}\to 4\ell $ candidate events. Observed events (black markers) and expected background estimates (solid histograms) from MC simulation (ZZ/Z$ \gamma^* $) or control samples in data ($ \mathrm{Z}+\mathrm{X} $) are shown. The $ \gamma $H signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{4\ell}= $ 1 fb for either the $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $ (solid) and $ c_{z\gamma} $ (dashed) coupling hypothesis. |
png pdf |
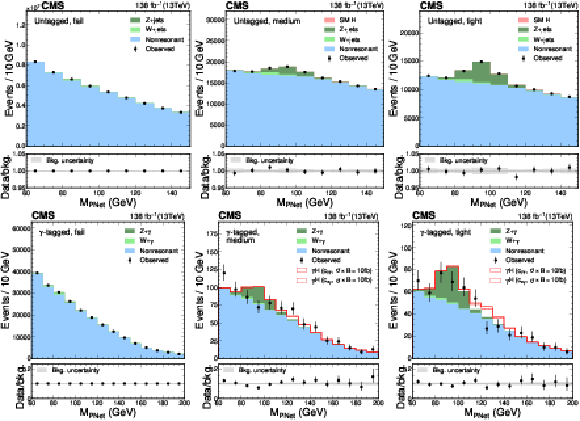
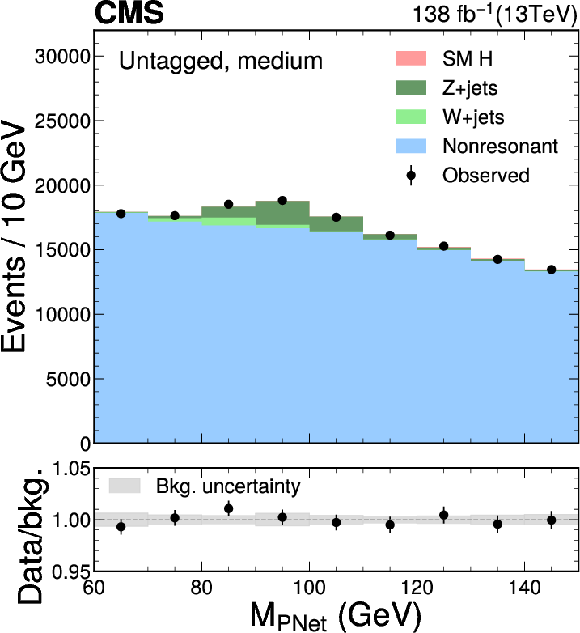
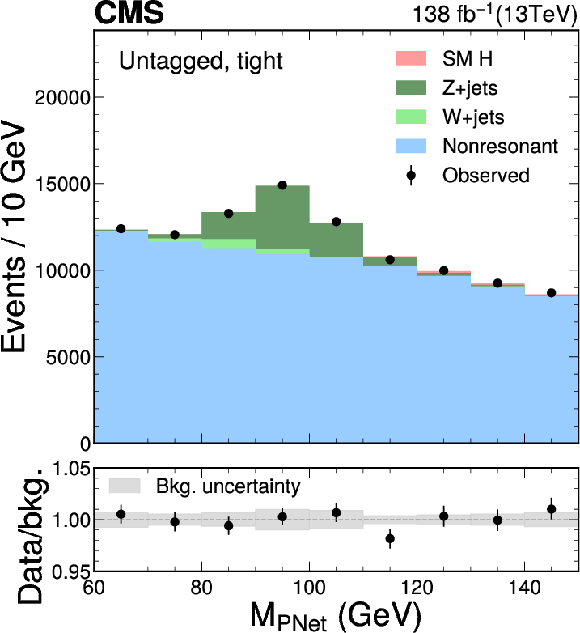
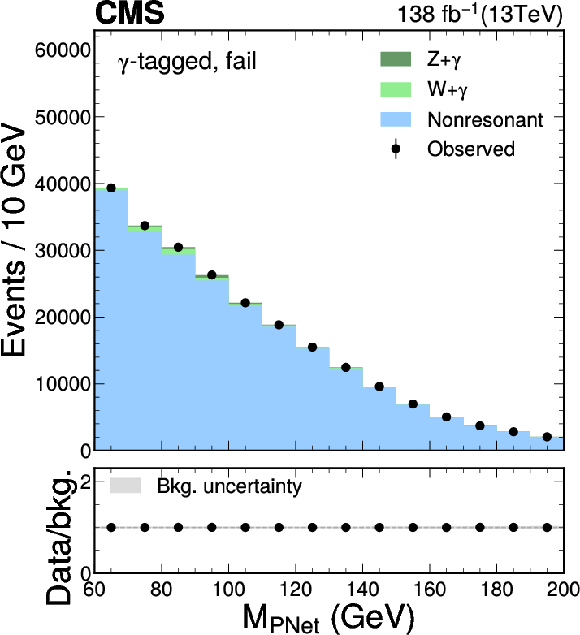
Figure 6:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
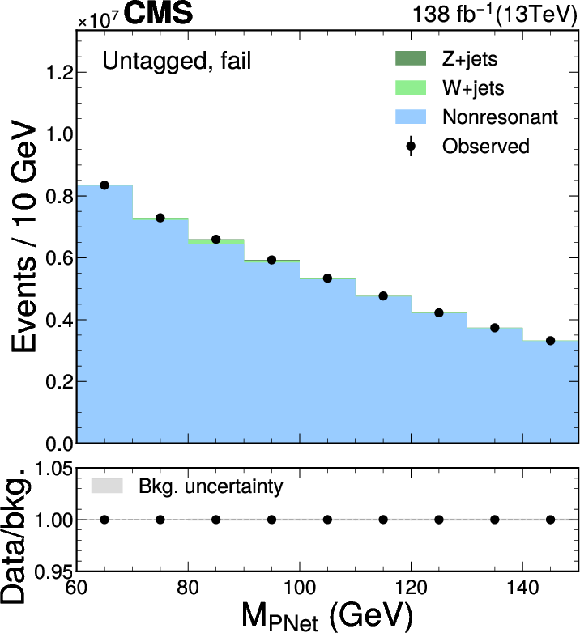
png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-c:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-d:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
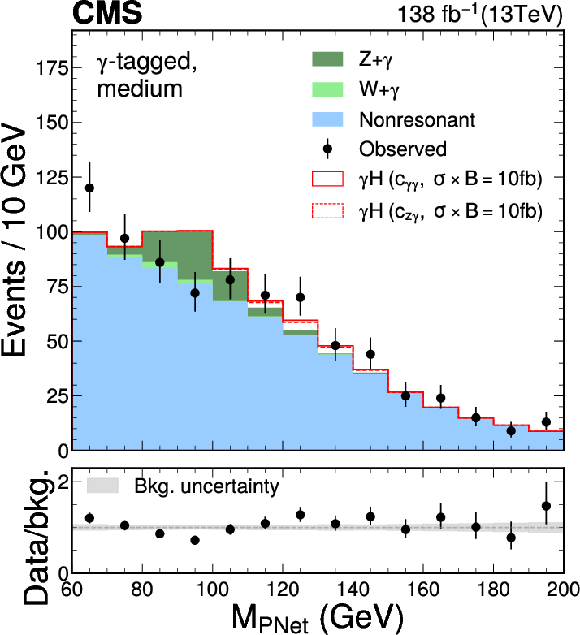
png pdf |
Figure 6-e:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
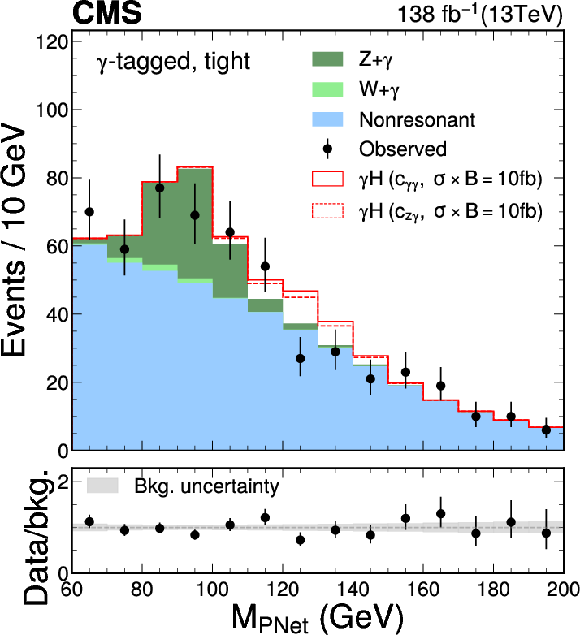
png pdf |
Figure 6-f:
The $ M_{\textrm{PNet}} $ distributions for the number of observed events (black markers) compared with the backgrounds estimated in the fit to the data (filled histograms) in the $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ channel. Fail (left), medium (middle) and tight (right) regions of the $ \gamma $-tagged (lower) and Untagged (upper) categories are shown. The signal contribution, stacked on top of background, is shown with an open histogram for an assumed cross section of $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} \mathcal{B}_{\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}}}= $ 10 fb. |
png pdf |
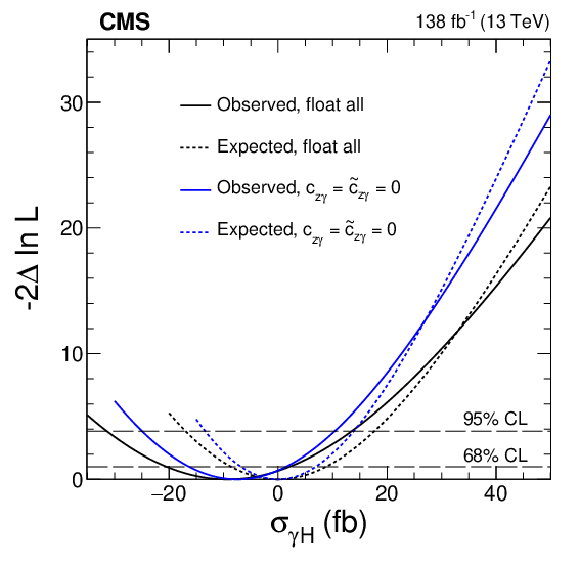
Figure 7:
Constraints on $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} $ from the combination of the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and 4 $ \ell $ channels. The results are shown with only $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $ and $ \widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma} $ floating in the fit (blue) and with all four couplings allowed to float (black). Observed (solid) and expected (dashed) likelihood scans are shown. The dashed horizontal lines show the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
png pdf |
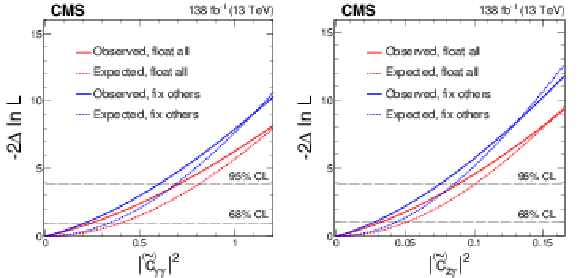
Figure 8:
Constraints on the square of $ |c_{\gamma\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma}| $) and $ |c_{z\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{z\gamma}| $) from the combination of the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and 4 $ \ell $ channels. The other couplings are either fixed to the null SM expectation (blue) or are left floating in the fit (red). Observed (solid) and expected (dashed) likelihood scans are shown. The dashed horizontal lines show the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
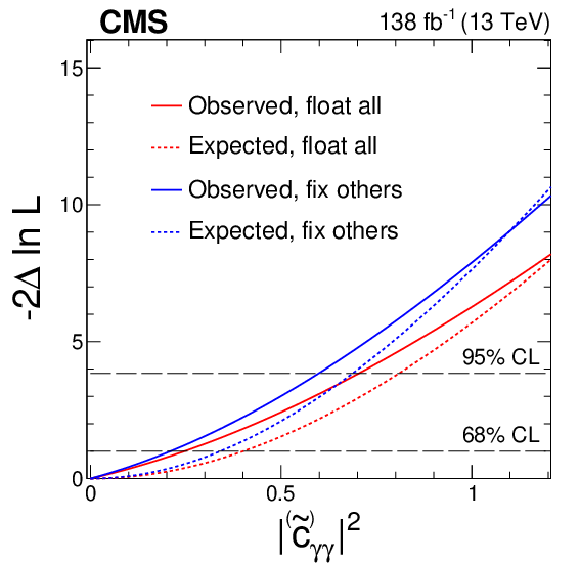
png pdf |
Figure 8-a:
Constraints on the square of $ |c_{\gamma\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma}| $) and $ |c_{z\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{z\gamma}| $) from the combination of the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and 4 $ \ell $ channels. The other couplings are either fixed to the null SM expectation (blue) or are left floating in the fit (red). Observed (solid) and expected (dashed) likelihood scans are shown. The dashed horizontal lines show the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
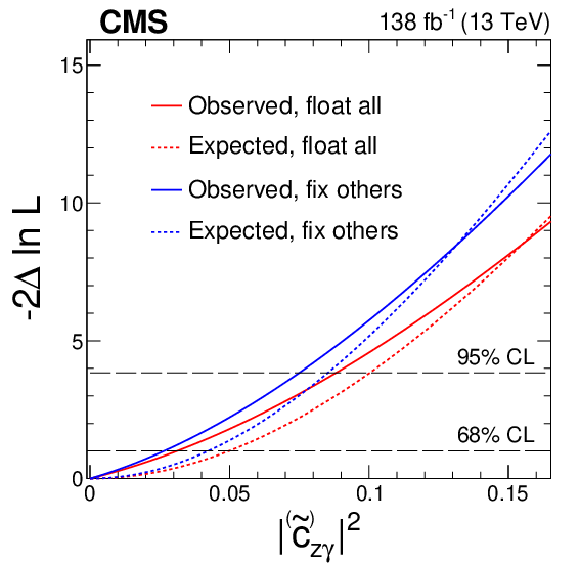
png pdf |
Figure 8-b:
Constraints on the square of $ |c_{\gamma\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma}| $) and $ |c_{z\gamma}| $ (or $ |\widetilde{c}_{z\gamma}| $) from the combination of the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and 4 $ \ell $ channels. The other couplings are either fixed to the null SM expectation (blue) or are left floating in the fit (red). Observed (solid) and expected (dashed) likelihood scans are shown. The dashed horizontal lines show the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
png pdf |
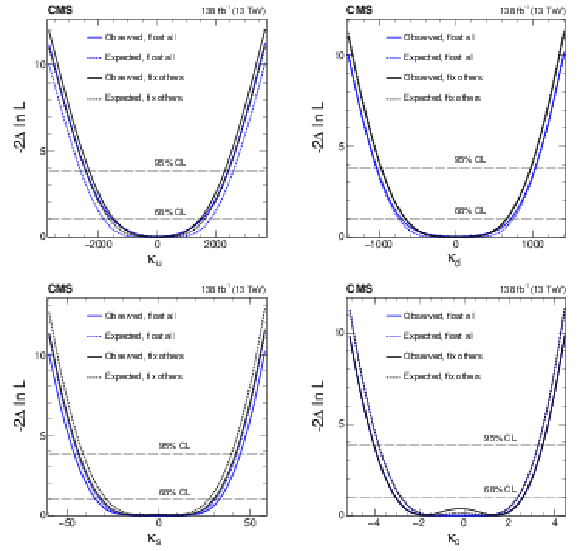
Figure 9:
Constraints on $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In scenario one (black), all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In scenario two (blue), the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed: $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \Gamma^\text{BSM}_\mathrm{H}\ge $ 0. Both observed (solid) and expected (dashed) constraints are presented. The crossings of dashed horizontal lines and the likelihood curves indicate the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
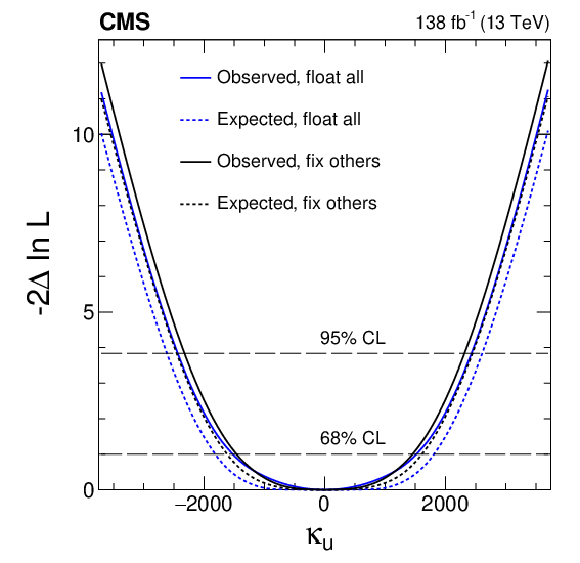
png pdf |
Figure 9-a:
Constraints on $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In scenario one (black), all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In scenario two (blue), the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed: $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \Gamma^\text{BSM}_\mathrm{H}\ge $ 0. Both observed (solid) and expected (dashed) constraints are presented. The crossings of dashed horizontal lines and the likelihood curves indicate the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
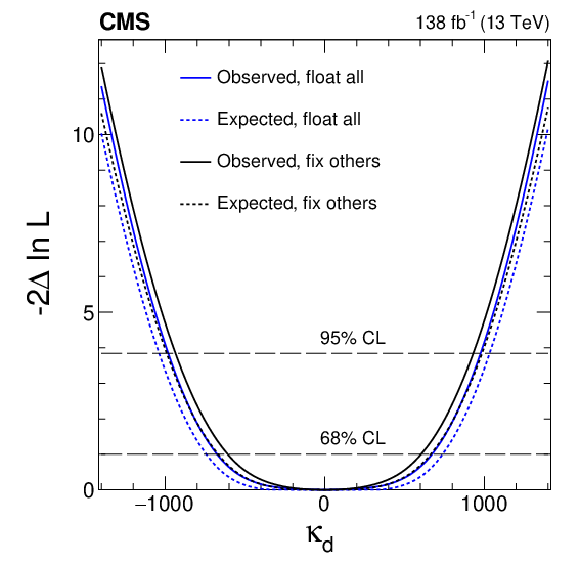
png pdf |
Figure 9-b:
Constraints on $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In scenario one (black), all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In scenario two (blue), the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed: $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \Gamma^\text{BSM}_\mathrm{H}\ge $ 0. Both observed (solid) and expected (dashed) constraints are presented. The crossings of dashed horizontal lines and the likelihood curves indicate the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
png pdf |
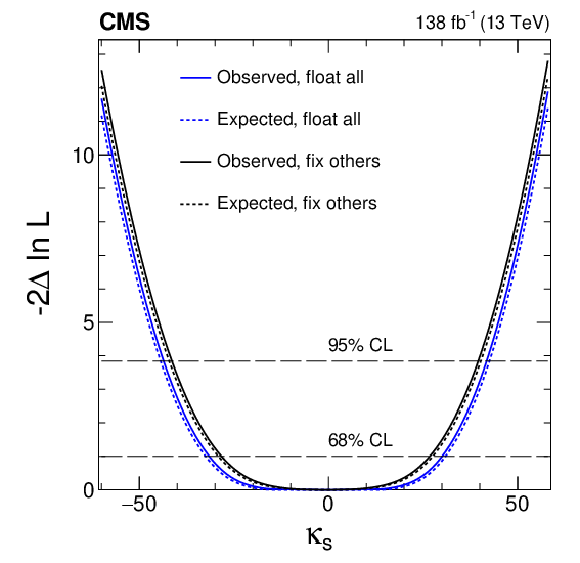
Figure 9-c:
Constraints on $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In scenario one (black), all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In scenario two (blue), the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed: $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \Gamma^\text{BSM}_\mathrm{H}\ge $ 0. Both observed (solid) and expected (dashed) constraints are presented. The crossings of dashed horizontal lines and the likelihood curves indicate the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
png pdf |
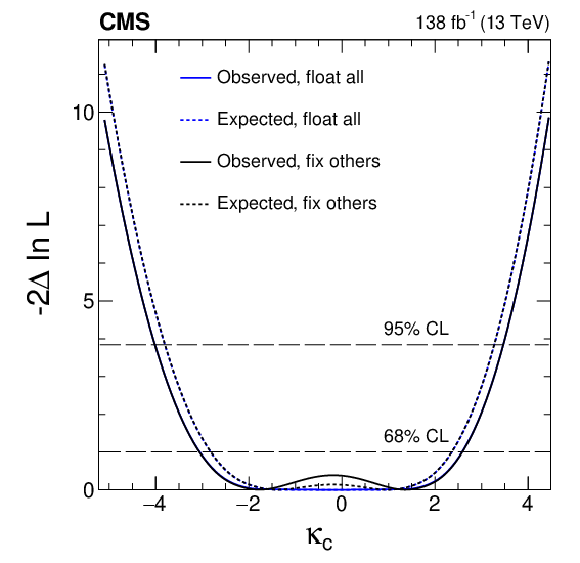
Figure 9-d:
Constraints on $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In scenario one (black), all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In scenario two (blue), the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed: $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \Gamma^\text{BSM}_\mathrm{H}\ge $ 0. Both observed (solid) and expected (dashed) constraints are presented. The crossings of dashed horizontal lines and the likelihood curves indicate the 68 and 95% CL intervals. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
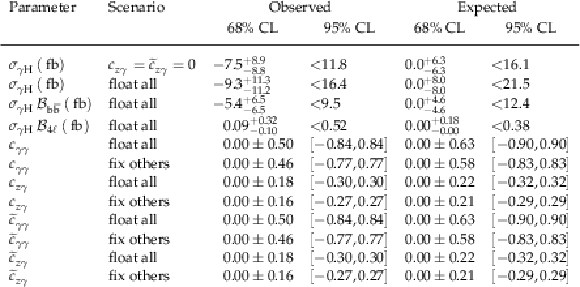
Table 1:
Observed and expected constraints on the $ \gamma $H cross section $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} $ and on the $ c_{\gamma\gamma} $, $ c_{z\gamma} $, $ \widetilde{c}_{\gamma\gamma} $, and $ \widetilde{c}_{z\gamma} $ couplings using the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and 4 $ \ell $ channels combined. The third and fourth rows show constraints on cross section multiplied by the branching fraction using the $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channels only, respectively. The 68% (central value with uncertainties) and 95% (upper limit or allowed intervals) CL intervals are shown. |
png pdf |
Table 2:
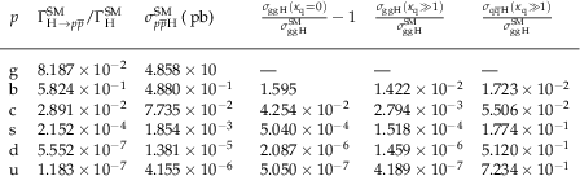
Central values of the input and derived parameters used in calculations involving Eqs. (4) and (5). The list of partons ($ p $) comprises gluons ($ \mathrm{g} $) and five quark flavors ($ \mathrm{q} $). All cross sections $ \sigma_i $ are computed for the inclusive on-shell H boson production using the SM values for all couplings, except for the specific coupling $ \kappa_{\mathrm{q}} $ that is explicitly mentioned. |

png pdf |
Table 3:
Observed and expected constraints on the $ \kappa_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \kappa_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{c}} $ couplings are shown using the $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ channel. In one scenario, all couplings except the one being shown are fixed at their SM values. In the other scenario, the Yukawa couplings for the three other light quarks are left unconstrained, and BSM contributions are allowed. The 68% (central value with error bars) and 95% (bracketed range or upper limit) CL intervals are displayed. |
png pdf |
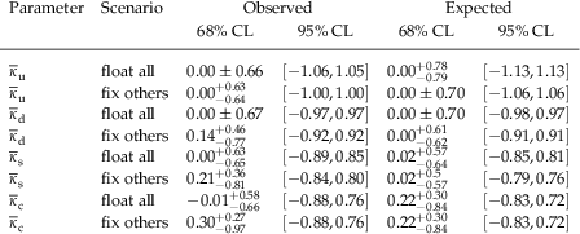
Table 4:
Observed and expected constraints on the $ \overline{\kappa}_{\mathrm{u}} $, $ \overline{\kappa}_{\mathrm{d}} $, $ \overline{\kappa}_{\mathrm{s}} $, and $ \overline{\kappa}_{\mathrm{c}} $ defined as $ \overline{\kappa}_{\mathrm{q}}=y_{\mathrm{q}}v/m_{\mathrm{b}} $, following the same conventions as outlined in Table 3. |
| Summary |
| A search for $ \gamma $H production is performed with the data from the CMS experiment at the LHC corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $ at a proton-proton center-of-mass collision energy of 13 TeV. The analysis focuses on the topology of a boosted H boson recoiling against a high-energy photon. The final states of $ \mathrm{H}\to \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ are analyzed. This study examines effective $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z}\gamma $ and $ \mathrm{H}\gamma\gamma $ anomalous couplings within the context of an effective field theory. In this approach, the observed (expected) constraint on the $ \gamma $H production cross section is $ \sigma_{\gamma\mathrm{H}} < 16.4 (21.5) $ fb at 95% CL. Simultaneous constraints on four anomalous couplings involving $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z}\gamma $ and $ \mathrm{H}\gamma\gamma $ are provided. Additionally, the production rate for $ \mathrm{H}\to4\ell $ is examined to assess potential enhancements in the Yukawa couplings between light quarks and the H boson. This includes examining modifications to both direct quark-antiquark annihilation and gluon fusion loop processes. Assuming the standard model Yukawa couplings for the bottom and top quarks ($ \kappa_{\mathrm{b}}=\kappa_{\mathrm{t}}= $ 1), along with the constraints on the $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V} $ couplings ($ \kappa_{\mathrm{W}\mathrm{W}}^2\le $ 1 and $ \kappa_{\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}}^2\le $ 1), the following simultaneous constraints are obtained: $ \kappa_\mathrm{u}=( $ 0.0 $ \pm $ 1.5 $)\times $ 10$^{3} $, $ \kappa_\mathrm{d}=( $ 0.0 $ ^{+6.7}_{-6.8} )\times $ 10$^2$, $ \kappa_\mathrm{s}= $ 0 $ ^{+30}_{-32} $, and $ \kappa_\mathrm{c}= $ 0.0 $ ^{+2.3}_{-2.8} $. The hypothesis that up- or down-type quarks in the first or second generation have the same Yukawa couplings as those in the third generation is excluded with a CL greater than 95%. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the standard model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1 | 1207.7214 |
| 2 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 3 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson with mass near 125 GeV in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2013) 081 | CMS-HIG-12-036 1303.4571 |
| 4 | S. L. Glashow | Partial-symmetries of weak interactions | NP 22 (1961) 579 | |
| 5 | F. Englert and R. Brout | Broken symmetry and the mass of gauge vector mesons | PRL 13 (1964) 321 | |
| 6 | P. W. Higgs | Broken symmetries, massless particles and gauge fields | PL 12 (1964) 132 | |
| 7 | P. W. Higgs | Broken symmetries and the masses of gauge bosons | PRL 13 (1964) 508 | |
| 8 | G. S. Guralnik, C. R. Hagen, and T. W. B. Kibble | Global conservation laws and massless particles | PRL 13 (1964) 585 | |
| 9 | S. Weinberg | A model of leptons | PRL 19 (1967) 1264 | |
| 10 | A. Salam | Weak and electromagnetic interactions | in Elementary particle physics: relativistic groups and analyticity, N. Svartholm, ed., Almqvist & Wiksell, Stockholm, Proceedings of the eighth Nobel symposium, 1968 | |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | On the mass and spin-parity of the Higgs boson candidate via its decays to Z boson pairs | PRL 110 (2013) 081803 | CMS-HIG-12-041 1212.6639 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the properties of a Higgs boson in the four-lepton final state | PRD 89 (2014) 092007 | CMS-HIG-13-002 1312.5353 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on the spin-parity and anomalous $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V} $ couplings of the Higgs boson in proton collisions at 7 and 8 TeV | PRD 92 (2015) 012004 | CMS-HIG-14-018 1411.3441 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | Limits on the Higgs boson lifetime and width from its decay to four charged leptons | PRD 92 (2015) 072010 | CMS-HIG-14-036 1507.06656 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Combined search for anomalous pseudoscalar $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V} $ couplings in VH ($ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $) production and $ \mathrm{H}\to\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V} $ decay | PLB 759 (2016) 672 | CMS-HIG-14-035 1602.04305 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous Higgs boson couplings using production and decay information in the four-lepton final state | PLB 775 (2017) 1 | CMS-HIG-17-011 1707.00541 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of the Higgs boson width and anomalous HVV couplings from on-shell and off-shell production in the four-lepton final state | PRD 99 (2019) 112003 | CMS-HIG-18-002 1901.00174 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous HVV couplings from the production of Higgs bosons decaying to $ \tau $ lepton pairs | PRD 100 (2019) 112002 | CMS-HIG-17-034 1903.06973 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous Higgs boson couplings to vector bosons and fermions in its production and decay using the four-lepton final state | PRD 104 (2021) 052004 | CMS-HIG-19-009 2104.12152 |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the Higgs boson width and evidence of its off-shell contributions to ZZ production | Nature Phys. 18 (2022) 1329 | CMS-HIG-21-013 2202.06923 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Constraints on anomalous Higgs boson couplings to vector bosons and fermions from the production of Higgs bosons using the $\tau\tau$ final state | PRD 108 (2023) 032013 | CMS-HIG-20-007 2205.05120 |
| 22 | ATLAS Collaboration | Evidence for the spin-0 nature of the Higgs boson using ATLAS data | PLB 726 (2013) 120 | 1307.1432 |
| 23 | ATLAS Collaboration | Study of the spin and parity of the Higgs boson in diboson decays with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 75 (2015) 476 | 1506.05669 |
| 24 | ATLAS Collaboration | Test of CP invariance in vector-boson fusion production of the Higgs boson using the Optimal Observable method in the ditau decay channel with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 76 (2016) 658 | 1602.04516 |
| 25 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of inclusive and differential cross sections in the $ \mathrm{H} \rightarrow \mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z}^{*} \rightarrow 4\ell $ decay channel in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 10 (2017) 132 | 1708.02810 |
| 26 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the Higgs boson coupling properties in the $ H\rightarrow ZZ^{*} \rightarrow 4\ell $ decay channel at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 03 (2018) 095 | 1712.02304 |
| 27 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurements of Higgs boson properties in the diphoton decay channel with 36 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 98 (2018) 052005 | 1802.04146 |
| 28 | ATLAS Collaboration | Higgs boson production cross-section measurements and their EFT interpretation in the 4 $ \ell $ decay channel at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 80 (2020) 957 | 2004.03447 |
| 29 | ATLAS Collaboration | Test of CP invariance in Higgs boson vector-boson-fusion production using the $ \mathrm{H}\rightarrow{\gamma}{\gamma} $ channel with the ATLAS detector | PRL 131 (2023) 061802 | 2208.02338 |
| 30 | ATLAS Collaboration | Test of CP-invariance of the Higgs boson in vector-boson fusion production and its decay into four leptons | JHEP 05 (2023) 105 | 2304.09612 |
| 31 | D. de Florian et al. | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 4. deciphering the nature of the Higgs sector | CERN Report CERN-2017-002-M link |
1610.07922 |
| 32 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Evidence for the Higgs boson decay to a Z boson and a photon at the LHC | PRL 132 (2024) 021803 | 2309.03501 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of $ \mathrm{W}\mathrm{W}\gamma $ production and search for $ \mathrm{H}\gamma $ production in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 132 (2024) 121901 | CMS-SMP-22-006 2310.05164 |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow $ \mathrm{H}\gamma $ resonances in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 122 (2019) 081804 | CMS-EXO-17-019 1808.01257 |
| 35 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for heavy resonances decaying to a photon and a hadronically decaying $ \mathrm{Z}/\mathrm{W}/\mathrm{H} $ boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 98 (2018) 032015 | 1805.01908 |
| 36 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for heavy resonances decaying into a photon and a hadronically decaying Higgs boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRL 125 (2020) 251802 | 2008.05928 |
| 37 | A. Abbasabadi, D. Bowser-Chao, D. A. Dicus, and W. W. Repko | Higgs-photon associated production at hadron colliders | PRD 58 (1998) 057301 | hep-ph/9706335 |
| 38 | H. Khanpour, S. Khatibi, and M. M. Najafabadi | Probing Higgs boson couplings in $ \mathrm{H}+\gamma $ production at the LHC | PLB 773 (2017) 462 | 1702.05753 |
| 39 | L. Shi, Z. Liang, B. Liu, and Z. He | Constraining the anomalous Higgs boson coupling in $ \mathrm{H}+\gamma $ production | Chin. Phys. C 43 (2019) 043001 | 1811.02261 |
| 40 | J. Davis et al. | Constraining anomalous Higgs boson couplings to virtual photons | PRD 105 (2022) 096027 | 2109.13363 |
| 41 | I. Brivio, Y. Jiang, and M. Trott | The SMEFTsim package, theory and tools | JHEP 12 (2017) 070 | 1709.06492 |
| 42 | I. Brivio | SMEFTsim 3.0 -- a practical guide | JHEP 04 (2021) 073 | 2012.11343 |
| 43 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 44 | A. Dedes et al. | Feynman rules for the standard model effective field theory in R$ _{\xi} $ -gauges | JHEP 06 (2017) 143 | 1704.03888 |
| 45 | ATLAS Collaboration | Drell--Yan tails beyond the standard model | JHEP 03 (2023) 064 | |
| 46 | A. L. Kagan et al. | Exclusive window onto Higgs Yukawa couplings | PRL 114 (2015) 101802 | 1406.1722 |
| 47 | J. A. Aguilar-Saavedra, J. M. Cano, and J. M. No | More light on Higgs flavor at the LHC: Higgs boson couplings to light quarks through $ \mathrm{H}+\gamma $ production | PRD 103 (2021) 095023 | 2008.12538 |
| 48 | Y. Zhou | Constraining the Higgs boson coupling to light quarks in the $ \mathrm{H}\rightarrow\mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z} $ final states | PRD 93 (2016) 013019 | 1505.06369 |
| 49 | Y. Zhou | Probing anomalous couplings of the Higgs boson to weak bosons and fermions with precision calculations | PhD thesis, Johns Hopkins University, CERN-THESIS-2019-007, 2019 link |
|
| 50 | E. Balzani, R. Gröber, and M. Vitti | Light-quark Yukawa couplings from off-shell Higgs production | JHEP 10 (2023) 027 | 2304.09772 |
| 51 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Higgs boson decay to a charm quark-antiquark pair in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 131 (2023) 061801 | CMS-HIG-21-008 2205.05550 |
| 52 | ATLAS Collaboration | Direct constraint on the Higgs-charm coupling from a search for Higgs boson decays into charm quarks with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 82 (2022) 717 | 2201.11428 |
| 53 | F. Bishara, U. Haisch, P. F. Monni, and E. Re | Constraining light-quark Yukawa couplings from Higgs distributions | PRL 118 (2017) 121801 | 1606.09253 |
| 54 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement and interpretation of differential cross sections for Higgs boson production at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PLB 792 (2019) 369 | CMS-HIG-17-028 1812.06504 |
| 55 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the total and differential Higgs boson production cross-sections at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector by combining the $ \mathrm{H}\rightarrow \mathrm{Z}\mathrm{Z} \rightarrow 4\ell $ and $ \mathrm{H} \rightarrow{\gamma}{\gamma} $ decay channels | JHEP 05 (2023) 028 | 2207.08615 |
| 56 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of inclusive and differential cross sections for the Higgs boson production and decay to four-leptons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 08 (2023) 040 | CMS-HIG-21-009 2305.07532 |
| 57 | G. Perez, Y. Soreq, E. Stamou, and K. Tobioka | Constraining the charm Yukawa and Higgs-quark coupling universality | PRD 92 (2015) 033016 | 1503.00290 |
| 58 | G. T. Bodwin, F. Petriello, S. Stoynev, and M. Velasco | Higgs boson decays to quarkonia and the $ \mathrm{H}\overline{\mathrm{c}}\mathrm{c} $ coupling | PRD 88 (2013) 053003 | 1306.5770 |
| 59 | Y. Soreq, H. X. Zhu, and J. Zupan | Light quark Yukawa couplings from Higgs kinematics | JHEP 12 (2016) 045 | 1606.09621 |
| 60 | CMS Collaboration | HEPData record for this analysis | link | |
| 61 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 62 | CMS Tracker Group Collaboration | The CMS Phase-1 Pixel Detector Upgrade | JINST 16 (2021) P02027 | 2012.14304 |
| 63 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 64 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 65 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS high-level trigger during LHC Run 2 | JINST 19 (2024) P11021 | CMS-TRG-19-001 2410.17038 |
| 66 | CMS Collaboration | Technical proposal for the Phase-II upgrade of the Compact Muon Solenoid | CMS Technical Proposal CERN-LHCC-2015-010, CMS-TDR-15-02, 2015 CDS |
|
| 67 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 68 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_{\mathrm{T}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 69 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 70 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 71 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT 4---a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 72 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the inelastic proton-proton cross section at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2018) 161 | CMS-FSQ-15-005 1802.02613 |
| 73 | NNPDF Collaboration | Unbiased global determination of parton distributions and their uncertainties at NNLO and at LO | NPB 855 (2012) 153 | 1107.2652 |
| 74 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 75 | Y. Gao et al. | Spin determination of single-produced resonances at hadron colliders | PRD 81 (2010) 075022 | 1001.3396 |
| 76 | S. Bolognesi et al. | Spin and parity of a single-produced resonance at the LHC | PRD 86 (2012) 095031 | 1208.4018 |
| 77 | I. Anderson et al. | Constraining anomalous $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{V}\mathrm{V} $ interactions at proton and lepton colliders | PRD 89 (2014) 035007 | 1309.4819 |
| 78 | A. V. Gritsan, R. Röntsch, M. Schulze, and M. Xiao | Constraining anomalous Higgs boson couplings to the heavy flavor fermions using matrix element techniques | PRD 94 (2016) 055023 | 1606.03107 |
| 79 | A. V. Gritsan et al. | New features in the JHU generator framework: constraining Higgs boson properties from on-shell and off-shell production | PRD 102 (2020) 056022 | 2002.09888 |
| 80 | J. M. Campbell and R. K. Ellis | MCFM for the Tevatron and the LHC | Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 205-206 (2010) 10 | 1007.3492 |
| 81 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 82 | E. Bagnaschi, G. Degrassi, P. Slavich, and A. Vicini | Higgs production via gluon fusion in the POWHEG approach in the SM and in the MSSM | JHEP 02 (2012) 088 | 1111.2854 |
| 83 | P. Nason and C. Oleari | NLO Higgs boson production via vector-boson fusion matched with shower in POWHEG | JHEP 02 (2010) 037 | 0911.5299 |
| 84 | G. Luisoni, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and F. Tramontano | $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{W}^{\pm} $/$\mathrm{HZ}$ + 0 and 1 jet at NLO with the POWHEG BOX interfaced to GoSam and their merging within MiNLO | JHEP 10 (2013) 083 | 1306.2542 |
| 85 | H. B. Hartanto, B. Jager, L. Reina, and D. Wackeroth | Higgs boson production in association with top quarks in the POWHEG BOX | PRD 91 (2015) 094003 | 1501.04498 |
| 86 | J. Alwall et al. | Comparative study of various algorithms for the merging of parton showers and matrix elements in hadronic collisions | EPJC 53 (2007) 473 | 0706.2569 |
| 87 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 88 | J. M. Lindert et al. | Precise predictions for V+jets dark matter backgrounds | EPJC 77 (2017) 829 | 1705.04664 |
| 89 | A. Denner, S. Dittmaier, M. Hecht, and C. Pasold | NLO QCD and electroweak corrections to Z+$ \gamma $ production with leptonic Z-boson decays | JHEP 02 (2016) 057 | 1510.08742 |
| 90 | M. Grazzini, S. Kallweit, and D. Rathlev | ZZ production at the LHC: fiducial cross sections and distributions in NNLO QCD | PLB 750 (2015) 407 | 1507.06257 |
| 91 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Vector boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2011) 018 | 1105.0020 |
| 92 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Bounding the Higgs width at the LHC using full analytic results for $ \mathrm{g}\mathrm{g}\to \mathrm{e}^{-}\mathrm{e}^{+} \mu^{-} \mu^{+} $ | JHEP 04 (2014) 060 | 1311.3589 |
| 93 | J. M. Campbell and R. K. Ellis | Higgs constraints from vector boson fusion and scattering | JHEP 04 (2015) 030 | 1502.02990 |
| 94 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of properties of the Higgs boson decaying into the four-lepton final state in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2017) 047 | CMS-HIG-16-041 1706.09936 |
| 95 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of production cross sections of the Higgs boson in the four-lepton final state in proton proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | EPJC 81 (2021) 488 | CMS-HIG-19-001 2103.04956 |
| 96 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 97 | H. Qu and L. Gouskos | Jet tagging via particle clouds | PRD 101 (2020) 056019 | 1902.08570 |
| 98 | CMS Collaboration | Mass regression of highly-boosted jets using graph neural networks | CMS Detector Performance Note CMS-DP-2021-017, 2021 CDS |
|
| 99 | CMS Collaboration | Calibration of the mass-decorrelated ParticleNet tagger for boosted $ \mathrm{b}\overline{\mathrm{b}} $ and $ \mathrm{c}\overline{\mathrm{c}} $ jets using LHC Run 2 data | CMS Detector Performance Note CMS-DP-2022-005, 2022 CDS |
|
| 100 | CMS Collaboration | Search for nonresonant pair production of highly energetic Higgs bosons decaying to bottom quarks | PRL 131 (2023) 041803 | 2205.06667 |
| 101 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 102 | E. Bols et al. | Jet flavour classification using DeepJet | JINST 15 (2020) P12012 | 2008.10519 |
| 103 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of heavy-flavour jet identification in boosted topologies in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2023 CMS-PAS-BTV-22-001 |
CMS-PAS-BTV-22-001 |
| 104 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS statistical analysis and combination tool: Combine | Comput. Softw. Big Sci. 8 (2024) 19 | CMS-CAT-23-001 2404.06614 |
| 105 | L. Demortier | P values and nuisance parameters | in Statistical issues for LHC physics, Proceedings, PHYSTAT-LHC, Geneva, 2007 link |
|
| 106 | R. G. Lomax and D. L. Hahs-Vaughn | Statistical concepts: a second course | Taylor and Francis, 2012 | |
| 107 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 108 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 link |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 109 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 link |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 110 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 111 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 112 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: the $ \text{CL}_\text{s} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 113 | ATLAS Collaboration | A detailed map of Higgs boson interactions by the ATLAS experiment ten years after the discovery | Nature 607 (2022) 52 | 2207.00092 |
| 114 | CMS Collaboration | A portrait of the Higgs boson by the CMS experiment ten years after the discovery | Nature 607 (2022) 60 | CMS-HIG-22-001 2207.00043 |
| 115 | M. Spira | QCD effects in Higgs physics | Fortsch. Phys. 46 (1998) 203 | hep-ph/9705337 |
| 116 | G.-y. Huang and S. Zhou | Precise values of running quark and lepton masses in the standard model | PRD 103 (2021) 016010 | 2009.04851 |
| 117 | R. V. Harlander, S. Liebler, and H. Mantler | SusHi: A program for the calculation of Higgs production in gluon fusion and bottom-quark annihilation in the standard model and the MSSM | Comput. Phys. Commun. 184 (2013) 1605 | 1212.3249 |
| 118 | R. V. Harlander | Higgs production in heavy quark annihilation through next-to-next-to-leading order QCD | EPJC 76 (2016) 252 | 1512.04901 |
| 119 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 3. Higgs properties | CERN Yellow Rep. Monogr. 4 (2013) | 1307.1347 |
| 120 | ATLAS Collaboration | Evidence of off-shell Higgs boson production from ZZ leptonic decay channels and constraints on its total width with the ATLAS detector | PLB 846 (2023) 138223 | 2304.01532 |
| 121 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the Higgs boson mass and width using the four-lepton final state in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | CMS-HIG-21-019 2409.13663 |
|

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|