

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-HIG-21-007 ; CERN-EP-2023-004 | ||
| A search for decays of the Higgs boson to invisible particles in events with a top-antitop quark pair or a vector boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 2 March 2023 | ||
| Eur. Phys. J. C 83 (2023) 933 | ||
| Abstract: A search for decays to invisible particles of Higgs bosons produced in association with a top-antitop quark pair or a vector boson, which both decay to a fully hadronic final state, has been performed using proton-proton collision data collected at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV by the CMS experiment at the LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The 95% confidence level upper limit set on the branching fraction of the 125 GeV Higgs boson to invisible particles, $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $, is 0.47 (0.40 expected), assuming standard model production cross sections. The results of this analysis are combined with previous $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ searches carried out at $ \sqrt{s}=$ 7, 8, and 13 TeV in complementary production modes. The combined upper limit at 95% confidence level on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ is 0.15 (0.08 expected). | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2303.01214 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
Figure 1:
Representative LO Feynman diagrams for the SM Higgs boson production channels $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Representative LO Feynman diagrams for the SM Higgs boson production channels $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
Representative LO Feynman diagrams for the SM Higgs boson production channels $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH. |

png pdf |
Figure 2:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the $ \mu $+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
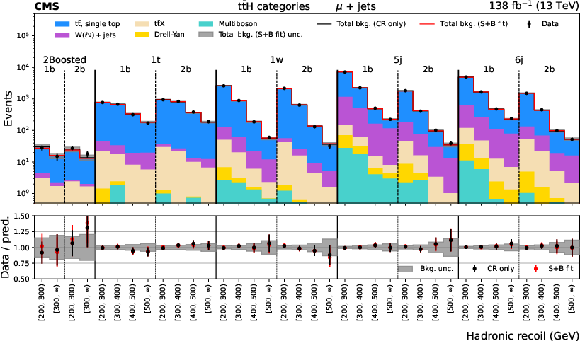
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the $ \mu $+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the $ \mu $+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |

png pdf |
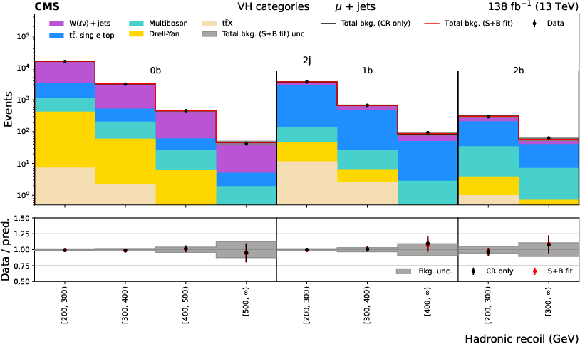
Figure 3:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the e+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the e+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
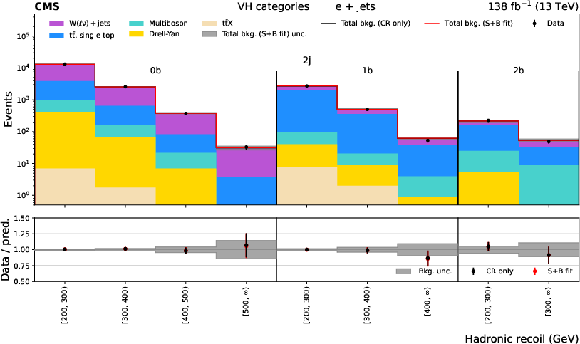
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the e+jets CR. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |

png pdf |
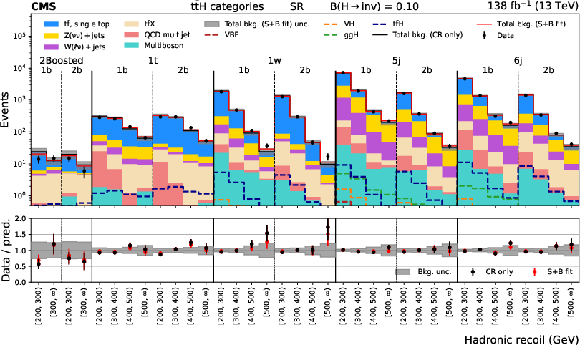
Figure 4:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ category for the $ \mu\mu $+ jets, ee+jets, and $ \ell\ell $+jets CRs (upper plot), and the VH category for the $ \mu\mu $+jets, ee+jets, and $ \gamma $+jets CRs (lower plot). The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
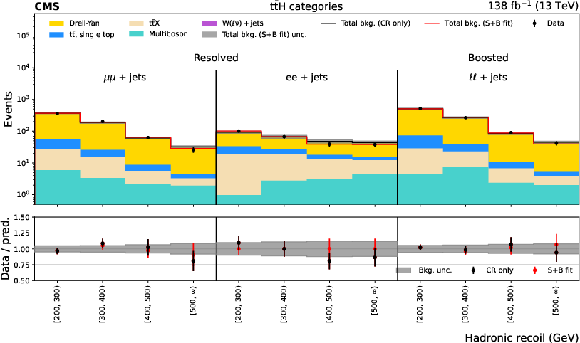
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ category for the $ \mu\mu $+ jets, ee+jets, and $ \ell\ell $+jets CRs (upper plot), and the VH category for the $ \mu\mu $+jets, ee+jets, and $ \gamma $+jets CRs (lower plot). The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |

png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ category for the $ \mu\mu $+ jets, ee+jets, and $ \ell\ell $+jets CRs (upper plot), and the VH category for the $ \mu\mu $+jets, ee+jets, and $ \gamma $+jets CRs (lower plot). The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
png pdf |
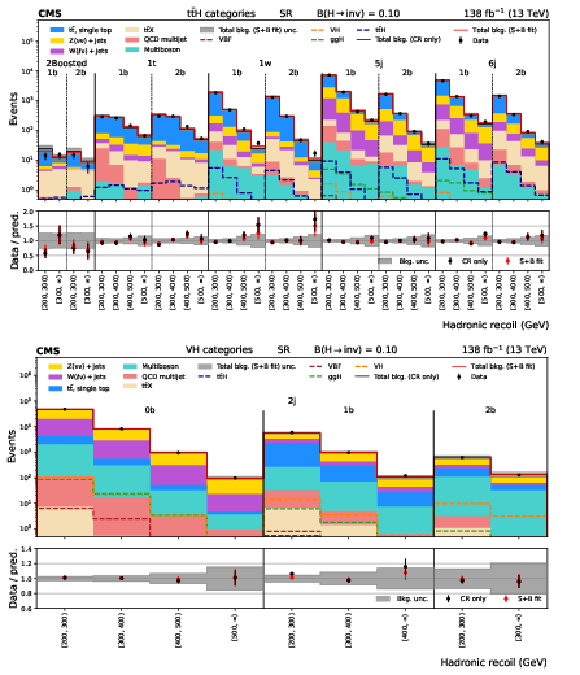
Figure 5:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the SR, showing the signal contributions from $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $, VH, $ \mathrm{g}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{H} $, and VBF weighted by $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} = $0.10. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the SR, showing the signal contributions from $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $, VH, $ \mathrm{g}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{H} $, and VBF weighted by $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} = $0.10. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |

png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
Distributions of hadronic recoil in the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ (upper plot) and VH (lower plot) categories for the SR, showing the signal contributions from $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $, VH, $ \mathrm{g}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{H} $, and VBF weighted by $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} = $0.10. The black histogram shows the total background (bkg.) prediction from a CR only, B-only fit, while the red histogram shows the yields from a CR+SR S+B fit. |
png pdf |
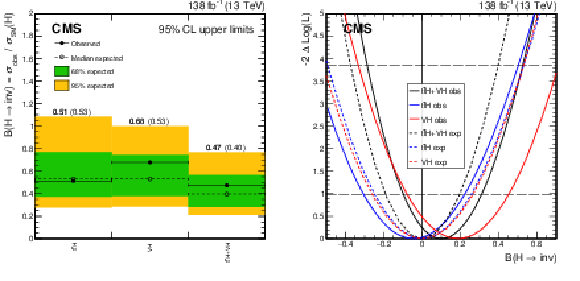
Figure 6:
Left: Observed and expected limits at 95% CL for the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories using 2016--2018 data. Right: The profile likelihood scan corresponding to observed and expected (where $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})}= $ 0) limits in the fit to the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories. |

png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
Left: Observed and expected limits at 95% CL for the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories using 2016--2018 data. Right: The profile likelihood scan corresponding to observed and expected (where $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})}= $ 0) limits in the fit to the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
Left: Observed and expected limits at 95% CL for the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories using 2016--2018 data. Right: The profile likelihood scan corresponding to observed and expected (where $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})}= $ 0) limits in the fit to the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH categories. |
png pdf |
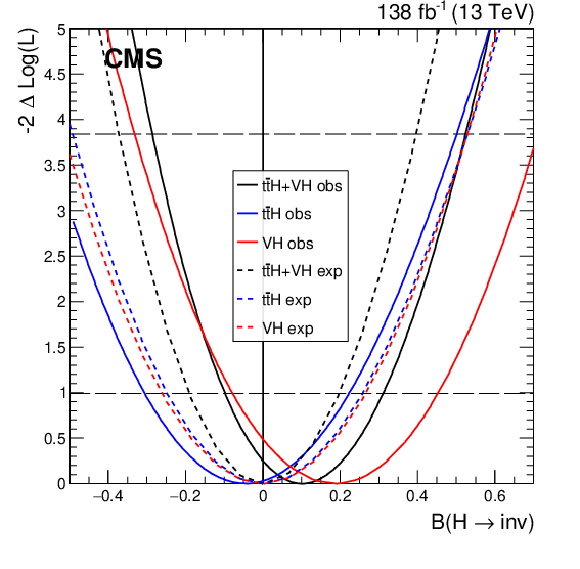
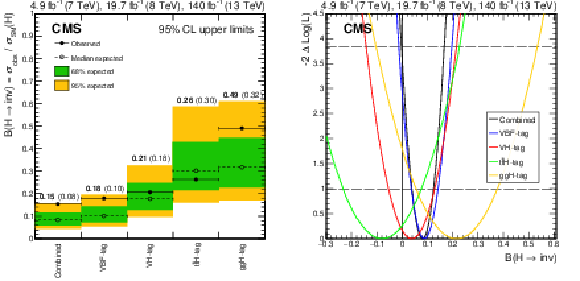
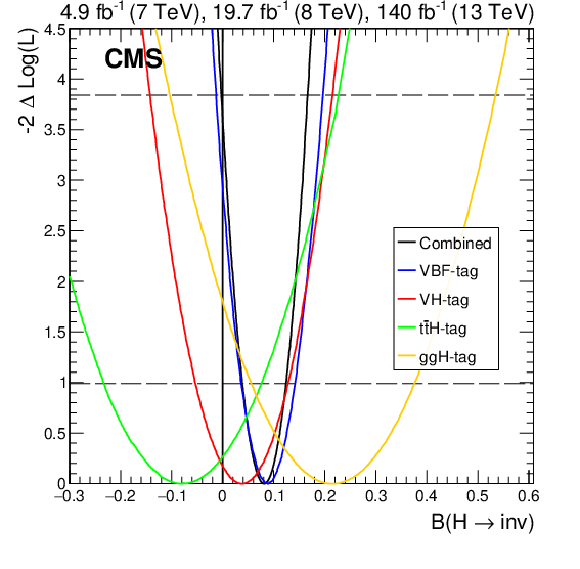
Figure 7:
Left: Exclusion limits at 95% CL on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $. The results are shown separately for each Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2, as well as combined across modes. Right: Scan of the profile negative log-likelihood as a function of $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ broken down by the Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2. |

png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
Left: Exclusion limits at 95% CL on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $. The results are shown separately for each Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2, as well as combined across modes. Right: Scan of the profile negative log-likelihood as a function of $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ broken down by the Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2. |
png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
Left: Exclusion limits at 95% CL on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $. The results are shown separately for each Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2, as well as combined across modes. Right: Scan of the profile negative log-likelihood as a function of $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ broken down by the Higgs boson production mode as tagged by the input analyses for Run 1 and Run 2. |
png pdf |
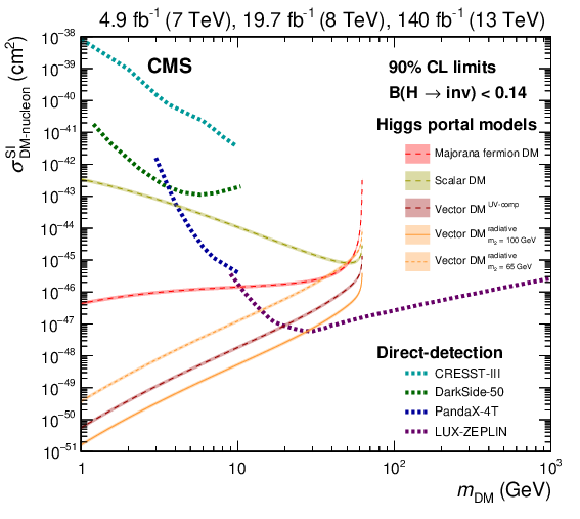
Figure 8:
Upper limits on $ \sigma^{\text{SI}}_{\text{{DM\mbox{-}nucleon}}} $ as a function of DM candidate mass $ m_{\text{DM}} $. Results are presented for a fermion (red) and scalar (yellow) DM candidate. In addition, a vector DM candidate is studied using two UV-comp approaches, the first denoted Vector DM$ ^{\text{UV-comp}} $ [20] (burgundy), and the second a radiative portal version denoted Vector DM$ ^{\text{radiative}}_{m_{2}} $ [23] (orange) with a dark Higgs boson mass of $ m_2 = $ 65 and 100 GeV. Uncertainties are derived from Refs. [99,100,19]. Results are compared to direct-detection searches from CRESST-III [95] (truncated at $ m_{\text{DM}} > $ 1 GeV), DarkSide-50 [96], PandaX-4T [97] and LUX-ZEPLIN [98]. |
png pdf |
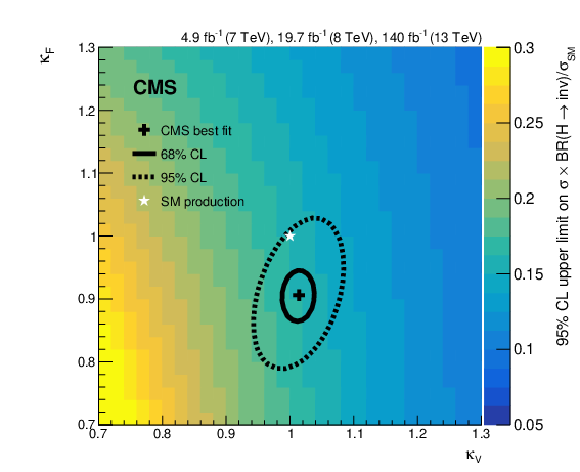
Figure 9:
Observed 95% CL upper limit on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ as a function of coupling strength modifiers, $ \kappa_{\text{V}} $ and $ \kappa_{\text{F}} $, for a Higgs boson of mass 125 GeV. Best estimates for $ \kappa_{\text{V}} $ and $ \kappa_{\text{F}} $ from Ref. [11] are shown as a black cross, together with 68 and 95% CL contours. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Offline selection applied to all categories and regions in this analysis to improve signal purity and reduce overlap with the phase space of other $ \mathrm{H} \to \text{inv} $ searches. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Categorisation of the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ and VH production modes in the analysis. No additional selections are applied to the boosted $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ subcategories. |
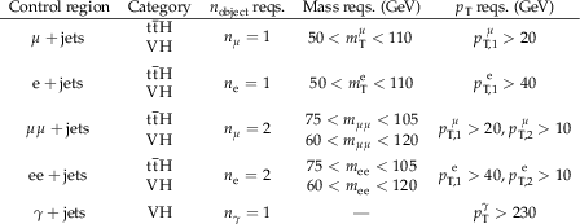
png pdf |
Table 3:
Summary of all CR requirements, excluding selections suppressing the QCD multijet background, and excluding the requirement of $ \Delta\phi ($recoil, $\vec{p}_{\mathrm{T},\text{track}}^{\text{miss}}) > \pi$ /2 applied to the $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ category in the dilepton CRs. No mass requirements are imposed in the $ \gamma $+jets. |

png pdf |
Table 4:
Meaning of the symbols used in Eqs. 4 and 5 that define the likelihood function. |

png pdf |
Table 5:
The ranges corresponding to the maximum and minimum deviations of the event yields from their nominal values, provided where applicable across each region, year of data-taking, category, recoil bin, and all SM background processes, when the respective systematic uncertainty is changed within $ \pm $1 standard deviation. |

png pdf |
Table 6:
Total post-fit yields in the SRs in each recoil bin and analysis category obtained by summing the contributions from the individual data-taking periods. B-only fits are performed for either CR+SR or CR only cases. The extracted signal yields from an S+B fit are also reported, where the signal strength is weighted by $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})}=$ 0.10. |

png pdf |
Table 7:
The observed and expected impacts on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ for different groups of uncertainties, where the expected results are produced with $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} = $ 0. |

png pdf |
Table 8:
Data sets and their respective integrated luminosities used for each production mode across Run 1 and Run 2. For some data-taking periods, no $ \mathrm{H} \to \text{inv} $ search have been performed for the given production mode, and are not included in the combination. |

png pdf |
Table 9:
The observed best fit estimates of $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $, for each analysis channel in the combination, and the 95% CL observed and expected (exp) upper limits on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $. |
| Summary |
| The results of a search for invisible decays of the Higgs boson produced in association with a top-antitop quark pair ($ {\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $) or a vector boson (VH, where V stands for either a W or Z boson), which decays to a fully hadronic final state, are presented. The analysis is based on proton-proton collision data collected at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV during the 2016-2018 data-taking period by the CMS experiment at the LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The $ {\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} \mathrm{H} $ production mechanism is investigated using final states containing b jets, or boosted t quarks or W bosons. The VH production channel focuses on resolving a dijet pair with an invariant mass that is compatible with that of a W or Z boson. No significant excess of events is observed above the predicted SM background. A 95% confidence level upper limit of 0.47 (0.40 expected) is set on the branching fraction of the decay of the Higgs boson to an invisible final state, $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $, assuming SM production cross sections. The results are combined with previous $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ searches carried out at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7, 8, and 13 TeV in complementary production modes. The combined 95% confidence level upper limit on $ {\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{H} \to \text{inv})} $ of 0.15 (0.08 expected) is obtained using Run 1 (2011-2012) and Run 2 (2015--2018) data. The combination represents an improvement in sensitivity of 20% relative to the most sensitive single channel. The results are interpreted in the context of a set of Higgs portal models of dark matter interactions to produce model-dependent exclusion limits that complement direct-detection experiments for light mass dark matter candidates. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | F. Englert and R. Brout | Broken symmetry and the mass of gauge vector mesons | PRL 13 (1964) 321 | |
| 2 | P. W. Higgs | Broken symmetries, massless particles and gauge fields | PL 12 (1964) 132 | |
| 3 | P. W. Higgs | Broken symmetries and the masses of gauge bosons | PRL 13 (1964) 508 | |
| 4 | G. S. Guralnik, C. R. Hagen, and T. W. B. Kibble | Global conservation laws and massless particles | PRL 13 (1964) 585 | |
| 5 | P. W. Higgs | Spontaneous symmetry breakdown without massless bosons | PR 145 (1966) 1156 | |
| 6 | T. W. B. Kibble | Symmetry breaking in non-abelian gauge theories | PR 155 (1967) 1554 | |
| 7 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the standard model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1 | 1207.7214 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson with mass near 125 GeV in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2013) 081 | CMS-HIG-12-036 1303.4571 |
| 10 | ATLAS Collaboration | A detailed map of Higgs boson interactions by the ATLAS experiment ten years after the discovery | Nature 607 (2022) 52 | 2207.00092 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | A portrait of the Higgs boson by the CMS experiment ten years after the discovery | Nature 607 (2022) 60 | CMS-HIG-22-001 2207.00043 |
| 12 | Particle Data Group | Review of particle physics | PTEP 2022 (2022) 083C01 | |
| 13 | R. E. Shrock and M. Suzuki | Invisible decays of Higgs bosons | PLB 110 (1982) 250 | |
| 14 | G. Bélanger et al. | The MSSM invisible Higgs in the light of dark matter and g$-$2 | PLB 519 (2001) 93 | hep-ph/0106275 |
| 15 | A. Datta, K. Huitu, J. Laamanen, and B. Mukhopadhyaya | Linear collider signals of an invisible Higgs boson in theories of large extra dimensions | PRD 70 (2004) 075003 | hep-ph/0404056 |
| 16 | D. Dominici and J. F. Gunion | Invisible Higgs decays from Higgs-graviscalar mixing | PRD 80 (2009) 115006 | 0902.1512 |
| 17 | S. Argyropoulos, O. Brandt, and U. Haisch | Collider searches for dark matter through the Higgs lens | Symmetry 13 (2021) 2406 | 2109.13597 |
| 18 | S. Kanemura, S. Matsumoto, T. Nabeshima, and N. Okada | Can WIMP dark matter overcome the nightmare scenario? | PRD 82 (2010) 055026 | 1005.5651 |
| 19 | A. Djouadi, O. Lebedev, Y. Mambrini, and J. Quevillon | Implications of LHC searches for Higgs--portal dark matter | PLB 709 (2012) 65 | 1112.3299 |
| 20 | S. Baek, P. Ko, W.-I. Park, and E. Senaha | Higgs portal vector dark matter: revisited | JHEP 05 (2013) 036 | 1212.2131 |
| 21 | A. Djouadi, A. Falkowski, Y. Mambrini, and J. Quevillon | Direct detection of Higgs--portal dark matter at the LHC | EPJC 73 (2013) 2455 | 1205.3169 |
| 22 | A. Beniwal et al. | Combined analysis of effective Higgs--portal dark matter models | PRD 93 (2016) 115016 | 1512.06458 |
| 23 | A. DiFranzo, P. J. Fox, and T. M. P. Tait | Vector dark matter through a radiative Higgs portal | JHEP 04 (2016) 135 | 1512.06853 |
| 24 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for an invisibly decaying Higgs boson or dark matter candidates produced in association with a $ Z $ boson in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 776 (2018) 318 | 1708.09624 |
| 25 | ATLAS Collaboration | Combination of searches for invisible Higgs boson decays with the ATLAS experiment | PRL 122 (2019) 231801 | 1904.05105 |
| 26 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in events with an energetic jet and missing transverse momentum in pp collisions at $ \sqrt {s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 103 (2021) 112006 | 2102.10874 |
| 27 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for associated production of a z boson with an invisibly decaying Higgs boson or dark matter candidates at $ \sqrt {s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 829 (2022) 137066 | 2111.08372 |
| 28 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for invisible Higgs-boson decays in events with vector-boson fusion signatures using 139 fb$ ^{-1} $ of proton-proton data recorded by the ATLAS experiment | JHEP 08 (2022) 104 | 2202.07953 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Search for direct top squark pair production in events with one lepton, jets, and missing transverse momentum at 13 TeV with the CMS experiment | JHEP 05 (2020) 032 | CMS-SUS-19-009 1912.08887 |
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | Search for top squark pair production using dilepton final states in pp collision data collected at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | EPJC 81 (2021) 3 | CMS-SUS-19-011 2008.05936 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Combined searches for the production of supersymmetric top quark partners in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | EPJC 81 (2021) 970 | CMS-SUS-20-002 2107.10892 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark matter produced in association with a leptonically decaying z boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | EPJC 81 (2021) 13 | CMS-EXO-19-003 2008.04735 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new particles in events with energetic jets and large missing transverse momentum in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2021) 153 | CMS-EXO-20-004 2107.13021 |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | Search for invisible decays of the Higgs boson produced via vector boson fusion in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRD 105 (2022) 092007 | CMS-HIG-20-003 2201.11585 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 36 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 41 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P10005 | CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 46 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 48 | C. Oleari | The POWHEG-BOX | Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 205 (2010) 36 | 1007.3893 |
| 49 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 50 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 51 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 52 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4 --- a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 53 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | EPJC 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 54 | H. B. Hartanto, B. Jager, L. Reina, and D. Wackeroth | Higgs boson production in association with top quarks in the POWHEG BOX | PRD 91 (2015) 094003 | 1501.04498 |
| 55 | P. Nason and C. Oleari | NLO Higgs boson production via vector-boson fusion matched with shower in POWHEG | JHEP 02 (2010) 037 | 0911.5299 |
| 56 | G. Luisoni, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and F. Tramontano | HW$ ^{\pm} $/HZ + 0 and 1 jet at NLO with the POWHEG BOX interfaced to GoSam and their merging within MiNLO | JHEP 10 (2013) 083 | 1306.2542 |
| 57 | E. Bagnaschi, G. Degrassi, P. Slavich, and A. Vicini | Higgs production via gluon fusion in the POWHEG approach in the SM and in the MSSM | JHEP 02 (2012) 088 | 1111.2854 |
| 58 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 4. deciphering the nature of the Higgs sector | CERN Report CERN-2017-002-M, 2016 link |
1610.07922 |
| 59 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 60 | S. Zanoli et al. | Next-to-next-to-leading order event generation for VH production with H $ {\rightarrow b\overline{b}} $ decay | JHEP 07 (2022) 008 | 2112.04168 |
| 61 | M. L. Mangano, M. Moretti, F. Piccinini, and M. Treccani | Matching matrix elements and shower evolution for top-quark production in hadronic collisions | JHEP 01 (2007) 013 | hep-ph/0611129 |
| 62 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, P. Nason, and E. Re | Top-pair production and decay at NLO matched with parton showers | JHEP 04 (2015) 114 | 1412.1828 |
| 63 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | NLO single-top production matched with shower in POWHEG: $ s $- and $ t $-channel contributions | JHEP 09 (2009) 111 | 0907.4076 |
| 64 | E. Re | Single-top Wt-channel production matched with parton showers using the POWHEG method | EPJC 71 (2011) 1547 | 1009.2450 |
| 65 | M. Czakon et al. | Top-pair production at the LHC through NNLO QCD and NLO EW | JHEP 10 (2017) 186 | 1705.04105 |
| 66 | P. Artoisenet, R. Frederix, O. Mattelaer, and R. Rietkerk | Automatic spin-entangled decays of heavy resonances in monte carlo simulations | JHEP 03 (2013) 015 | 1212.3460 |
| 67 | T. Melia, P. Nason, R. Rontsch, and G. Zanderighi | W$ ^+ $W$ ^- $, WZ and ZZ production in the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 11 (2011) 078 | 1107.5051 |
| 68 | M. Cacciari and G. P. Salam | Pileup subtraction using jet areas | PLB 659 (2008) 119 | 0707.1378 |
| 69 | CMS Collaboration | Technical proposal for the phase-II upgrade of the compact muon solenoid | CMS Technical Proposal CERN-LHCC-2015-010, CMS-TDR-15-02, 2015 CDS |
|
| 70 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ \mathrm{k_{T}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 71 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | Fastjet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 72 | CMS Collaboration | Study of pileup removal algorithms for jets | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2014 CMS-PAS-JME-14-001 |
CMS-PAS-JME-14-001 |
| 73 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P05011 | CMS-BTV-16-002 1712.07158 |
| 74 | CMS Collaboration | Pileup mitigation at CMS in 13 TeV data | JINST 15 (2020) P09018 | CMS-JME-18-001 2003.00503 |
| 75 | D. Bertolini, P. Harris, M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup per particle identification | JHEP 10 (2014) 059 | 1407.6013 |
| 76 | A. J. Larkoski, S. Marzani, G. Soyez, and J. Thaler | Soft drop | JHEP 05 (2014) 146 | 1402.2657 |
| 77 | M. Dasgupta, A. Fregoso, S. Marzani, and G. P. Salam | Towards an understanding of jet substructure | JHEP 09 (2013) 029 | 1307.0007 |
| 78 | J. M. Butterworth, A. R. Davison, M. Rubin, and G. P. Salam | Jet substructure as a new Higgs search channel at the LHC | PRL 100 (2008) 242001 | 0802.2470 |
| 79 | J. Thaler and K. Van Tilburg | Identifying boosted objects with $ N $-subjettiness | JHEP 03 (2011) 015 | 1011.2268 |
| 80 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy, energetic, hadronically decaying particles using machine-learning techniques | JINST 15 (2020) P06005 | CMS-JME-18-002 2004.08262 |
| 81 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 82 | T. Sakuma, H. Flächer, and D. Smith | Alternative angular variables for suppression of QCD multijet events in new physics searches with missing transverse momentum at the LHC | 1803.07942 | |
| 83 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of electron reconstruction and selection with the CMS detector in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P06005 | CMS-EGM-13-001 1502.02701 |
| 84 | J. M. Lindert, S. Pozzorini, R. Boughezal et al. | Precise predictions for V+jets dark matter backgrounds | EPJC 77 (2017) 829 | 1705.04664 |
| 85 | CMS Collaboration | Precise determination of the mass of the Higgs boson and tests of compatibility of its couplings with the standard model predictions using proton collisions at 7 and 8 TeV | EPJC 75 (2015) 212 | CMS-HIG-14-009 1412.8662 |
| 86 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations, and LHC Higgs Combination Group | Procedure for the LHC Higgs boson search combination in summer 2011 | Technical report CMS-NOTE-2011-005, ATL-PHYS-PUB-2011-11, 2011 | |
| 87 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The CL$ _{\text{s}} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 88 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 89 | CMS Collaboration | Searches for invisible decays of the Higgs boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7, 8, and 13 TeV | JHEP 02 (2017) 135 | CMS-HIG-16-016 1610.09218 |
| 90 | CMS Collaboration | Search for invisible decays of Higgs bosons in the vector boson fusion and associated ZH production modes | EPJC 74 (2014) 2980 | CMS-HIG-13-030 1404.1344 |
| 91 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark matter in proton-proton collisions at 8 TeV with missing transverse momentum and vector boson tagged jets | JHEP 12 (2016) 083 | CMS-EXO-12-055 1607.05764 |
| 92 | S. Baker and R. D. Cousins | Clarification of the use of chi square and likelihood functions in fits to histograms | NIM 221 (1984) 437 | |
| 93 | CMS Collaboration | HEPData record for this analysis | link | |
| 94 | M. Zaazoua, L. Truong, K. A. Assamagan, and F. Fassi | Higgs portal vector dark matter interpretation: Review of effective field theory approach and ultraviolet complete models | LHEP 2022 (2022) 270 | 2107.01252 |
| 95 | CRESST Collaboration | First results from the CRESST-III low-mass dark matter program | PRD 100 (2019) 102002 | 1904.00498 |
| 96 | DarkSide-50 Collaboration | Search for low-mass dark matter WIMPs with 12 ton-day exposure of DarkSide-50 | 2207.11966 | |
| 97 | PandaX Collaboration | A first search for solar $ ^8 $B neutrino in the PandaX-4T experiment using neutrino-nucleus coherent scattering | 2207.04883 | |
| 98 | LZ Collaboration | First dark matter search results from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment | 2207.03764 | |
| 99 | R. D. Young and A. W. Thomas | Octet baryon masses and sigma terms from an SU(3) chiral extrapolation | PRD 81 (2010) 014503 | 0901.3310 |
| 100 | MILC Collaboration | The strange quark condensate in the nucleon in 2+1 flavor QCD | PRL 103 (2009) 122002 | 0905.2432 |
| 101 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 3. Higgs properties | Technical report, 2013 link |
1307.1347 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|