

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-EXO-21-012 | ||
| Search for dark matter particles produced in W$^{+}$W$^{-} $ events with transverse momentum imbalance in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the CMS detector | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 8 March 2023 | ||
| Abstract: A search for dark matter particles is performed using events with a pair of W bosons and large missing transverse momentum. Candidates are selected by requiring one or two leptons (electrons or muons) from the W boson decays. The analysis is based on proton-proton collision data taken at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV by the CMS experiment at the LHC and corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 137 fb$ ^{-1} $. No significant excess over the expected standard model background is observed in the semi- and di-leptonic final states of the W$^{+}$W$^{-}$ decay channel. Limits are set on dark matter production in the context of a dark Higgs simplified model, with a dark Higgs mass above the W$^{+}$W$^{-}$ mass threshold. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, Submitted to JHEP. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
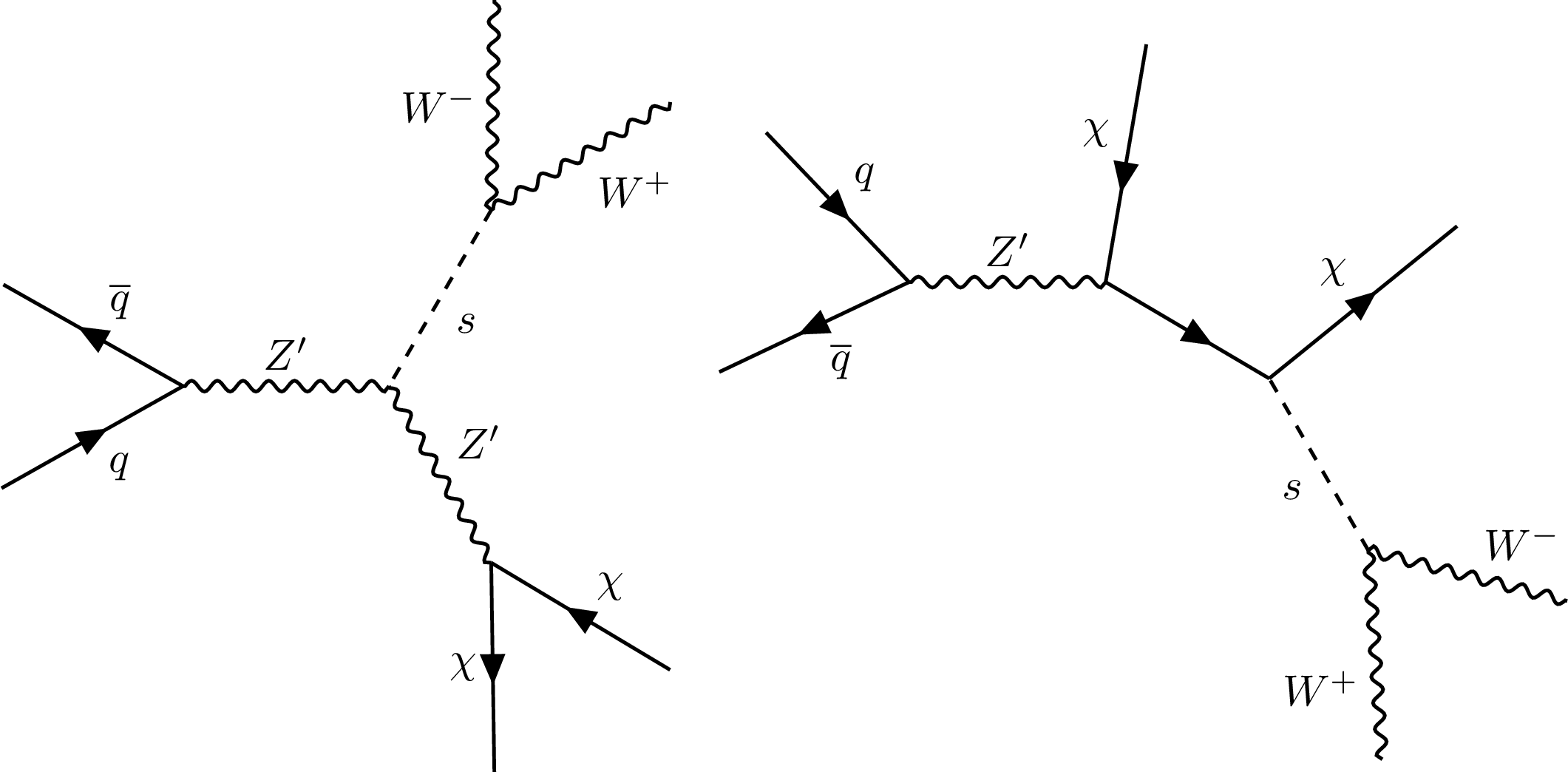
Figure 1:
Representative Born-level Feynman diagrams for the benchmark signal model considered in this note: $ q \bar q \to \mathrm{Z}^{'} \to s \chi \chi $, and $ s \to \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $. |
png pdf |
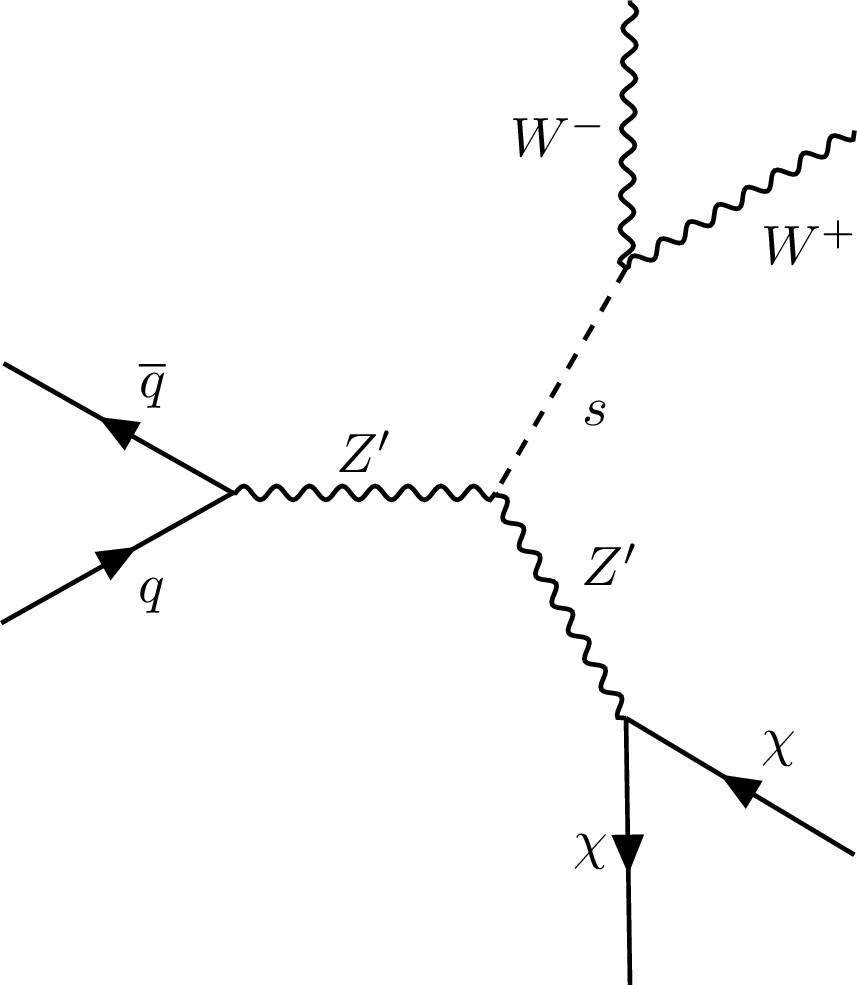
Figure 1-a:
Representative Born-level Feynman diagrams for the benchmark signal model considered in this note: $ q \bar q \to \mathrm{Z}^{'} \to s \chi \chi $, and $ s \to \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $. |
png pdf |
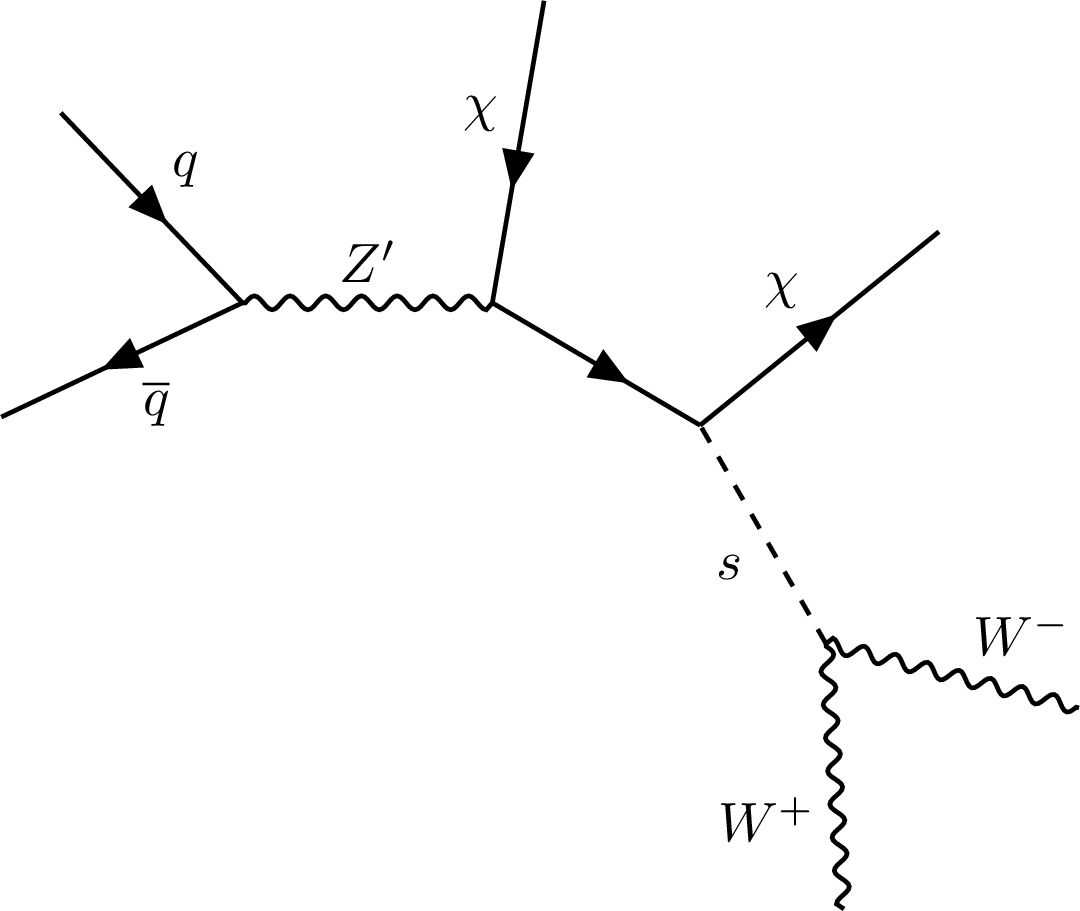
Figure 1-b:
Representative Born-level Feynman diagrams for the benchmark signal model considered in this note: $ q \bar q \to \mathrm{Z}^{'} \to s \chi \chi $, and $ s \to \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $. |
png pdf |
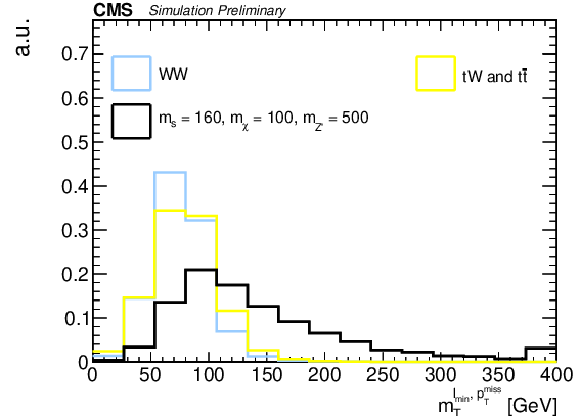
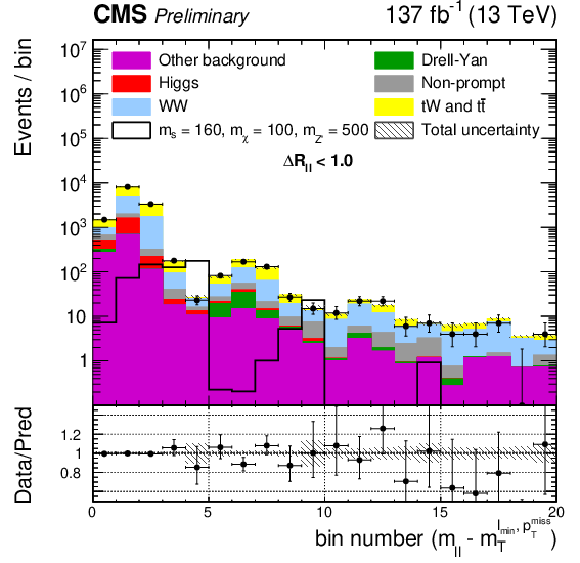
Figure 2:
Normalized $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\, \text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ distribution in the di-leptonic channel for a signal with $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV, after the event preselection criteria are applied. Predictions of the two main backgrounds of the analysis, WW and $ \mathrm{t}\mathrm{W} $\text{and} $ {\mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}}} $, are shown as blue and yellow solid lines respectively. The last bin includes the overflow. |
png pdf |
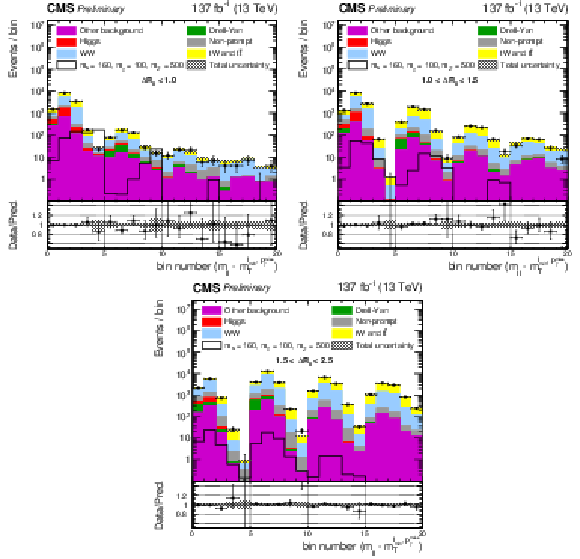
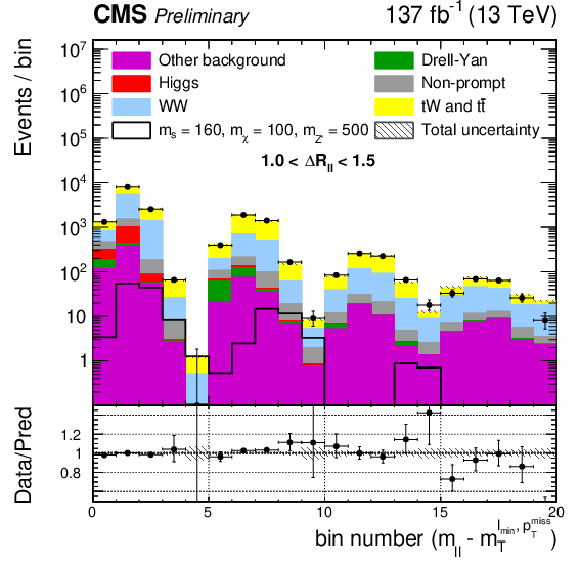
Figure 3:
Unrolled $ m_{\ell\ell}-m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ post-fit distributions in the di-leptonic channel for three signal regions SR1 (top left), SR2 (top right), and SR3 (bottom), for the full data set. The histogram bins are spaced uniformly. Each group of five bins (from left to right) corresponds to the $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ distribution in a $ m_{\ell\ell} $ region, placed in ascending order. The black line indicates the signal prediction for $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Unrolled $ m_{\ell\ell}-m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ post-fit distributions in the di-leptonic channel for three signal regions SR1 (top left), SR2 (top right), and SR3 (bottom), for the full data set. The histogram bins are spaced uniformly. Each group of five bins (from left to right) corresponds to the $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ distribution in a $ m_{\ell\ell} $ region, placed in ascending order. The black line indicates the signal prediction for $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Unrolled $ m_{\ell\ell}-m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ post-fit distributions in the di-leptonic channel for three signal regions SR1 (top left), SR2 (top right), and SR3 (bottom), for the full data set. The histogram bins are spaced uniformly. Each group of five bins (from left to right) corresponds to the $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ distribution in a $ m_{\ell\ell} $ region, placed in ascending order. The black line indicates the signal prediction for $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-c:
Unrolled $ m_{\ell\ell}-m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ post-fit distributions in the di-leptonic channel for three signal regions SR1 (top left), SR2 (top right), and SR3 (bottom), for the full data set. The histogram bins are spaced uniformly. Each group of five bins (from left to right) corresponds to the $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\ell\,\text{min}, p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss}} $ distribution in a $ m_{\ell\ell} $ region, placed in ascending order. The black line indicates the signal prediction for $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
png pdf |
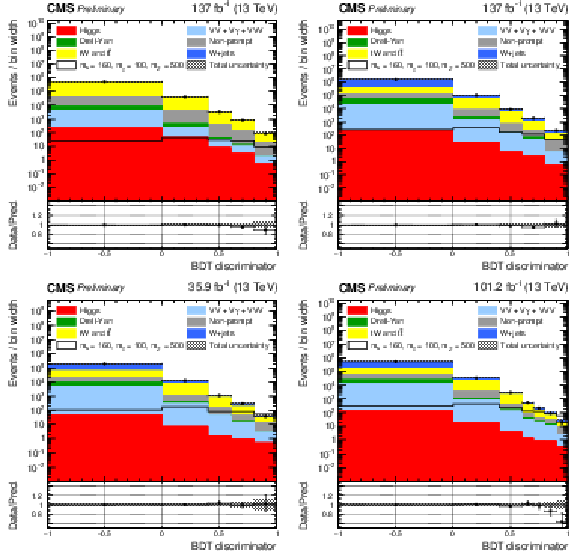
Figure 4:
Post-fit BDT distributions in the semi-leptonic channel for the full data set in the top CR (top left) and $ \mathrm{W}+ $jets CR (top right). The signal region has different binning in 2016 (bottom left) and 2017-2018 (bottom right) to ensure good statistical precision in all bins. The red line indicates the signal prediction when $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
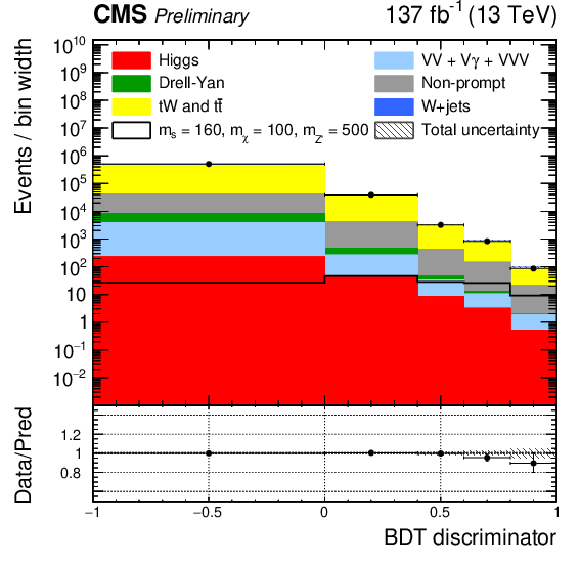
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Post-fit BDT distributions in the semi-leptonic channel for the full data set in the top CR (top left) and $ \mathrm{W}+ $jets CR (top right). The signal region has different binning in 2016 (bottom left) and 2017-2018 (bottom right) to ensure good statistical precision in all bins. The red line indicates the signal prediction when $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
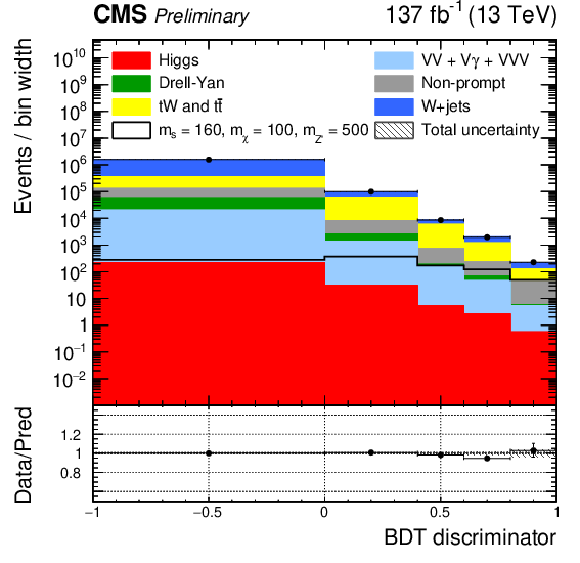
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Post-fit BDT distributions in the semi-leptonic channel for the full data set in the top CR (top left) and $ \mathrm{W}+ $jets CR (top right). The signal region has different binning in 2016 (bottom left) and 2017-2018 (bottom right) to ensure good statistical precision in all bins. The red line indicates the signal prediction when $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
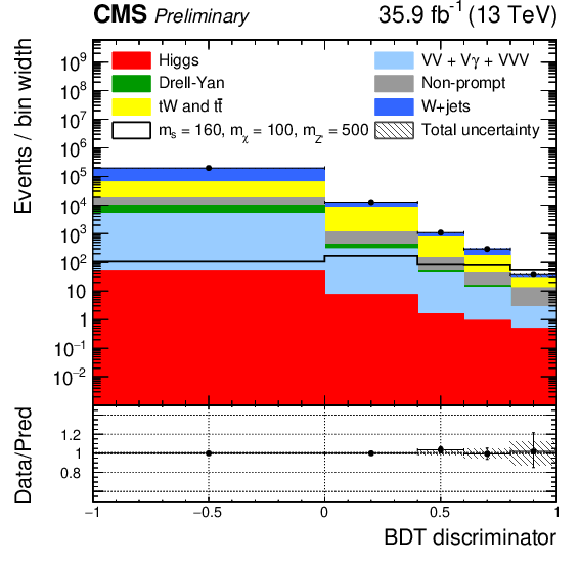
png pdf |
Figure 4-c:
Post-fit BDT distributions in the semi-leptonic channel for the full data set in the top CR (top left) and $ \mathrm{W}+ $jets CR (top right). The signal region has different binning in 2016 (bottom left) and 2017-2018 (bottom right) to ensure good statistical precision in all bins. The red line indicates the signal prediction when $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
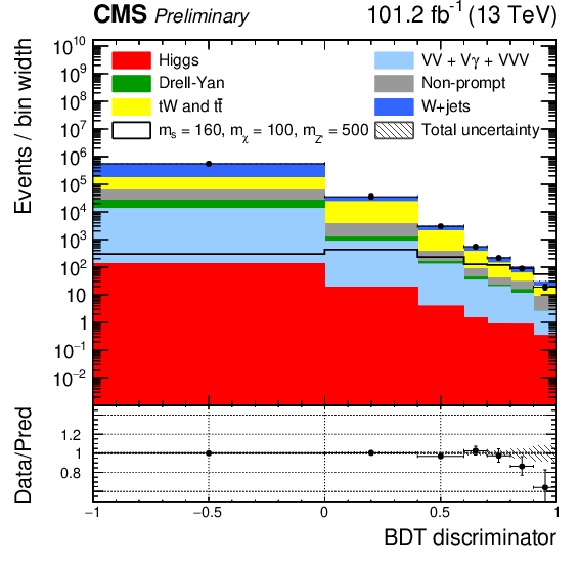
png pdf |
Figure 4-d:
Post-fit BDT distributions in the semi-leptonic channel for the full data set in the top CR (top left) and $ \mathrm{W}+ $jets CR (top right). The signal region has different binning in 2016 (bottom left) and 2017-2018 (bottom right) to ensure good statistical precision in all bins. The red line indicates the signal prediction when $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
png pdf |
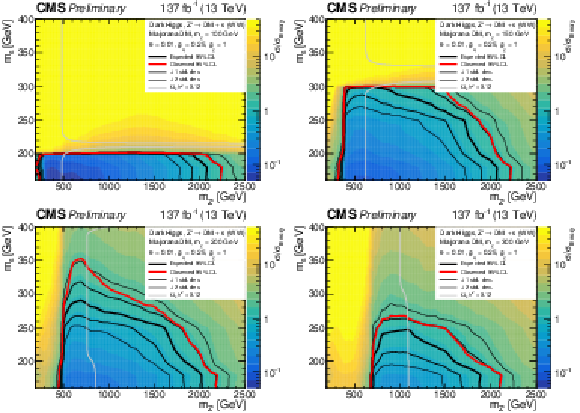
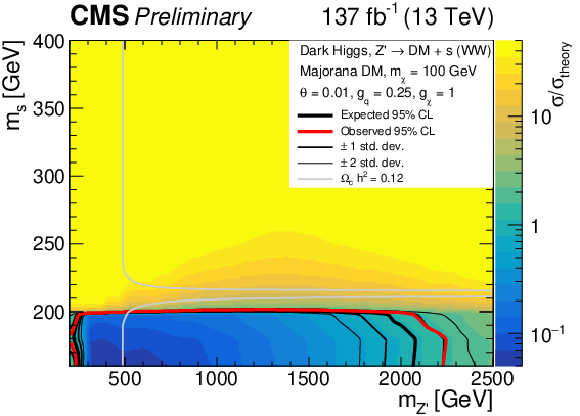
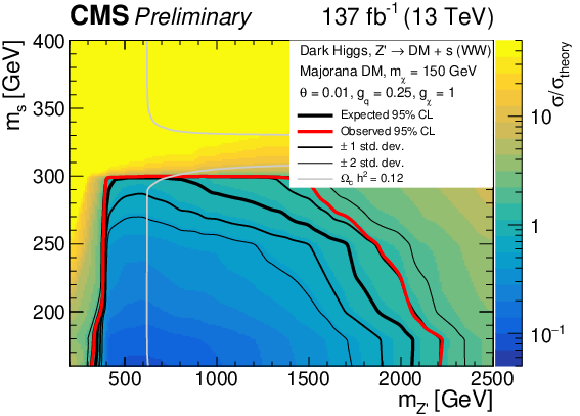
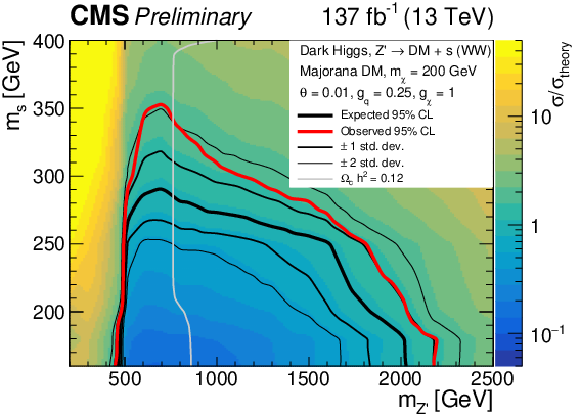
Figure 5:
Observed (expected) exclusion regions at 95% CL for the dark Higgs model in the ($ m_{s} $, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $) plane, marked by the solid red (black) line. The expected $ \pm $ 1$ \sigma $ and $ \pm $ 2$ \sigma $ bands are shown as the thinner black lines. Upper left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, upper right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 150 GeV, lower left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 200 GeV, lower right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 300 GeV. The gray line indicates were the model parameters produce exactly the observed relic density $ \Omega_c h^2 = $ 0.12 [7]. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
Observed (expected) exclusion regions at 95% CL for the dark Higgs model in the ($ m_{s} $, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $) plane, marked by the solid red (black) line. The expected $ \pm $ 1$ \sigma $ and $ \pm $ 2$ \sigma $ bands are shown as the thinner black lines. Upper left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, upper right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 150 GeV, lower left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 200 GeV, lower right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 300 GeV. The gray line indicates were the model parameters produce exactly the observed relic density $ \Omega_c h^2 = $ 0.12 [7]. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
Observed (expected) exclusion regions at 95% CL for the dark Higgs model in the ($ m_{s} $, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $) plane, marked by the solid red (black) line. The expected $ \pm $ 1$ \sigma $ and $ \pm $ 2$ \sigma $ bands are shown as the thinner black lines. Upper left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, upper right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 150 GeV, lower left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 200 GeV, lower right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 300 GeV. The gray line indicates were the model parameters produce exactly the observed relic density $ \Omega_c h^2 = $ 0.12 [7]. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-c:
Observed (expected) exclusion regions at 95% CL for the dark Higgs model in the ($ m_{s} $, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $) plane, marked by the solid red (black) line. The expected $ \pm $ 1$ \sigma $ and $ \pm $ 2$ \sigma $ bands are shown as the thinner black lines. Upper left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, upper right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 150 GeV, lower left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 200 GeV, lower right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 300 GeV. The gray line indicates were the model parameters produce exactly the observed relic density $ \Omega_c h^2 = $ 0.12 [7]. |
png pdf |
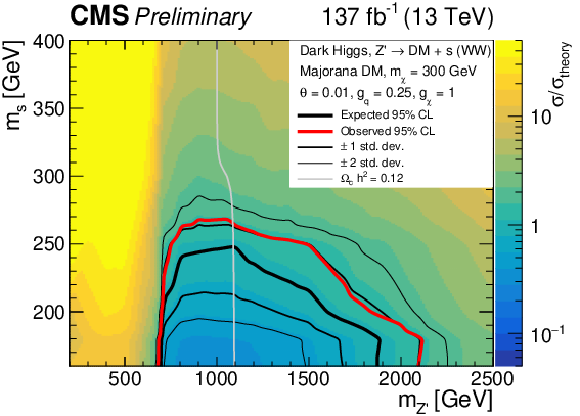
Figure 5-d:
Observed (expected) exclusion regions at 95% CL for the dark Higgs model in the ($ m_{s} $, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $) plane, marked by the solid red (black) line. The expected $ \pm $ 1$ \sigma $ and $ \pm $ 2$ \sigma $ bands are shown as the thinner black lines. Upper left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, upper right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 150 GeV, lower left: $ m_{\chi} = $ 200 GeV, lower right: $ m_{\chi} = $ 300 GeV. The gray line indicates were the model parameters produce exactly the observed relic density $ \Omega_c h^2 = $ 0.12 [7]. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Summary of all variables considered in the BDT for the semi-leptonic channel. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Summary of the event preselection criteria in the di-leptonic channel. |

png pdf |
Table 3:
Selection criteria for the leptons for 2016, 2017 and 2018 data in the semi-leptonic channel. The $ p_{\mathrm{T}} $ thresholds are chosen to be on the single lepton trigger threshold. |
png pdf |
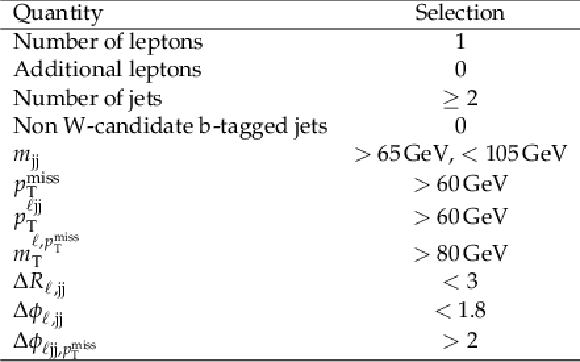
Table 4:
Summary of the event preselection criteria for the semi-leptonic channel. |
png pdf |
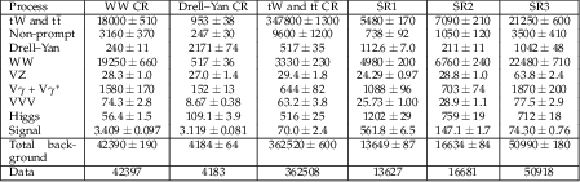
Table 5:
Data and background yields for each data period and signal region in the di-leptonic channel. Central values and uncertainties of the background contributions correspond to the post-fit values. The signal prediction corresponds to pre-fit yields and uncertainties for a sample with $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
png pdf |
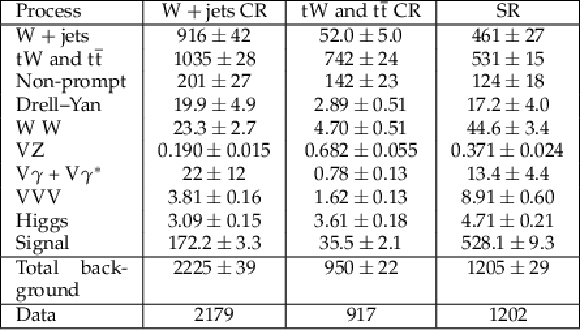
Table 6:
Data and background yields for the semi-leptonic channel with a BDT discriminator score above 0.6. Central values and uncertainties of the background contributions correspond to the post-fit values. The signal prediction corresponds to the pre-fit yields and uncertainties for a sample with $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV, $ m_{\chi} = $ 100 GeV, and $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} = $ 500 GeV. |
| Summary |
| A search for dark matter particles produced in association with a dark Higgs boson has been presented. A sample of proton-proton collision data at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV is used, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 137 fb$ ^{-1} $. The decay mode of the dark Higgs boson to a W$^{+}$W$^{-}$pair has been explored; this is the first time the CMS Collaboration explores this new physics scenario. Results from the combination of di-leptonic and semi-leptonic analysis channels of the W$^{+}$W$^{-}$pair are presented. No significant deviation from the Standard Model prediction is observed, so upper limits at 95% confidence level on the production cross section of dark matter are set on the dark Higgs model parameters. This analysis extends the search from previous public results to a wider DM mass range, from 100 GeV to 300 GeV, and extends the limit on $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ masses in the region 160 GeV $< m_{s} \lesssim $ 250 GeV for $ m_{DM} = $ 200 GeV. The most stringent limit is set for a $ m_{DM} = $ 200 GeV, excluding $ m_{s} $ masses up to $ \approx $350 GeV at $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} $ masses of 700 GeV, and up to $ m_{\mathrm{Z}^{'}} \approx $ 2200 GeV for a $ m_{s} = $ 160 GeV. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | R. J. Gaitskell | Direct detection of dark matter | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 54 (2004) 315 | |
| 2 | V. Trimble | Existence and nature of dark matter in the universe | Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 25 (1987) 425 | |
| 3 | T. A. Porter, R. P. Johnson, and P. W. Graham | Dark Matter searches with astroparticle data | Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 49 (2011) 155 | 1104.2836 |
| 4 | G. Bertone, D. Hooper, and J. Silk | Particle dark matter: evidence, candidates and constraints | Phys. Rept. 405 (2005) 279 | hep-ph/0404175 |
| 5 | J. L. Feng | Dark matter candidates from particle physics and methods of detection | Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 48 (2010) 495 | 1003.0904 |
| 6 | R. J. Scherrer and M. S. Turner | On the relic, cosmic abundance of stable, weakly interacting massive particles | PRD 33 (1986) 1585 | |
| 7 | Planck Collaboration | Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters | Astron. Astrophys. 641 (2020) A6 | |
| 8 | G. Steigman and M. S. Turner | Cosmological constraints on the properties of weakly interacting massive particles | NPB 253 (1985) 375 | |
| 9 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter and other new phenomena in events with an energetic jet and large missing transverse momentum using the ATLAS detector | JHEP 01 (2018) 126 | 1711.03301 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in final states with an energetic jet or a hadronically decaying W or Z boson and transverse momentum imbalance at $ \sqrt{s}=$ 13 TeV | PRD 97 (2018) 092005 | CMS-EXO-16-048 1712.02345 |
| 11 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter produced in association with bottom or top quarks in $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 78 (2018) 18 | 1710.11412 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark matter in events with energetic, hadronically decaying top quarks and missing transverse momentum at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 06 (2018) 027 | CMS-EXO-16-051 1801.08427 |
| 13 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV in final states containing an energetic photon and large missing transverse momentum with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 77 (2017) 393 | 1704.03848 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in the monophoton final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 10 (2017) 073 | CMS-EXO-16-039 1706.03794 |
| 15 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for an invisibly decaying Higgs boson or dark matter candidates produced in association with a $ Z $ boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 776 (2018) 318 | 1708.09624 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in events with a leptonically decaying Z boson and a large transverse momentum imbalance in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | EPJC 78 (2018) 291 | CMS-EXO-16-052 1711.00431 |
| 17 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter in events with a hadronically decaying vector boson and missing transverse momentum in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 10 (2018) 180 | 1807.11471 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark matter particles produced in association with a Higgs boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 3 (2020) 25 | 1908.01713 |
| 19 | M. Duerr et al. | Hunting the dark Higgs | JHEP 4 (2017) 143 | 1701.08780 |
| 20 | ATLAS Collaboration and CMS Collaboration | Measurements of the Higgs boson production and decay rates and constraints on its couplings from a combined ATLAS and CMS analysis of the LHC pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 8 (2016) 45 | 1606.02266 |
| 21 | M. Duerr et al. | How to save the WIMP: global analysis of a dark matter model with two $ s $-channel mediators | JHEP 9 (2016) 42 | 1606.07609 |
| 22 | ATLAS Collaboration | RECAST framework reinterpretation of an ATLAS Dark Matter Search constraining a model of a dark Higgs boson decaying to two $ b $-quarks | technical report, CERN, 2019 | |
| 23 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter produced in association with a dark Higgs boson decaying into $ \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $ or ZZ in fully hadronic final states from $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV $ pp $ collisions recorded with the ATLAS detector | PRL 126 (2021) 121802 | |
| 24 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for dark matter produced in association with a dark higgs boson decaying into $ \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $ in the one-lepton final state at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using 139 fb$^{-1}$ of $ pp $ collisions recorded with the ATLAS detector | Submitted to JHEP., 2022 | 2211.07175 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS Experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | CMS Luminosity Measurements for the 2016 Data Taking Period | Physics Analysis Summary CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | Physics Analysis Summary CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | Physics Analysis Summary CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 30 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Event generator tunes obtained from underlying event and multiparton scattering measurements | EPJC 76 (2016) 155 | CMS-GEN-14-001 1512.00815 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 33 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions with QED corrections | NPB 877 (2013) 290 | 1308.0598 |
| 34 | NNPDF Collaboration | Unbiased global determination of parton distributions and their uncertainties at NNLO and at LO | NPB 855 (2012) 153 | 1107.2652 |
| 35 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | EPJC 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 36 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 2014 (2014) 79 | |
| 37 | D. Abercrombie et al. | Dark matter benchmark models for early LHC Run-2 searches: Report of the ATLAS/CMS Dark Matter Forum | Phys. Dark Univ. 27 (2020) 100371 | |
| 38 | T. Melia, P. Nason, R. Rontsch, and G. Zanderighi | W$ ^+ $W$ ^- $, WZ and ZZ production in the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 11 (2011) 078 | 1107.5051 |
| 39 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Vector boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2011) 018 | 1105.0020 |
| 40 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and W. T. Giele | A multi-threaded version of MCFM | EPJC 75 (2015) 246 | 1503.06182 |
| 41 | P. Meade, H. Ramani, and M. Zeng | Transverse momentum resummation effects in $ \mathrm{W}^+\mathrm{W}^- $ measurements | PRD 90 (2014) 114006 | 1407.4481 |
| 42 | P. Jaiswal and T. Okui | Explanation of the WW excess at the LHC by jet-veto resummation | PRD 90 (2014) 073009 | 1407.4537 |
| 43 | S. Gieseke, T. Kasprzik, and J. H. Kühn | Vector-boson pair production and electroweak corrections in herwig++ | ||
| 44 | F. Caola, K. Melnikov, R. Röntsch, and L. Tancredi | QCD corrections to $ \mathrm{W}^+\mathrm{W}^- $ production through gluon fusion | PLB 754 (2016) 275 | 1511.08617 |
| 45 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 46 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 47 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 48 | E. Bagnaschi, G. Degrassi, P. Slavich, and A. Vicini | Higgs production via gluon fusion in the POWHEG approach in the SM and in the MSSM | JHEP 02 (2012) 088 | 1111.2854 |
| 49 | P. Nason and C. Oleari | NLO Higgs boson production via vector-boson fusion matched with shower in POWHEG | JHEP 02 (2010) 037 | 0911.5299 |
| 50 | G. Luisoni, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and F. Tramontano | $ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{W}^{\pm}/\mathrm{H}\mathrm{Z} $ + 0 and 1 jet at NLO with the POWHEG BOX interfaced to GoSam and their merging within MiNLO | JHEP 10 (2013) 083 | 1306.2542 |
| 51 | H. B. Hartanto, B. Jager, L. Reina, and D. Wackeroth | Higgs boson production in association with top quarks in the POWHEG BOX | PRD 91 (2015) 094003 | 1501.04498 |
| 52 | S. Bolognesi et al. | On the spin and parity of a single-produced resonance at the LHC | PRD 86 (2012) 095031 | 1208.4018 |
| 53 | M. Czakon et al. | Top-pair production at the LHC through NNLO QCD and NLO EW | JHEP 10 (2017) 186 | 1705.04105 |
| 54 | J. M. Lindert et al. | Precise predictions for V + jets dark matter backgrounds | EPJC 77 (2017) 12 | |
| 55 | K. Melnikov and F. Petriello | Electroweak gauge boson production at hadron colliders through $ O(\alpha_s^2) $ | PRD 74 (2006) 114017 | hep-ph/0609070 |
| 56 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the $ \mathrm{t}\bar{\mathrm{t}} $ production cross section in the $ \mathrm{e}\mu $ channel in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 08 (2016) 029 | CMS-TOP-13-004 1603.02303 |
| 57 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4---a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 58 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 59 | W. Waltenberger, R. Frühwirth, and P. Vanlaer | Adaptive vertex fitting | JPG 34 (2007) N343 | |
| 60 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_{\mathrm{T}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 61 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 62 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of electron reconstruction and selection with the CMS detector in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P06005 | CMS-EGM-13-001 1502.02701 |
| 63 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 64 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the reconstruction and identification of high-momentum muons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P02027 | CMS-MUO-17-001 1912.03516 |
| 65 | CMS Collaboration | Jet algorithms performance in 13 TeV data | Physics Analysis Summary, , . \url https://cds.cern.ch/record/2256875, 2017 CMS-PAS-JME-16-003 |
CMS-PAS-JME-16-003 |
| 66 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | |
| 67 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P05011 | CMS-BTV-16-002 1712.07158 |
| 68 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 69 | D. Bertolini, P. Harris, M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup per particle identification | JHEP 10 (2014) 059 | 1407.6013 |
| 70 | L. Moneta et al. | The RooStats Project | PoS ACAT 057, 2010 link |
1009.1003 |
| 71 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | [Erratum: Eur.Phys.J.C 73, 2501 ()], 2011 EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 |
1007.1727 |
| 72 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of properties of the Higgs boson decaying to a W boson pair in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PLB 791 (2019) 96 | CMS-HIG-16-042 1806.05246 |
| 73 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the inelastic proton-proton cross section at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2018) 161 | CMS-FSQ-15-005 1802.02613 |
| 74 | F. Caola et al. | QCD corrections to vector boson pair production in gluon fusion including interference effects with off-shell Higgs at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2016) 087 | 1605.04610 |
| 75 | C. Arina et al. | Indirect dark-matter detection with maddm v3.2 -- lines and loops | link | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|