

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-TOP-25-016 ; CERN-EP-2025-287 | ||
| Characterization of the quantum state of top quark pairs produced in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV using the beam and helicity bases | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 19 December 2025 | ||
| Accepted for publication in Phys. Rev. D | ||
| Abstract: Measurements of the spin correlation coefficients in the beam basis are presented for top quark-antiquark ($ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $) systems produced in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV collected by the CMS experiment in 2016-2018, and corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The $ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $ system is reconstructed from final states containing an electron or muon, and jets. Together with the previously reported results in the helicity basis, these measurements are used to decompose the system into the Bell and spin eigenstates in various kinematic regions. The spin correlation coefficients are also used to evaluate properties of the $ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $ quantum state, such as the purity, von Neumann entropy, and entanglement. All results are consistent with standard model predictions. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2512.17557 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
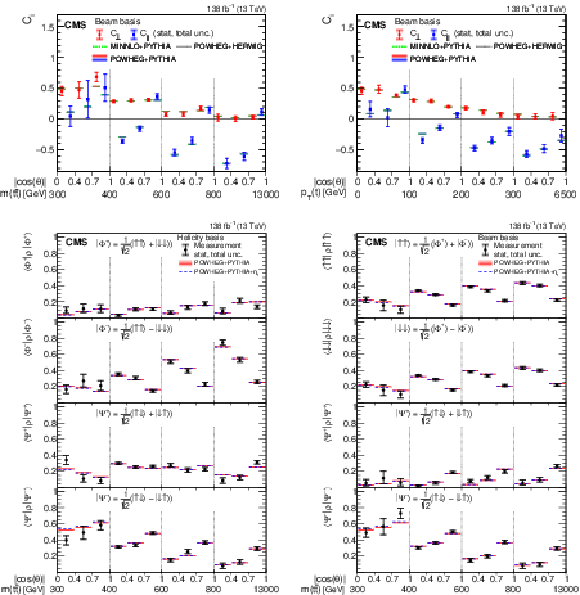
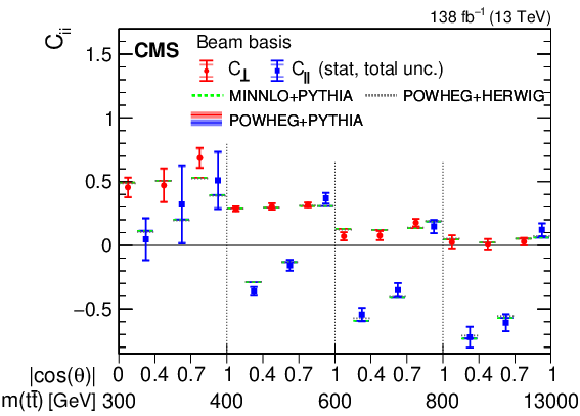
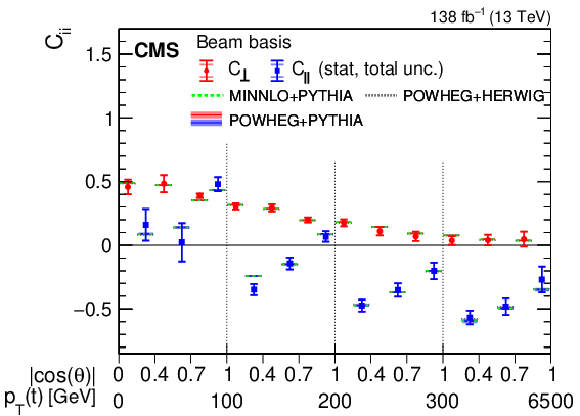
Figure 1:
Results of the spin correlation coefficients in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (left) and $ p_{\mathrm{T}}(\mathrm{t}) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (right) in the beam basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainties and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + HERWIG, MINNLO+ PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Results of the spin correlation coefficients in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (left) and $ p_{\mathrm{T}}(\mathrm{t}) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (right) in the beam basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainties and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + HERWIG, MINNLO+ PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
Results of the spin correlation coefficients in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (left) and $ p_{\mathrm{T}}(\mathrm{t}) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ (right) in the beam basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainties and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + HERWIG, MINNLO+ PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
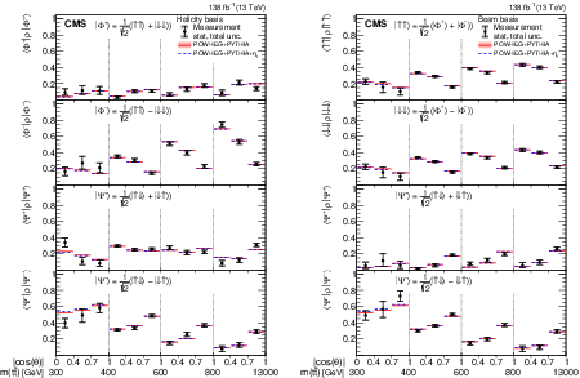
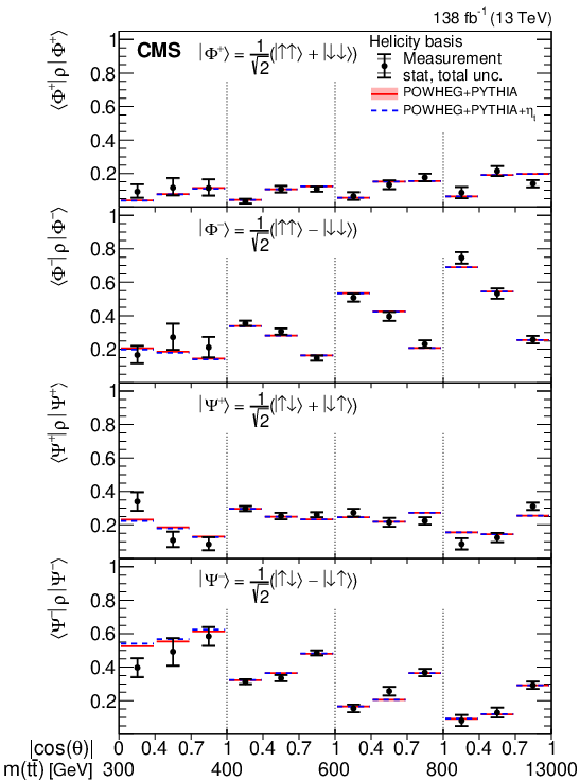
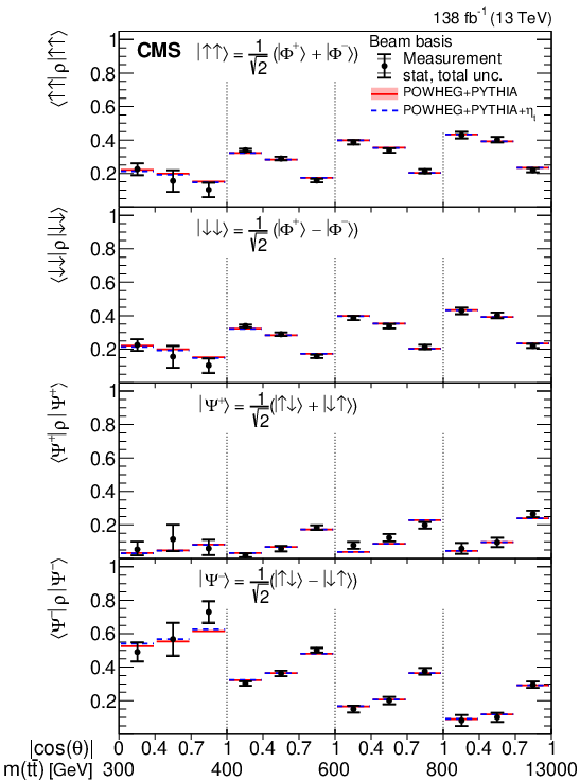
Figure 2:
Results of the state decomposition in terms of the Bell and spin states in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA +{\HepParticle$ \eta \mathrm{t} $. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
Results of the state decomposition in terms of the Bell and spin states in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA +{\HepParticle$ \eta \mathrm{t} $. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
Results of the state decomposition in terms of the Bell and spin states in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, and POWHEG + PYTHIA +{\HepParticle$ \eta \mathrm{t} $. The POWHEG + PYTHIA prediction is displayed with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
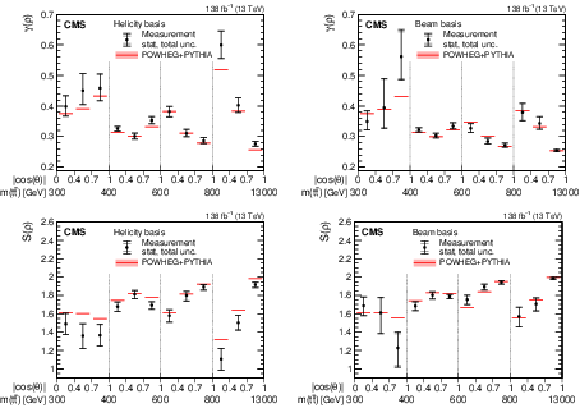
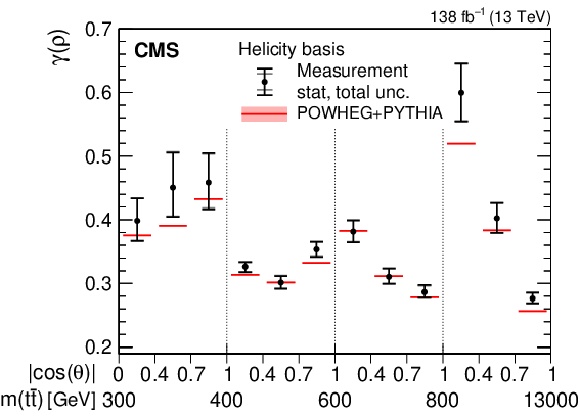
Figure 3:
Results of the purity $ \gamma(\rho) $ (upper) and entropy $ S(\rho) $ (lower) measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Results of the purity $ \gamma(\rho) $ (upper) and entropy $ S(\rho) $ (lower) measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
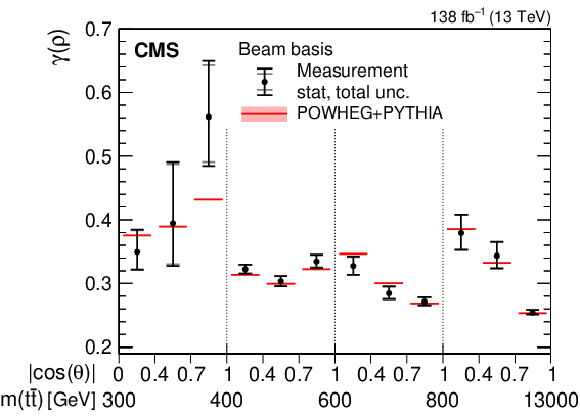
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Results of the purity $ \gamma(\rho) $ (upper) and entropy $ S(\rho) $ (lower) measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
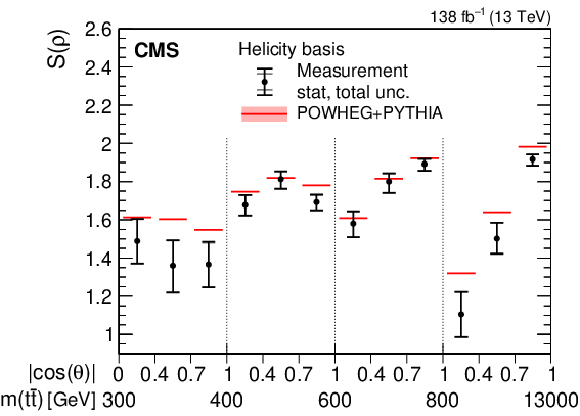
png pdf |
Figure 3-c:
Results of the purity $ \gamma(\rho) $ (upper) and entropy $ S(\rho) $ (lower) measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
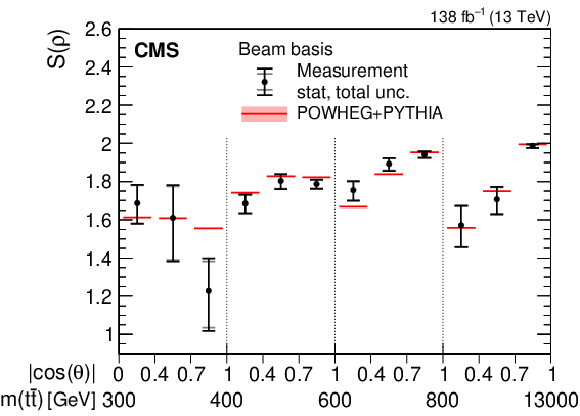
png pdf |
Figure 3-d:
Results of the purity $ \gamma(\rho) $ (upper) and entropy $ S(\rho) $ (lower) measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. |
png pdf |
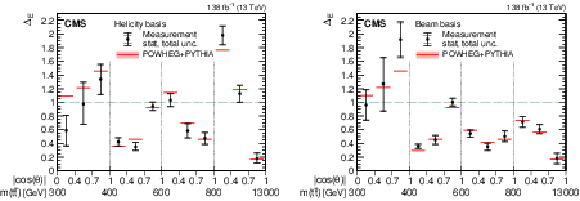
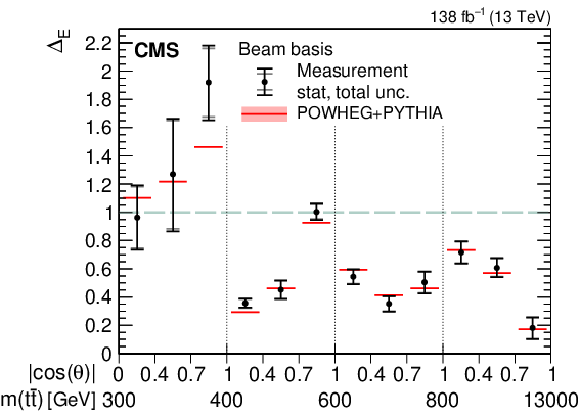
Figure 4:
Results of the entanglement marker $ \Delta_{\mathrm{E}} $ measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. The dashed green line represents the lower bound for entangled states. |
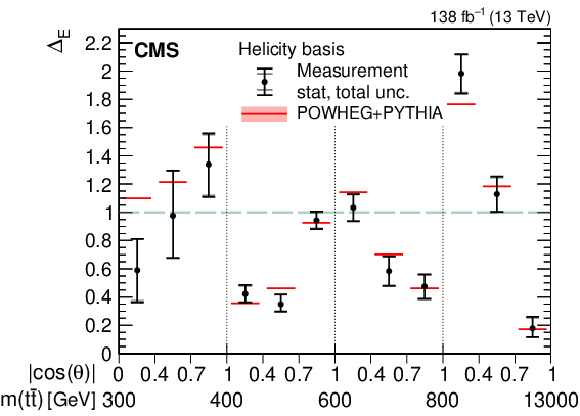
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Results of the entanglement marker $ \Delta_{\mathrm{E}} $ measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. The dashed green line represents the lower bound for entangled states. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Results of the entanglement marker $ \Delta_{\mathrm{E}} $ measurements in bins of $ m({\mathrm{t}\overline{\mathrm{t}}} ) $ vs. $ |\cos(\theta)| $ in the helicity (left) and beam (right) basis. The measurements (markers) are shown with the statistical (inner error bars) and total (outer error bars) uncertainty and compared to the predictions from POWHEG + PYTHIA, shown with the ME scale and PDF uncertainties. The dashed green line represents the lower bound for entangled states. |
| Summary |
| In summary, the spin correlation measurements of the top quark-antiquark ($ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $) system from Ref. [8] are extended to include results in the beam basis for the first time. This is done with bins in two dimensions, comprising the top quark scattering angle and either the invariant mass of the $ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $ system or the transverse momentum of the top quark, using proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV recorded by the CMS experiment at the LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The density matrix is decomposed into eigenstates, which are identified as Bell states in the helicity basis and spin states in the beam basis. We also present the first experimental results for the purity, von Neumann entropy, and entanglement of the $ \mathrm{t} \overline{\mathrm{t}} $ system in both bases. All the measurements are consistent with standard model expectations. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | Particle Data Group , S. Navas et al. | Review of particle physics | PRD 110 (2024) 030001 | |
| 2 | G. Mahlon and S. J. Parke | Spin correlation effects in top quark pair production at the LHC | PRD 81 (2010) 074024 | 1001.3422 |
| 3 | W. Bernreuther | Top-quark physics at the LHC | JPG 35 (2008) 083001 | 0805.1333 |
| 4 | W. Bernreuther, D. Heisler, and Z.-G. Si | A set of top quark spin correlation and polarization observables for the LHC: Standard model predictions and new physics contributions | JHEP 12 (2015) 026 | 1508.05271 |
| 5 | M. Baumgart and B. Tweedie | A new twist on top quark spin correlations | JHEP 03 (2013) 117 | 1212.4888 |
| 6 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of quantum entanglement with top quarks at the ATLAS detector | Nature 633 (2024) 542 | 2311.07288 |
| 7 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of quantum entanglement in top quark pair production in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | Rep. Prog. Phys. 87 (2024) 117801 | CMS-TOP-23-001 2406.03976 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of polarization and spin correlation and observation of entanglement in top quark pairs using lepton+jets events from proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PRD 110 (2024) 112016 | CMS-TOP-23-007 2409.11067 |
| 9 | W. Bernreuther, A. Brandenburg, Z. G. Si, and P. Uwer | Top quark pair production and decay at hadron colliders | NPB 690 (2004) 81 | hep-ph/0403035 |
| 10 | K. Cheng, T. Han, and M. Low | Optimizing entanglement and Bell inequality violation in top antitop events | PRD 111 (2025) 033004 | 2407.01672 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Development of the CMS detector for the CERN LHC Run 3 | JINST 19 (2024) P05064 | CMS-PRF-21-001 2309.05466 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS high-level trigger during LHC Run 2 | JINST 19 (2024) P11021 | CMS-TRG-19-001 2410.17038 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_{\!\tau} $ in $ {\mathrm{p}\mathrm{p}} $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P10005 | CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in $ {\mathrm{p}\mathrm{p}} $ collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 26 | Y. Afik and J. R. M. de Nova | Entanglement and quantum tomography with top quarks at the LHC | Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136 (2021) 907 | 2003.02280 |
| 27 | U. Fano | Pairs of two-level systems | Rev. Mod. Phys. 55 (1983) 855 | |
| 28 | M. A. Nielsen and I. L. Chuang | Quantum computation and quantum information. 10th anniversary edition | Cambridge University Press, -1-107-00217-3, 2010 ISBN 97 (2010) 8 |
|
| 29 | U. Fano | Description of states in quantum mechanics by density matrix and operator techniques | Rev. Mod. Phys. 29 (1957) 74 | |
| 30 | A. Peres | Separability criterion for density matrices | PRL 77 (1996) 1413 | quant-ph/9604005 |
| 31 | P. Horodecki | Separability criterion and inseparable mixed states with positive partial transposition | Phys. Lett. A 232 (1997) 333 | quant-ph/9703004 |
| 32 | Y. Afik and J. R. M. de Nova | Quantum information with top quarks in QCD | Quantum 6 (2022) 820 | 2203.05582 |
| 33 | S. A. Abel, M. Dittmar, and H. K. Dreiner | Testing locality at colliders via Bell's inequality? | PLB 280 (1992) 304 | |
| 34 | T. Han, M. Low, and T. A. Wu | Quantum entanglement and Bell inequality violation in semi-leptonic top decays | JHEP 07 (2024) 192 | 2310.17696 |
| 35 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 36 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 37 | S. Frixione, G. Ridolfi, and P. Nason | A positive-weight next-to-leading-order Monte Carlo for heavy flavour hadroproduction | JHEP 09 (2007) 126 | 0707.3088 |
| 38 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 40 | M. Bähr et al. | HERWIG++ physics and manual | EPJC 58 (2008) 639 | 0803.0883 |
| 41 | CMS Collaboration | Development and validation of HERWIG 7 tunes from CMS underlying-event measurements | EPJC 81 (2021) 312 | CMS-GEN-19-001 2011.03422 |
| 42 | J. Mazzitelli et al. | Next-to-next-to-leading order event generation for top-quark pair production | PRL 127 (2021) 062001 | 2012.14267 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | HEPData record for this analysis | link | |
| 44 | V. S. Fadin, V. A. Khoze, and T. Sjostrand | On the threshold behaviour of heavy top production | Z. Phys. C 48 (1990) 613 | |
| 45 | Y. Kiyo et al. | Top-quark pair production near threshold at LHC | EPJC 60 (2009) 375 | 0812.0919 |
| 46 | Y. Sumino and H. Yokoya | Bound-state effects on kinematical distributions of top quarks at hadron colliders | JHEP 09 (2010) 034 | 1007.0075 |
| 47 | W.-L. Ju et al. | Top quark pair production near threshold: single/double distributions and mass determination | JHEP 06 (2020) 158 | 2004.03088 |
| 48 | B. Fuks, K. Hagiwara, K. Ma, and Y.-J. Zheng | Signatures of toponium formation in LHC run 2 data | PRD 104 (2021) 034023 | 2102.11281 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|