

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-SUS-23-013 | ||
| Search for dark matter produced in association with a dark Higgs boson decaying into a bottom quark pair in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 2025-08-15 | ||
| Abstract: A search for dark matter produced in association with a dark Higgs boson decaying into a bottom quark pair has been performed in proton-proton collisions at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV collected with the CMS detector during the 2016-2018 data-taking period at the CERN LHC. The analyzed data sample corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The results are interpreted in terms of a novel theoretical model of dark matter production that, together with a spin-1 gauge boson mediator, predicts the existence of a Higgs-boson-like particle in the dark sector (i.e., a dark Higgs boson). This search focuses on an experimental signature with large missing transverse momentum from dark matter production and a resonant structure in the invariant mass of the bottom quark pair from the dark Higgs boson decay. Limits at the 95% confidence level on the signal strength for dark Higgs boson mass hypotheses below 160 GeV are set for the first time with CMS data. Values of the mediator mass up to 2.5-4.5 TeV are excluded depending on the dark Higgs boson mass. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
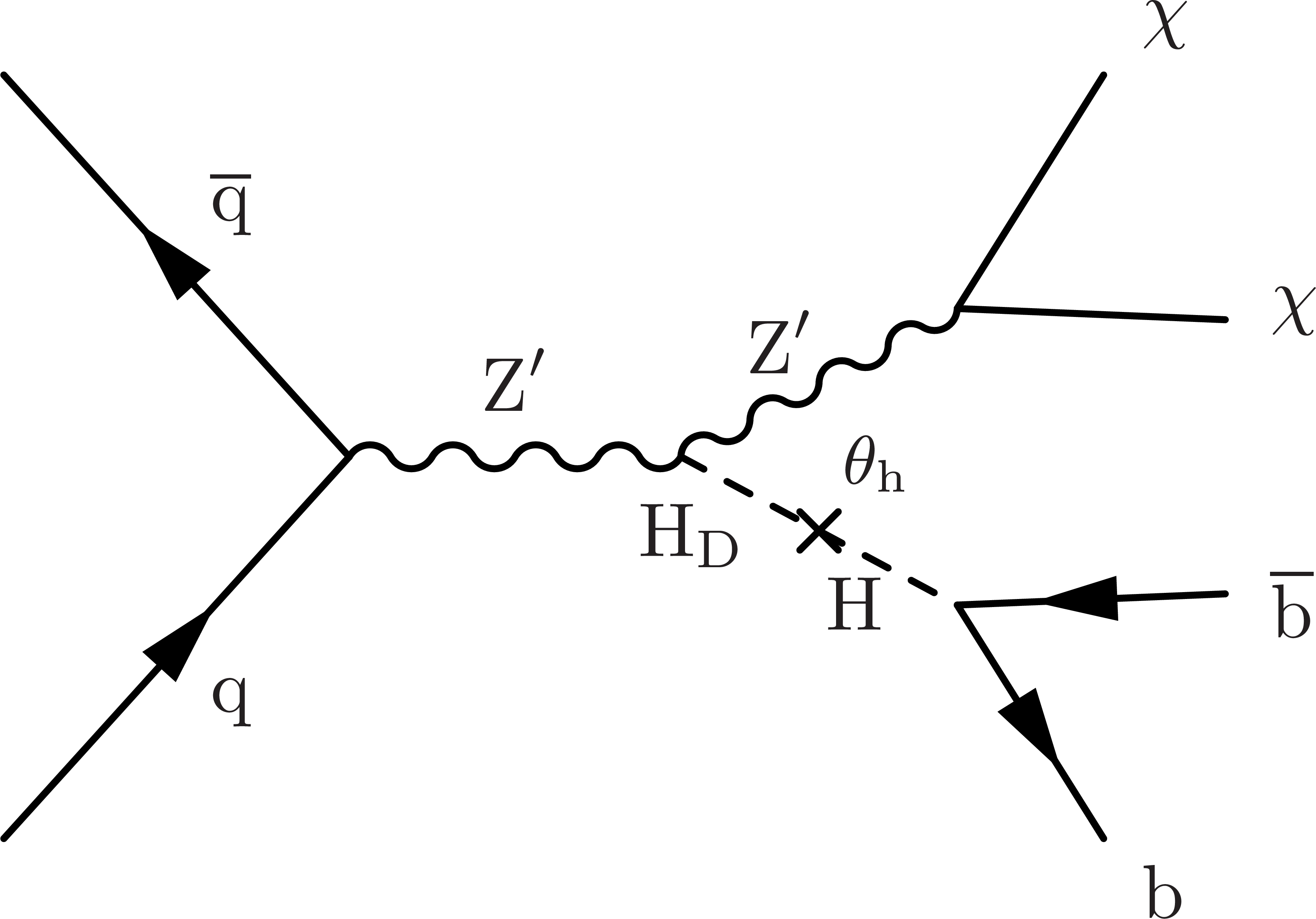
Figure 1:
Feynman diagram for the associated production of a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson and $ \chi $ particles. The interaction with SM quarks is mediated by a $ \mathrm{Z}^{'} $ boson, and the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mixes with the SM Higgs boson through the $ \theta_{\text{h}} $ mixing angle. In this paper we focus on the decay of the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson into a b quark-antiquark pair, which is dominant at lower masses. |
png pdf |
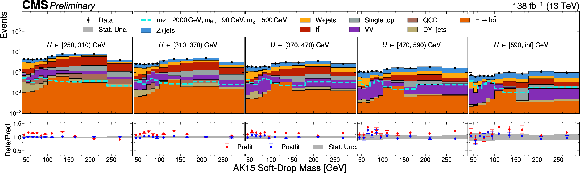
Figure 2:
Postfit $ m_{\text{SD}} $ distributions in bins of $ U $ for all three years combined. The upper panels present stacked postfit predictions for the backgrounds superimposed on the data. The lower panels present the ratio between the data and the background predictions. The ratio between the data and the postfit prediction is represented by the blue dots, while the ratio between the data and the prefit prediction is represented by the red ones. Only statistical uncertainties are shown. |
png pdf |
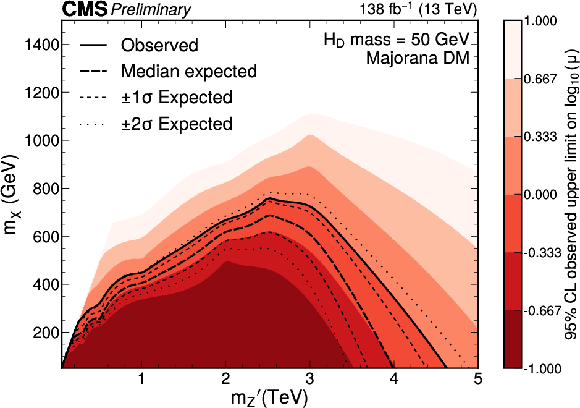
Figure 3:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 50 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
png pdf |
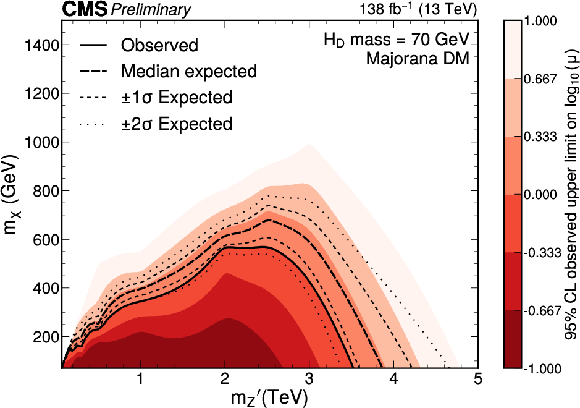
Figure 4:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 70 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
png pdf |
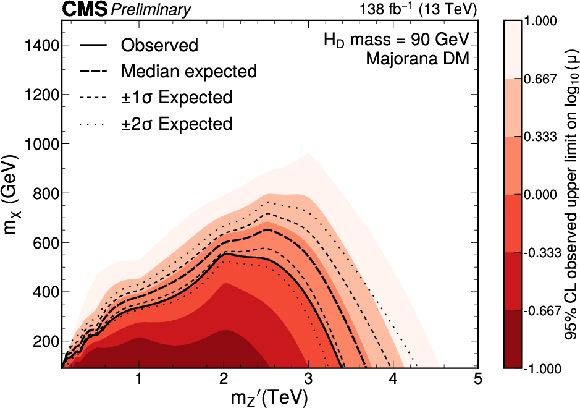
Figure 5:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 90 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
png pdf |
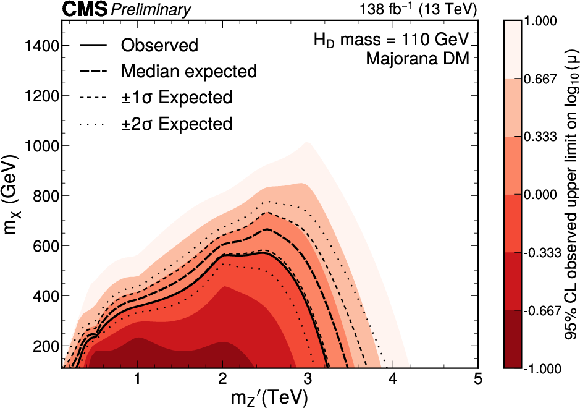
Figure 6:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 110 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
png pdf |
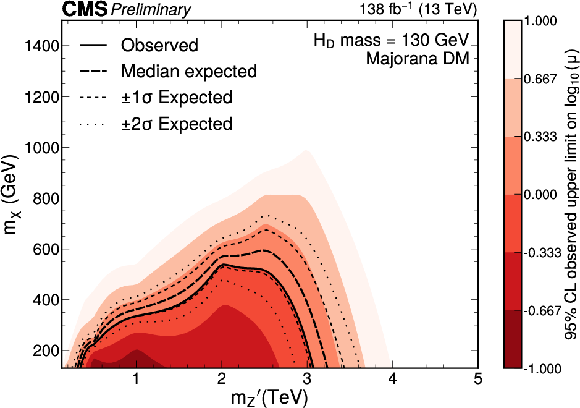
Figure 7:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 130 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
png pdf |
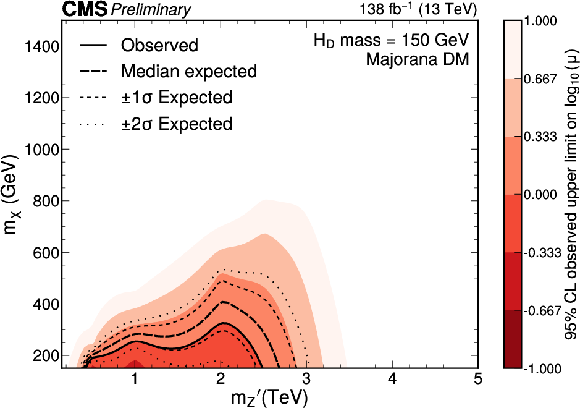
Figure 8:
Expected and observed exclusion limits at the 95% CL on the signal strength $ \mu=\sigma/\sigma_\text{theo} $ as a function of $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ for a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson mass of 150 GeV. Only scenarios where the DM particle is more massive than the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson are considered. The black solid line indicates the observed exclusion boundary corresponding to $ \mu= $ 1. The black dashed and dotted lines represent the expected exclusion and the 68 and 95% CL intervals around the expected boundary, respectively. Parameter combinations corresponding to larger values of $ \mu $ are excluded. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
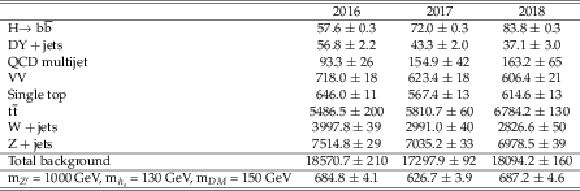
Table 1:
Expected yields from background processes in the SR. The values shown are from Monte Carlo simulation and the uncertainties are statistical-only. The expected yields for a reference signal hypothesis with m$ _{Z'} = $ 1000 GeV, m$ _{h_{s}} = $ 130 GeV, and m$ _{DM} = $ 150 GeV are also reported. |
png pdf |
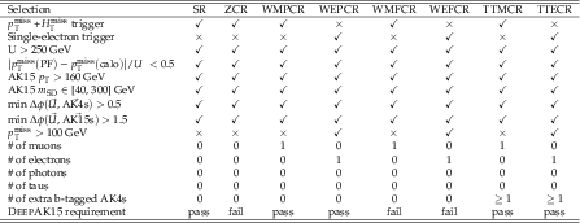
Table 2:
Summary of requirements that define the different analysis regions. A "\checkmark" means the requirement is enforced; an "X" means the variable is left unconstrained in that region (the cut is not applied). |

png pdf |
Table 3:
Summary of statistical and systematic uncertainties included in the analysis. The value given for each rate uncertainty is the pre-fit maximum value. Uncertainties in the shape of the distributions are instead labeled as such. |
| Summary |
| A search for physics beyond the standard model in events with a resonant pair of b quarks and large missing transverse momentum has been presented. A data set of proton-proton collisions at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $ is analyzed. A joint maximum likelihood fit spanning a set of signal and control regions is used to constrain the standard model background contributions to the data and to extract a possible signal. The result is interpreted in terms of exclusion limits at the 95% confidence level on the parameters of a model of production of a $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson in association with dark matter particles. Values of the mediator mass of up to 2.5-4.5 TeV are excluded, depending on the mass of the $ \mathrm{H}_{\text{D}} $ boson and assuming couplings of $ g_\mathrm{q}= $ 0.25 between the mediator and quarks, and $ g_{\chi} = $ 1.0 between the mediator and the DM particles. \newpage |
| References | ||||
| 1 | N. Arkani-Hamed, D. P. Finkbeiner, T. R. Slatyer, and N. Weiner | A theory of dark matter | Physical Review D 7 (2009) 9 | 0810.0713 |
| 2 | F. Zwicky | On the Masses of Nebulae and of Clusters of Nebulae | Astrophysical Journal 8 (1937) 6 | |
| 3 | G. Bertone, D. Hooper, and J. Silk | Particle dark matter: Evidence, candidates and constraints | Phys. Rept. 405 (2005) 279 | hep-ph/0404175 |
| 4 | D. Abercrombie et al. | Dark matter benchmark models for early lhc run-2 searches: Report of the atlas/cms dark matter forum | Physics of the Dark Universe 2 (2020) 7 | 1507.00966 |
| 5 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new particles in events with energetic jets and large missing transverse momentum in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2021) 153 | CMS-EXO-20-004 2107.13021 |
| 6 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in events with an energetic jet and missing transverse momentum in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}=13\text{ }\text{ }\mathrm{TeV} $ with the atlas detector | (Jun, ) 11, 2021 PRD 10 (2021) 3 |
2102.10874 |
| 7 | M. Duerr et al. | Hunting the dark Higgs | JHEP 04 (2017) 143 | 1701.08780 |
| 8 | N. F. Bell, Y. Cai, and R. K. Leane | Dark Forces in the Sky: Signals from Z$ ^{\prime} $ and the Dark Higgs | JCAP 08 (2016) 001 | 1605.09382 |
| 9 | F. Kahlhoefer, K. Schmidt-Hoberg, T. Schwetz, and S. Vogl | Implications of unitarity and gauge invariance for simplified dark matter models | JHEP 02 (2016) 016 | 1510.02110 |
| 10 | N. F. Bell, Y. Cai, and R. K. Leane | Impact of mass generation for spin-1 mediator simplified models | JCAP 01 (2017) 039 | 1610.03063 |
| 11 | LHC Dark Matter Working Group | Recommendations of the LHC dark matter working group: Comparing LHC searches for dark matter mediators in visible and invisible decay channels and calculations of the thermal relic density | Phys. Dark Univ. 26 (2019) 100377 | 1703.05703 |
| 12 | M. T. Frandsen et al. | LHC and Tevatron Bounds on the Dark Matter Direct Detection Cross-Section for Vector Mediators | JHEP 07 (2012) 123 | 1204.3839 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | A portrait of the Higgs boson by the CMS experiment ten years after the discovery. | Nature 607 (2022) 60 | CMS-HIG-22-001 2207.00043 |
| 14 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter produced in association with a dark Higgs boson decaying into $ W^{+}W^{-} $ in the one-lepton final state at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using 139 fb$ ^{-1} $ of $ pp $ collisions recorded with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 07 (2023) 116 | 2211.07175 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark matter particles in W$ ^{+} $W$ ^{-} $ events with transverse momentum imbalance in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 03 (2024) 134 | CMS-EXO-21-012 2310.12229 |
| 16 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for Dark Matter Produced in Association with a Dark Higgs Boson in the b\=b Final State Using pp Collisions at s=13 TeV with the ATLAS Detector | PRL 134 (2025) 121801 | 2407.10549 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Development of the CMS detector for the CERN LHC Run 3 | JINST 19 (2024) P05064 | CMS-PRF-21-001 2309.05466 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 20 | CMS Tracker Group Collaboration | The CMS phase-1 pixel detector upgrade | JINST 16 (2021) P02027 | 2012.14304 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Track impact parameter resolution for the full pseudo rapidity coverage in the 2017 dataset with the CMS phase-1 pixel detector | CMS Detector Performance Summary CMS-DP-2020-049, 2020 CDS |
|
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | 2017 tracking performance plots | CMS Detector Performance Summary CMS-DP-2017-015, 2017 CDS |
|
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | Technical proposal for the Phase-II upgrade of the Compact Muon Solenoid | CMS Technical Proposal CERN-LHCC-2015-010, CMS-TDR-15-02, 2015 CDS |
|
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS high-level trigger during LHC Run 2 | JINST 19 (2024) P11021 | CMS-TRG-19-001 2410.17038 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | Reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ lepton decays to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ at CMS | JINST 11 (2016) P01019 | CMS-TAU-14-001 1510.07488 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of hadronic tau lepton decays using a deep neural network | JINST 17 (2022) P07023 | CMS-TAU-20-001 2201.08458 |
| 32 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_{\mathrm{T}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 33 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | Fastjet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Pileup mitigation at CMS in 13 TeV data | JINST 15 (2020) P09018 | CMS-JME-18-001 2003.00503 |
| 36 | D. Berteloni, H. P., M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup per particle identification | JHEP 59 (2014) | 1407.6013 |
| 37 | E. Bols et al. | Jet Flavour Classification Using DeepJet | JINST 15 (2020) P12012 | 2008.10519 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Performance summary of AK4 jet b tagging with data from proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV with the CMS detector | technical report, 2023 CDS |
|
| 39 | M. Dasgupta, A. Fregoso, S. Marzani, and G. P. Salam | Towards an understanding of jet substructure | JHEP 09 (2013) 029 | 1307.0007 |
| 40 | J. M. Butterworth, A. R. Davison, M. Rubin, and G. P. Salam | Jet substructure as a new Higgs search channel at the LHC | PRL 100 (2008) 242001 | 0802.2470 |
| 41 | A. J. Larkoski, S. Marzani, G. Soyez, and J. Thaler | Soft drop | JHEP 201 (2014) 4 | 1402.2657 |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy, energetic, hadronically decaying particles using machine-learning techniques | JINST 15 (2020) P06005 | CMS-JME-18-002 2004.08262 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 44 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 46 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT 4---a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 47 | The NNPDF collaboration et al. | Parton distributions for the LHC run II | JHEP 04 (2015) 40 | 1410.8849 |
| 48 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | Eur. Phys. J. 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 49 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 50 | M. L. Mangano, M. Moretti, F. Piccinini, and M. Treccani | Matching matrix elements and shower evolution for top-quark production in hadronic collisions | JHEP 01 (2007) 013 | hep-ph/0611129 |
| 51 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 52 | M. Czakon, P. Fiedler, and A. Mitov | Total top-quark pair-production cross section at hadron colliders through $ o(\alpha^4_s) $ | PRL 110 (2013) 252004 | 1303.6254 |
| 53 | P. Nason | A New method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 54 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with Parton Shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 55 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 56 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | NLO single-top production matched with shower in POWHEG: $ s $- and $ t $-channel contributions | JHEP 09 (2009) 111 | 0907.4076 |
| 57 | E. Re | Single-top Wt-channel production matched with parton showers using the POWHEG method | EPJC 71 (2011) 1547 | 1009.2450 |
| 58 | M. Aliev et al. | HATHOR: HAdronic Top and Heavy quarks crOss section calculatoR | Comput. Phys. Commun. 182 (2011) 1034 | 1007.1327 |
| 59 | P. Kant et al. | HATHOR for single top-quark production: Updated predictions and uncertainty estimates for single top-quark production in hadronic collisions | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 74 | 1406.4403 |
| 60 | T. Gehrmann et al. | W$ ^+ $W$ ^- $ production at hadron colliders in next to next to leading order QCD | PRL 113 (2014) 212001 | 1408.5243 |
| 61 | J. M. Campbell and R. K. Ellis | An update on vector boson pair production at hadron colliders | PRD 60 (1999) 113006 | hep-ph/9905386 |
| 62 | J. M. Lindert et al. | Precise predictions for $ V+ $ jets dark matter backgrounds | Eur. Phys. J. 77 (2017) 829 | 1705.04664 |
| 63 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 64 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 link |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 65 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 link |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 66 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS missing transverse momentum reconstruction in pp data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P02006 | CMS-JME-13-003 1411.0511 |
| 67 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in final states with an energetic jet or a hadronically decaying $ {\mathrm{W}} $ or $ {\mathrm{Z}} $ boson and transverse momentum imbalance at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PRD 97 (2018) 092005 | CMS-EXO-16-048 1712.02345 |
| 68 | J. S. Conway | Incorporating Nuisance Parameters in Likelihoods for Multisource Spectra | in PHYSTAT 2011 link |
1103.0354 |
| 69 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The CL$ _{\text{s}} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 70 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 71 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|