

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-EXO-23-004 ; CERN-EP-2025-212 | ||
| Search for dijet resonances with data scouting in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 24 October 2025 | ||
| Accepted for publication in J. High Energy Phys. | ||
| Abstract: A search is presented for narrow resonances, with a mass between 0.6 and 1.8 TeV, decaying to pairs of jets, in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV. The search is performed using dijets that are reconstructed, selected, and recorded in a compact form by the high-level trigger in a technique referred to as ``data scouting", from data collected in 2016-2018 corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 117 fb$^{-1}$. The dijet mass spectra are well described by a smooth parameterization, and no significant evidence for the production of new particles is observed. Model-independent upper limits are presented on the product of the cross section, branching fraction, and acceptance for the individual cases of narrow quark-quark, quark-gluon, and gluon-gluon resonances, and are compared to the predictions from a variety of models of narrow dijet resonance production. The upper limit on the coupling of a dark matter mediator to quarks is presented as a function of the mediator mass. The sensitivity of this search goes beyond what is expected from statistical scaling with the integrated luminosity alone, as a consequence of the use of fewer parameters in the background function within a more robust statistical procedure. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2510.21641 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
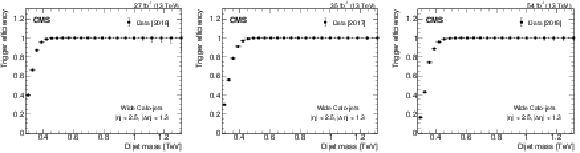
Figure 1:
The measured HLT trigger efficiency as a function of the offline dijet mass for wide Calo-jets, defined in Section 3, for 2016 (left), 2017 (middle), and 2018 (right) data. |
png pdf |
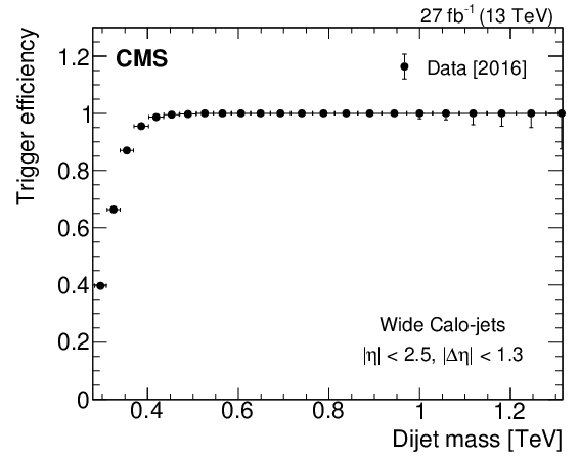
Figure 1-a:
The measured HLT trigger efficiency as a function of the offline dijet mass for wide Calo-jets, defined in Section 3, for 2016 (left), 2017 (middle), and 2018 (right) data. |
png pdf |
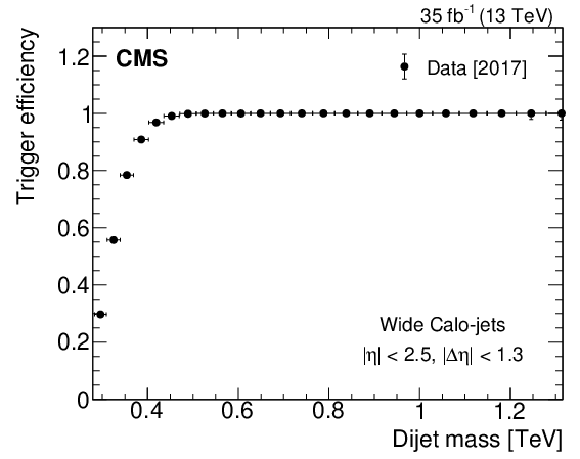
Figure 1-b:
The measured HLT trigger efficiency as a function of the offline dijet mass for wide Calo-jets, defined in Section 3, for 2016 (left), 2017 (middle), and 2018 (right) data. |
png pdf |
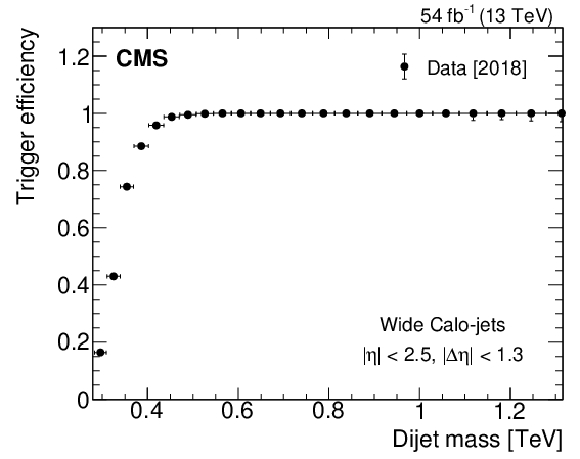
Figure 1-c:
The measured HLT trigger efficiency as a function of the offline dijet mass for wide Calo-jets, defined in Section 3, for 2016 (left), 2017 (middle), and 2018 (right) data. |
png pdf |
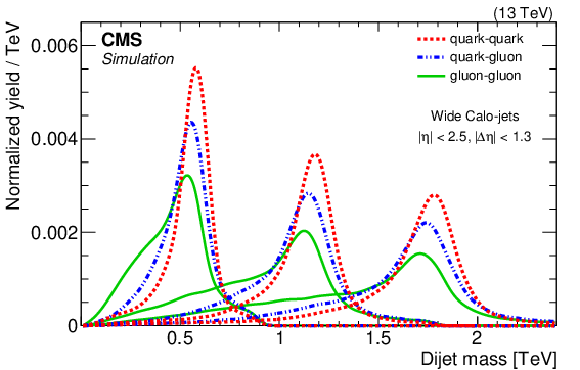
Figure 2:
Simulated signal shapes of narrow resonances from parton pairs quark-quark (dotted red curves), quark-gluon (dashed-dotted blue curves), and gluon-gluon (solid green curves) with masses of 0.6, 1.2, and 1.8 TeV. The reconstructed dijet mass spectra are for wide Calo-jets. |
png pdf |
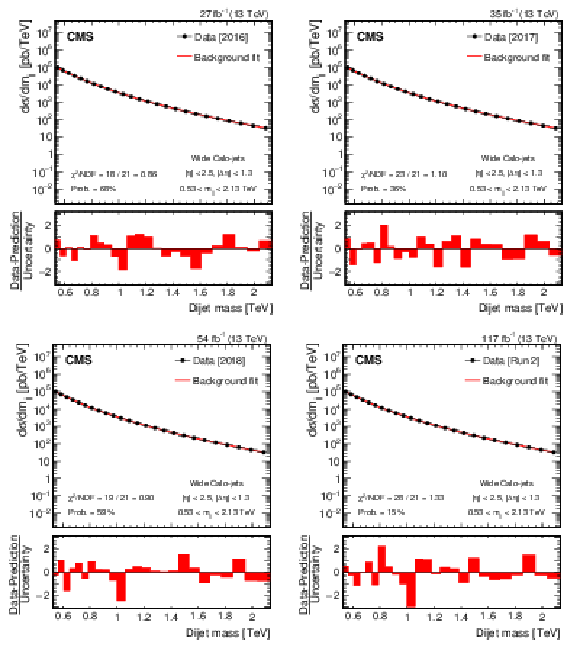
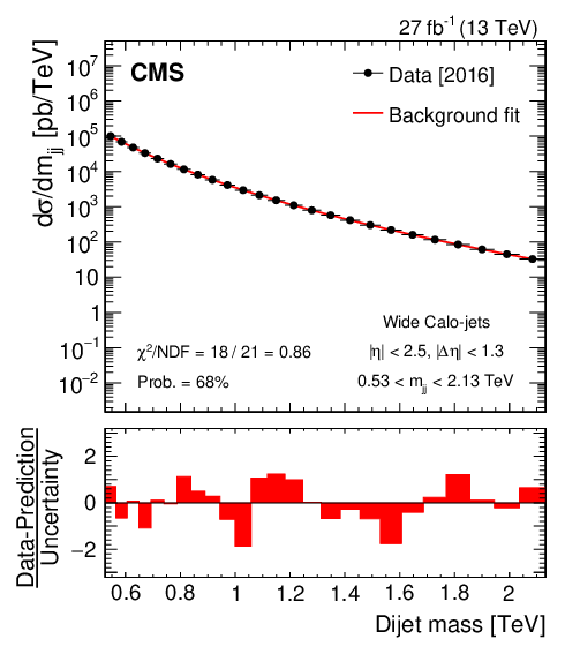
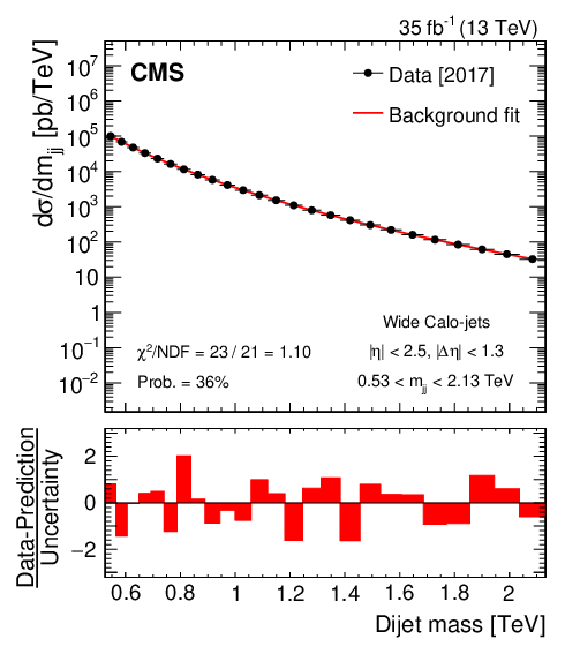
Figure 3:
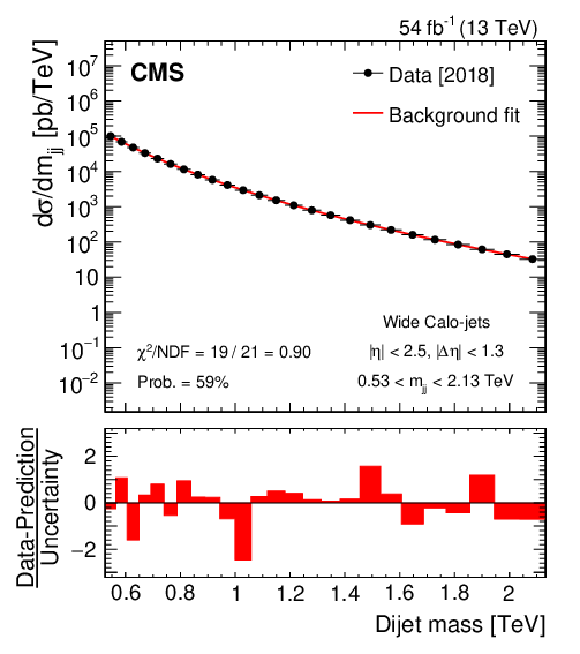
Dijet mass spectra for wide Calo-jets (points) compared to a parameterization of the background (solid curve) for the 2016 (upper left), 2017 (upper right), 2018 (lower left), and the combined (lower right) data sets. The horizontal lines on the data points in the upper panel show variable bin sizes, while the red bars in the lower panels show the bin-by-bin difference between the data and parameterization, normalized to the total uncertainty. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Dijet mass spectra for wide Calo-jets (points) compared to a parameterization of the background (solid curve) for the 2016 (upper left), 2017 (upper right), 2018 (lower left), and the combined (lower right) data sets. The horizontal lines on the data points in the upper panel show variable bin sizes, while the red bars in the lower panels show the bin-by-bin difference between the data and parameterization, normalized to the total uncertainty. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Dijet mass spectra for wide Calo-jets (points) compared to a parameterization of the background (solid curve) for the 2016 (upper left), 2017 (upper right), 2018 (lower left), and the combined (lower right) data sets. The horizontal lines on the data points in the upper panel show variable bin sizes, while the red bars in the lower panels show the bin-by-bin difference between the data and parameterization, normalized to the total uncertainty. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-c:
Dijet mass spectra for wide Calo-jets (points) compared to a parameterization of the background (solid curve) for the 2016 (upper left), 2017 (upper right), 2018 (lower left), and the combined (lower right) data sets. The horizontal lines on the data points in the upper panel show variable bin sizes, while the red bars in the lower panels show the bin-by-bin difference between the data and parameterization, normalized to the total uncertainty. |
png pdf |
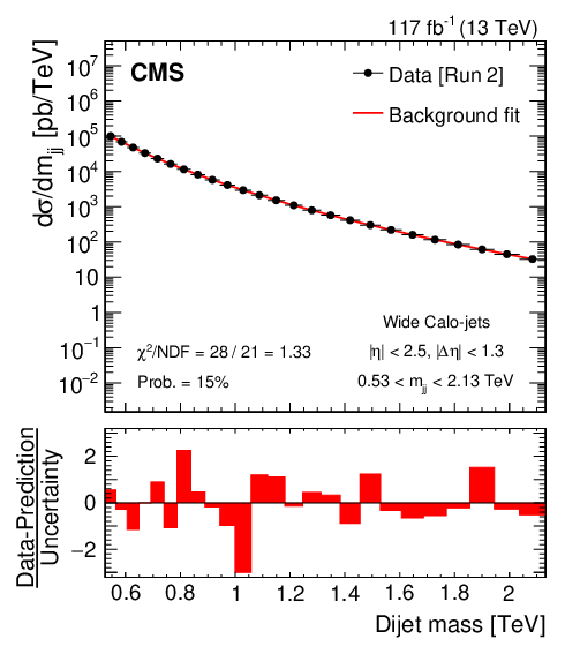
Figure 3-d:
Dijet mass spectra for wide Calo-jets (points) compared to a parameterization of the background (solid curve) for the 2016 (upper left), 2017 (upper right), 2018 (lower left), and the combined (lower right) data sets. The horizontal lines on the data points in the upper panel show variable bin sizes, while the red bars in the lower panels show the bin-by-bin difference between the data and parameterization, normalized to the total uncertainty. |
png pdf |
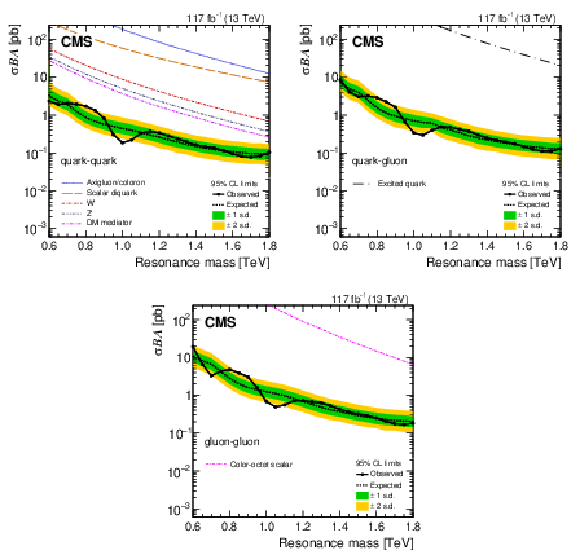
Figure 4:
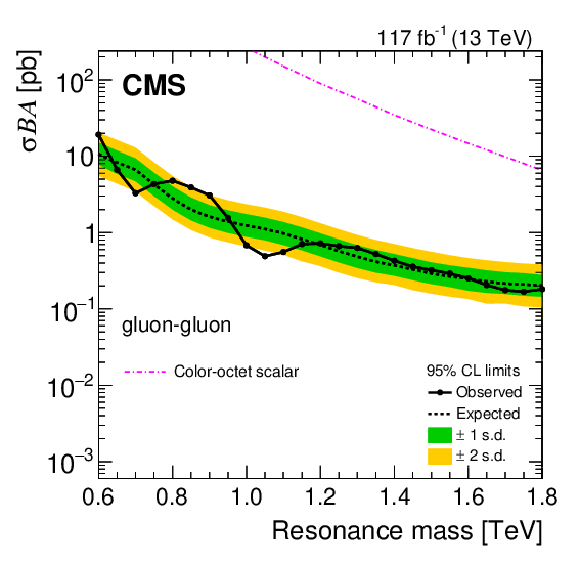
The observed 95% CL upper limits on the product of the cross section ($ \sigma $), branching fraction ($ B $), and acceptance ($ A $) for dijet resonances decaying to quark-quark (upper left), quark-gluon (upper right), and gluon-gluon (lower). The corresponding expected limits (dashed) and their variations at the 1 and 2 standard deviation levels (shaded bands) are also shown. Limits are compared to the predicted cross sections for new gauge bosons W' and Z' with SM-like couplings [1], axigluons [2], excited quarks [3,5], scalar diquarks [4], colorons [6], color-octet scalars [9], and DM mediators for the couplings $ g_{\mathrm{q}}= $ 0.25 and $ g_{\mathrm{DM}}= $ 1, and dark matter mass $ M_{\text{DM}}= $ 1 GeV [14,12]. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
The observed 95% CL upper limits on the product of the cross section ($ \sigma $), branching fraction ($ B $), and acceptance ($ A $) for dijet resonances decaying to quark-quark (upper left), quark-gluon (upper right), and gluon-gluon (lower). The corresponding expected limits (dashed) and their variations at the 1 and 2 standard deviation levels (shaded bands) are also shown. Limits are compared to the predicted cross sections for new gauge bosons W' and Z' with SM-like couplings [1], axigluons [2], excited quarks [3,5], scalar diquarks [4], colorons [6], color-octet scalars [9], and DM mediators for the couplings $ g_{\mathrm{q}}= $ 0.25 and $ g_{\mathrm{DM}}= $ 1, and dark matter mass $ M_{\text{DM}}= $ 1 GeV [14,12]. |
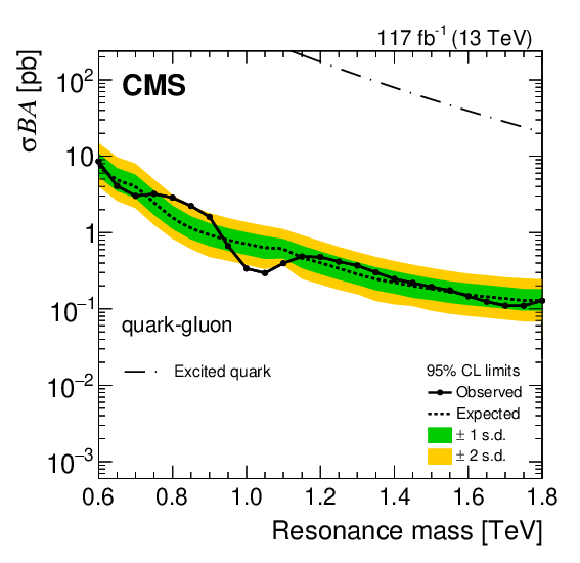
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
The observed 95% CL upper limits on the product of the cross section ($ \sigma $), branching fraction ($ B $), and acceptance ($ A $) for dijet resonances decaying to quark-quark (upper left), quark-gluon (upper right), and gluon-gluon (lower). The corresponding expected limits (dashed) and their variations at the 1 and 2 standard deviation levels (shaded bands) are also shown. Limits are compared to the predicted cross sections for new gauge bosons W' and Z' with SM-like couplings [1], axigluons [2], excited quarks [3,5], scalar diquarks [4], colorons [6], color-octet scalars [9], and DM mediators for the couplings $ g_{\mathrm{q}}= $ 0.25 and $ g_{\mathrm{DM}}= $ 1, and dark matter mass $ M_{\text{DM}}= $ 1 GeV [14,12]. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-c:
The observed 95% CL upper limits on the product of the cross section ($ \sigma $), branching fraction ($ B $), and acceptance ($ A $) for dijet resonances decaying to quark-quark (upper left), quark-gluon (upper right), and gluon-gluon (lower). The corresponding expected limits (dashed) and their variations at the 1 and 2 standard deviation levels (shaded bands) are also shown. Limits are compared to the predicted cross sections for new gauge bosons W' and Z' with SM-like couplings [1], axigluons [2], excited quarks [3,5], scalar diquarks [4], colorons [6], color-octet scalars [9], and DM mediators for the couplings $ g_{\mathrm{q}}= $ 0.25 and $ g_{\mathrm{DM}}= $ 1, and dark matter mass $ M_{\text{DM}}= $ 1 GeV [14,12]. |
png pdf |
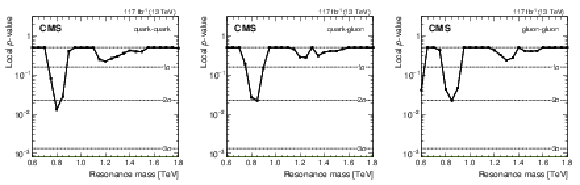
Figure 5:
Local $ p\text{-value} $, and the corresponding significance in standard deviations, for quark-quark (left), quark-gluon (middle), and gluon-gluon (right) resonances. |
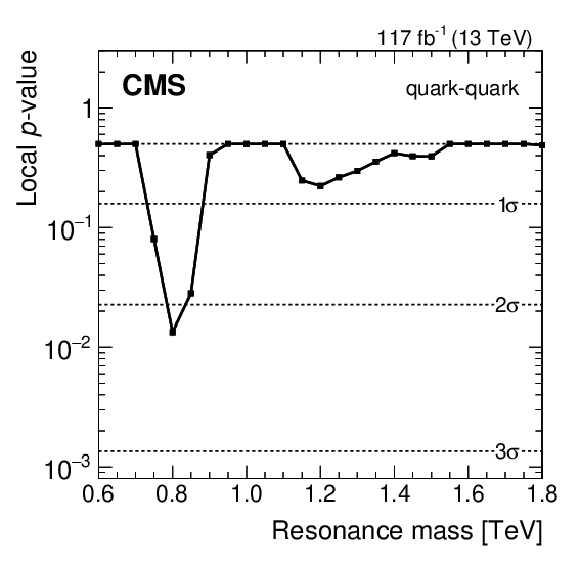
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
Local $ p\text{-value} $, and the corresponding significance in standard deviations, for quark-quark (left), quark-gluon (middle), and gluon-gluon (right) resonances. |
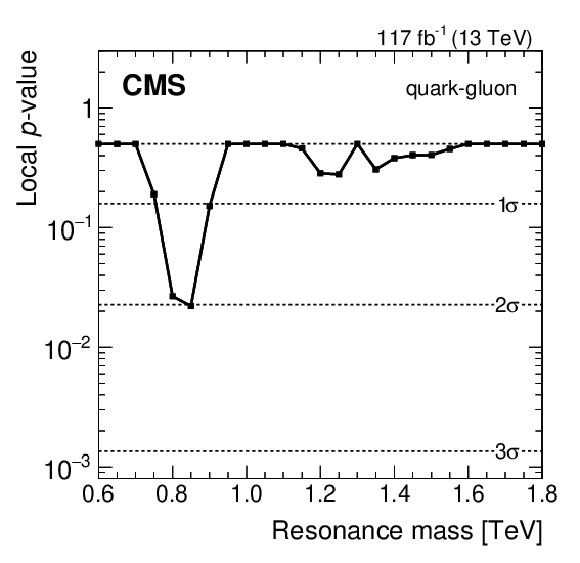
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
Local $ p\text{-value} $, and the corresponding significance in standard deviations, for quark-quark (left), quark-gluon (middle), and gluon-gluon (right) resonances. |
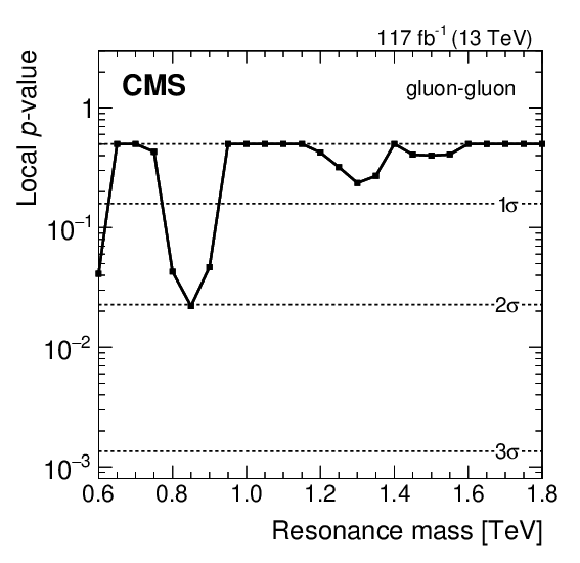
png pdf |
Figure 5-c:
Local $ p\text{-value} $, and the corresponding significance in standard deviations, for quark-quark (left), quark-gluon (middle), and gluon-gluon (right) resonances. |
png pdf |
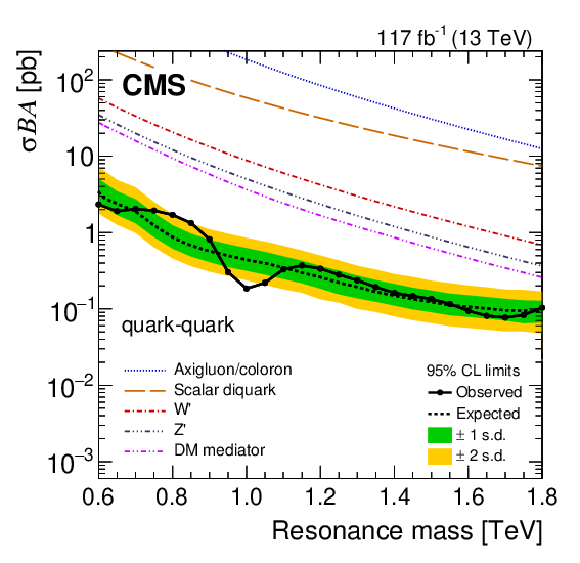
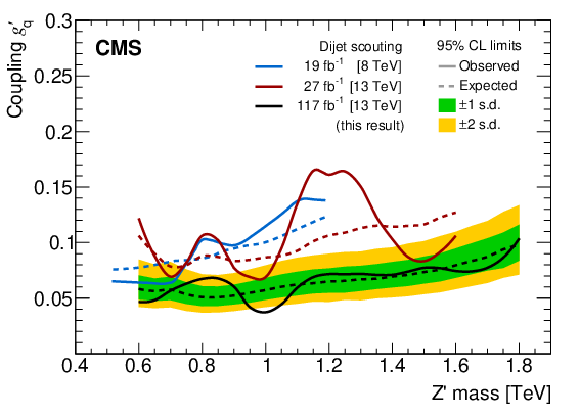
Figure 6:
The 95% CL upper limit on the universal quark coupling $ g_{\mathrm{q}}' $ as a function of resonance mass for a leptophobic Z' resonance that only couples to quarks. The observed limits (solid), expected limits (dashed), and their variation at the 1 and 2 standard deviation levels (shaded bands) are shown. Current limits (black) are compared with previously published ones from CMS at 8 TeV [35] (blue) and 13 TeV [29] (red). |
| Summary |
| Calorimeter jets from data scouting have been used to search for dijet resonances with masses between 0.6 and 1.8 TeV. The dijet mass spectra are observed to be smoothly falling distributions, and no significant evidence for resonant particle production is found. Signal significances and upper limits are presented as functions of the resonance mass, on the product of the cross section, branching fraction, and acceptance, for the individual cases of narrow quark-quark, quark-gluon, and gluon-gluon resonances that are applicable to any model of narrow dijet resonance production. The largest local significance is observed to be 2.2 standard deviations at a quark-quark resonance mass of 0.8 TeV. The limits exclude models of color-octet scalars, excited quarks, axigluons, colorons, scalar diquarks, W' and Z' bosons, and dark matter (DM) mediators, for the benchmark choices of the couplings, over the complete mass range considered. The limit on the coupling of DM mediators to quarks, in a simplified model of interactions between quarks and DM, is presented as a function of the mediator mass. The sensitivity of this search goes beyond what is expected from statistical scaling with the integrated luminosity alone, as a consequence of the use of fewer parameters in the background function within a more robust statistical procedure. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | E. Eichten, I. Hinchliffe, K. D. Lane, and C. Quigg | Supercollider physics | Rev. Mod. Phys. 56 (1984) 579 | |
| 2 | P. H. Frampton and S. L. Glashow | Chiral color: An alternative to the standard model | PLB 190 (1987) 157 | |
| 3 | U. Baur, I. Hinchliffe, and D. Zeppenfeld | Excited quark production at hadron colliders | Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 02 (1987) 1285 | |
| 4 | J. L. Hewett and T. G. Rizzo | Low-energy phenomenology of superstring-inspired E(6) models | Phys. Rept. 183 (1989) 193 | |
| 5 | U. Baur, M. Spira, and P. M. Zerwas | Excited quark and lepton production at hadron colliders | PRD 42 (1990) 815 | |
| 6 | E. H. Simmons | Coloron phenomenology | PRD 55 (1997) 1678 | hep-ph/9608269 |
| 7 | L. Randall and R. Sundrum | An alternative to compactification | PRL 83 (1999) 4690 | hep-th/9906064 |
| 8 | S. Cullen, M. Perelstein, and M. E. Peskin | TeV strings and collider probes of large extra dimensions | PRD 62 (2000) 055012 | hep-ph/0001166 |
| 9 | T. Han, I. Lewis, and Z. Liu | Colored resonant signals at the LHC: Largest rate and simplest topology | JHEP 12 (2010) 085 | 1010.4309 |
| 10 | R. S. Chivukula, E. H. Simmons, A. Farzinnia, and J. Ren | Hadron collider production of massive color-octet vector bosons at next-to-leading order | PRD 87 (2013) 094011 | 1303.1120 |
| 11 | M. Chala et al. | Constraining dark sectors with monojets and dijets | JHEP 07 (2015) 089 | 1503.05916 |
| 12 | J. Abdallah et al. | Simplified models for dark matter searches at the LHC | Phys. Dark Univ. 9-10 8, 2015 link |
1506.03116 |
| 13 | D. Abercrombie et al. | Dark matter benchmark models for early LHC Run-2 searches: Report of the ATLAS/CMS dark matter forum | Phys. Dark Univ. 26 (2019) 100371 | 1507.00966 |
| 14 | A. Boveia et. al. | Recommendations on presenting LHC searches for missing transverse energy signals using simplified $ s $-channel models of dark matter | Phys. Dark. Univ. 27 (2020) 100365 | 1603.04156 |
| 15 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new particles in two-jet final states in 7 TeV proton-proton collisions with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PRL 105 (2010) 161801 | 1008.2461 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dijet resonances in 7 TeV pp collisions at CMS | PRL 105 (2010) 211801 | CMS-EXO-10-010 1010.0203 |
| 17 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new physics in dijet mass and angular distributions in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV measured with the ATLAS detector | New J. Phys. 13 (2011) 053044 | 1103.3864 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonances in the dijet mass spectrum from 7 TeV pp collisions at CMS | PLB 704 (2011) 123 | CMS-EXO-11-015 1107.4771 |
| 19 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new physics in the dijet mass distribution using 1 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV collected by the ATLAS detector | PLB 708 (2012) 37 | 1108.6311 |
| 20 | ATLAS Collaboration | ATLAS search for new phenomena in dijet mass and angular distributions using pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2013) 029 | 1210.1718 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances and quantum black holes in inclusive and b-tagged dijet mass spectra from pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2013) 013 | CMS-EXO-11-094 1210.2387 |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances using the dijet mass spectrum in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | PRD 87 (2013) 114015 | CMS-EXO-12-016 1302.4794 |
| 23 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in the dijet mass distribution using pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 91 (2015) 052007 | 1407.1376 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonances and quantum black holes using dijet mass spectra in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | PRD 91 (2015) 052009 | CMS-EXO-12-059 1501.04198 |
| 25 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in dijet mass and angular distributions from pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 754 (2016) 302 | 1512.01530 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances decaying to dijets in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 116 (2016) 071801 | CMS-EXO-15-001 1512.01224 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dijet resonances in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV and constraints on dark matter and other models | PLB 769 (2017) 520 | CMS-EXO-16-032 1611.03568 |
| 28 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in dijet events using 37 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collision data collected at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 96 (2017) 052004 | 1703.09127 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow and broad dijet resonances in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV and constraints on dark matter mediators and other new particles | JHEP 08 (2018) 130 | CMS-EXO-16-056 1806.00843 |
| 30 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new resonances in mass distributions of jet pairs using 139 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 03 (2020) 145 | 1910.08447 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Search for high mass dijet resonances with a new background prediction method in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 05 (2020) 033 | CMS-EXO-19-012 1911.03947 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Search for low-mass quark-antiquark resonances produced in association with a photon at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PRL 123 (2019) 231803 | CMS-EXO-17-027 1905.10331 |
| 33 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for light resonances decaying to boosted quark pairs and produced in association with a photon or a jet in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 788 (2019) 316 | 1801.08769 |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | Search for low mass vector resonances decaying into quark-antiquark pairs in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PRD 100 (2019) 112007 | CMS-EXO-18-012 1909.04114 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances in dijet final states at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV with the novel CMS technique of data scouting | PRL 117 (2016) 031802 | CMS-EXO-14-005 1604.08907 |
| 36 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for low-mass dijet resonances using trigger-level jets with the ATLAS detector in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PRL 121 (2018) 081801 | 1804.03496 |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | Enriching the physics program of the CMS experiment via data scouting and data parking | Phys. Rept. 1115 (2025) 678 | CMS-EXO-23-007 2403.16134 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | HEPData record for this analysis | link | |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Development of the CMS detector for the CERN LHC Run 3 | JINST 19 (2024) P05064 | CMS-PRF-21-001 2309.05466 |
| 41 | M. Cacciari and G. P. Salam | Dispelling the $ N^{3} $ myth for the $ k_\mathrm{T} $ jet-finder | PLB 641 (2006) 57 | hep-ph/0512210 |
| 42 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_\mathrm{T} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 43 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 44 | M. Cacciari and G. P. Salam | Pileup subtraction using jet areas | PLB 659 (2008) 119 | 0707.1378 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 46 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS high-level trigger during LHC Run 2 | JINST 19 (2024) P11021 | CMS-TRG-19-001 2410.17038 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Pileup mitigation at CMS in 13 TeV data | JINST 15 (2020) P09018 | CMS-JME-18-001 2003.00503 |
| 49 | CMS Collaboration | Jet algorithms performance in 13 TeV data | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2017 CMS-PAS-JME-16-003 |
CMS-PAS-JME-16-003 |
| 50 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 51 | P. Skands, S. Carrazza, and J. Rojo | Tuning PYTHIA 8.1: the Monash 2013 tune | EPJC 74 (2014) 3024 | 1404.5630 |
| 52 | CMS Collaboration | Event generator tunes obtained from underlying event and multiparton scattering measurements | EPJC 76 (2016) 155 | CMS-GEN-14-001 1512.00815 |
| 53 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4 --- a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 54 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonant and nonresonant production of pairs of dijet resonances in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2023) 161 | CMS-EXO-21-010 2206.09997 |
| 55 | R. A. Fisher | On the interpretation of $ \chi^2 $ from contingency tables, and the calculation of p | J. Roy. Stat. Soc. 85 (1922) | |
| 56 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 57 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurements for the 2017 data taking period | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2017 CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 58 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurements for the 2018 data taking period | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2017 CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 59 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 60 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: the CL$ \mathrm{_s} $ technique | J. Phys. G 28 () 2693, 2002 link |
|
| 61 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS statistical analysis and combination tool: Combine | Comput. Softw. Big Sci. 8 (2024) 19 | CMS-CAT-23-001 2404.06614 |
| 62 | W. Verkerke and D. Kirkby | The RooFit toolkit for data modeling | in Proc. 13th Int. Conf. on Computing in High Energy and Nuclear Physics (CHEP): La Jolla CA, United States. 2003 link |
physics/0306116 |
| 63 | L. Moneta et al. | The RooStats project | in Proc. 13th Int. Workshop on Advanced Computing and Analysis Techniques in Physics Research (ACAT): Jaipur, India. 2010 link |
1009.1003 |
| 64 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 65 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for electroweak-scale dijet resonances using trigger-level analysis with the ATLAS detector in 132 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | Submitted to Phys. Rev. D, 2025 | 2509.01219 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|