

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIN-19-004 | ||
| Strange particle collectivity in pPb and PbPb | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| May 2021 | ||
| Abstract: The collective behavior of $\mathrm{K^0_S}$ and $\Lambda/\bar{\Lambda}$ strange hadrons is studied using the scalar-product and multiparticle correlation methods. Proton-lead (pPb) collisions at 8.16 TeV and lead-lead collisions at 5.02 TeV are studied. The data samples were collected by the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC. Nonflow effects in the pPb collisions are investigated by a subevent cumulant analysis and by including a veto on events where a jet with $p_{\mathrm{T}} > $ 20 GeV is observed. For the first time, the collectivity of strange particles is observed in proton-lead collisions. A comparison of the proton-lead and lead-lead results for both strange particles and charged-hadrons is used to show how flow fluctuations are affected by system size. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
inSPIRE record ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, Submitted to JHEP. |
||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
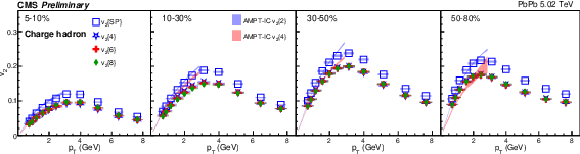
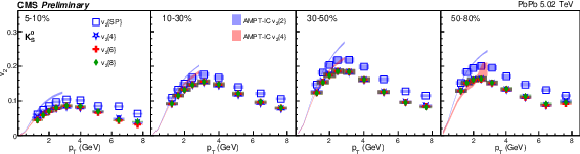
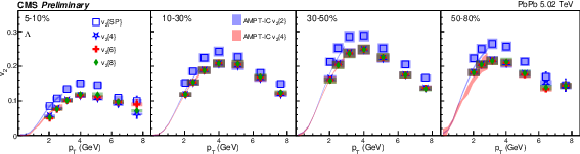
Figure 1:
The $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda$ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of 2- and 4-particle $v_2$ with AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
The $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda$ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of 2- and 4-particle $v_2$ with AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
The $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda$ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of 2- and 4-particle $v_2$ with AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-c:
The $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda$ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of 2- and 4-particle $v_2$ with AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
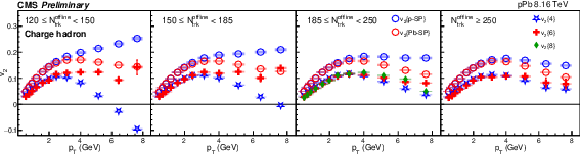
Figure 2:
The $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at 8.15 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
The $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at 8.15 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
The $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at 8.15 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-c:
The $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at 8.15 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 3:
The charge particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ for pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events (top), and their ratios (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
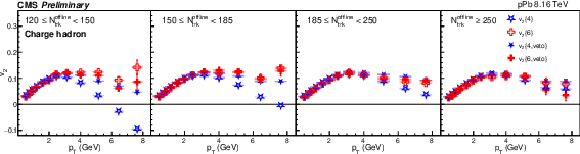
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
The charge particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ for pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events (top), and their ratios (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
The charge particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ for pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events (top), and their ratios (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 4:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
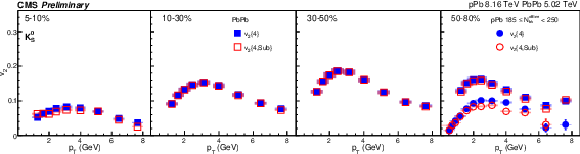
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 4-c:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
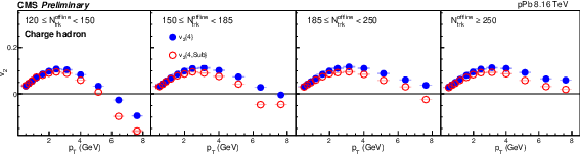
Figure 5:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}$ for pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
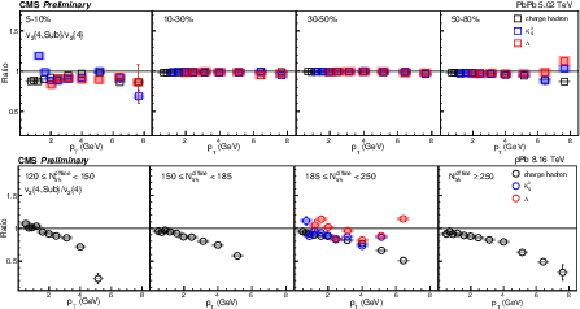
Figure 6:
The $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}/v_2\{4\}$ ratios of charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ and $\Lambda$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV (top) and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
The $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}/v_2\{4\}$ ratios of charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ and $\Lambda$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV (top) and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
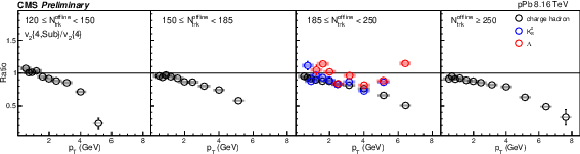
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
The $v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}/v_2\{4\}$ ratios of charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ and $\Lambda$ for PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV (top) and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV (bottom). The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
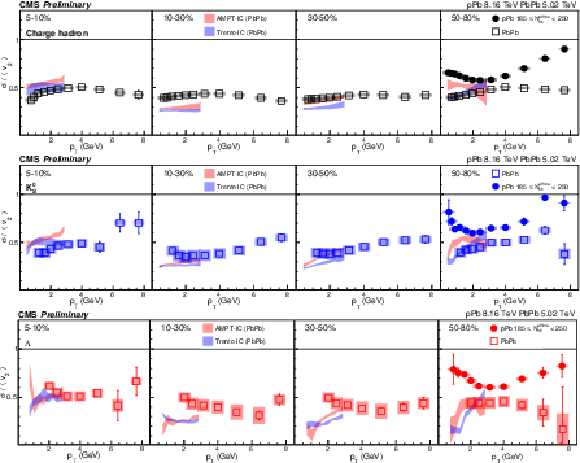
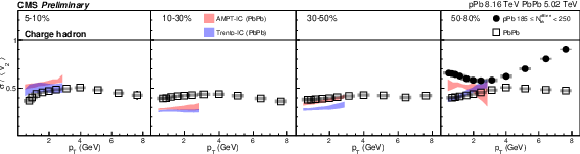
Figure 7:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with Trento and AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with Trento and AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with Trento and AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
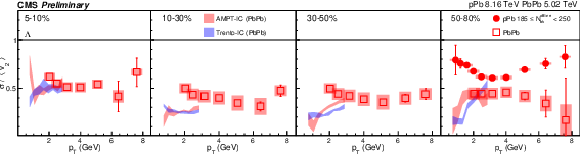
png pdf |
Figure 7-c:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron (top), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ (middle) and $\Lambda $ (bottom). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with Trento and AMPT initial conditions. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
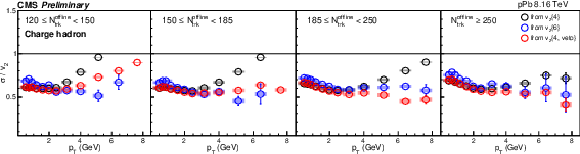
Figure 8:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of pPb collisions at 8.16 TeV for charge hadron derived from different multiparticle correlations. The shaded boxes are systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
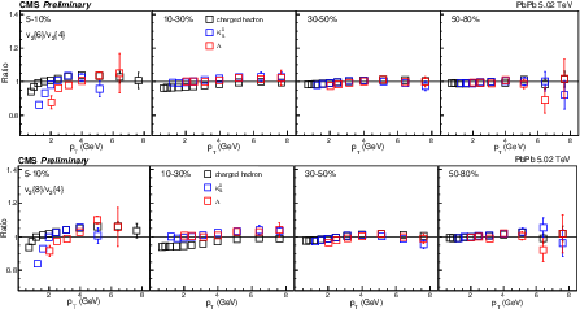
Figure 9:
The $v_2\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$ (top) and $v_2\{8\}/v_2\{4\}$ (bottom) in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$, and $\Lambda$. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |
png pdf |
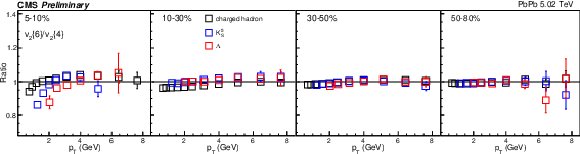
Figure 9-a:
The $v_2\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$ (top) and $v_2\{8\}/v_2\{4\}$ (bottom) in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$, and $\Lambda$. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |
png pdf |
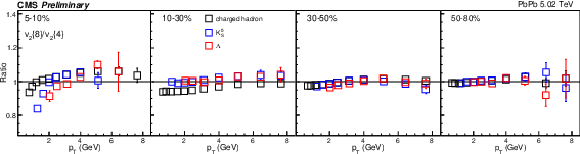
Figure 9-b:
The $v_2\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$ (top) and $v_2\{8\}/v_2\{4\}$ (bottom) in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV for charge hadron, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$, and $\Lambda$. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |
| Summary |
| In summary, the elliptic azimuthal anisotropies $v_2$ values have been measured using the scalar-product and the multiparticle Q-cumulant methods for identified ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$, $\Lambda$, and charged hadrons in PpPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and high-multiplicity pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV. Nonflow effects are studied for the 4-, 6- particle cumulant results. The large difference between the 4- and 6-particle correlation results can be explained by jet-related nonflow correlations, which can be suppressed by rejecting events with a jet ${p_{\mathrm{T}}}$ greater than 20 GeV. Another method for reducing short-range nonflow correlation, the subevent cumulant method, is also studied. The difference for the amount of nonflow suppression observed with the two methods is attributed to the effect of event plane decorrelation on the subevent method. For the first time, the collective multiparticle correlations of identified strange particles have been observed in pPb collisions. No obvious particle species dependence of the fluctuations in the $v_2$ values arising from the initial-state geometry is observed for either the PpPb or pPb systems. These flow fluctuation are observed to be larger in pPb collisions compared to PpPb collisions. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | PHOBOS Collaboration | System size dependence of cluster properties from two- particle angular correlations in Cu+Cu and Au+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRC 81 (2010) 024904 | 0812.1172 |
| 2 | STAR Collaboration | Distributions of charged hadrons associated with high transverse momentum particles in pp and Au+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 95 (2005) 152301 | nucl-ex/0501016 |
| 3 | STAR Collaboration | Long range rapidity correlations and jet production in high energy nuclear collisions | PRC 80 (2009) 064912 | 0909.0191 |
| 4 | PHOBOS Collaboration | High transverse momentum triggered correlations over a large pseudorapidity acceptance in Au+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 104 (2010) 062301 | 0903.2811 |
| 5 | STAR Collaboration | Three-particle coincidence of the long range pseudorapidity correlation in high energy nucleus-nucleus collisions | PRL 105 (2010) 022301 | 0912.3977 |
| 6 | CMS Collaboration | Long-range and short-range dihadron angular correlations in central PbPb collisions at a nucleon-nucleon center of mass energy of 2.76 TeV | JHEP 07 (2011) 076 | CMS-HIN-11-001 1105.2438 |
| 7 | CMS Collaboration | Centrality dependence of dihadron correlations and azimuthal anisotropy harmonics in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | EPJC 72 (2012) 2012 | CMS-HIN-11-006 1201.3158 |
| 8 | ALICE Collaboration | Elliptic flow of charged particles in Pb-Pb collisions at 2.76 TeV | PRL 105 (2010) 252302 | 1011.3914 |
| 9 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the azimuthal anisotropy for charged particle production in $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV lead-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRC 86 (2012) 014907 | 1203.3087 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the elliptic anisotropy of charged particles produced in PbPb collisions at nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy = 2.76 TeV | PRC 87 (2013) 014902 | CMS-HIN-10-002 1204.1409 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Studies of azimuthal dihadron correlations in ultra-central PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | JHEP 02 (2014) 088 | CMS-HIN-12-011 1312.1845 |
| 12 | J.-Y. Ollitrault | Anisotropy as a signature of transverse collective flow | PRD 46 (1992) 229 | |
| 13 | U. Heinz and R. Snellings | Collective flow and viscosity in relativistic heavy-ion collisions | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 63 (2013) 123 | 1301.2826 |
| 14 | C. Gale, S. Jeon, and B. Schenke | Hydrodynamic modeling of heavy-ion collisions | Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 28 (2013) 1340011 | 1301.5893 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of long-range near-side angular correlations in proton-proton collisions at the LHC | JHEP 09 (2010) 091 | CMS-QCD-10-002 1009.4122 |
| 16 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of long-range elliptic azimuthal anisotropies in $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 and 2.76 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS Detector | PRL 116 (2016) 172301 | 1509.04776 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of long-range near-side two-particle angular correlations in pp collisions at $ \sqrt s = $ 13 TeV | PRL 116 (2016) 172302 | CMS-FSQ-15-002 1510.03068 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of long-range near-side angular correlations in proton-lead collisions at the LHC | PLB 718 (2013) 795 | CMS-HIN-12-015 1210.5482 |
| 19 | ALICE Collaboration | Long-range angular correlations on the near and away side in $ \mathrm{pPb}\ $ collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 719 (2013) 29 | 1212.2001 |
| 20 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of associated near-side and away-side long-range correlations in $ \sqrt{s_{_{NN}}}= $ 5.02 tev proton-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRL 110 (2013) 182302 | 1212.5198 |
| 21 | LHCb Collaboration | Measurements of long-range near-side angular correlations in $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5 TeV proton-lead collisions in the forward region | PLB 762 (2016) 473 | 1512.00439 |
| 22 | S. Voloshin and Y. Zhang | Flow study in relativistic nuclear collisions by Fourier expansion of azimuthal particle distributions | Z. Phys. C 70 (1996) 665 | hep-ph/9407282 |
| 23 | B. H. Alver, C. Gombeaud, M. Luzum, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Triangular flow in hydrodynamics and transport theory | PRC 82 (2010) 034913 | 1007.5469 |
| 24 | B. Schenke, S. Jeon, and C. Gale | Elliptic and triangular flow in event-by-event D=3+1 viscous hydrodynamics | PRL 106 (2011) 042301 | 1009.3244 |
| 25 | Z. Qiu, C. Shen, and U. Heinz | Hydrodynamic elliptic and triangular flow in Pb-Pb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PLB 707 (2012) 151 | 1110.3033 |
| 26 | PHENIX Collaboration | Measurement of long-range angular correlation and quadrupole anisotropy of pions and (anti)protons in central $ d + $Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 114 (2015) 192301 | 1404.7461 |
| 27 | STAR Collaboration | Long-range pseudorapidity dihadron correlations in $ d $+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PLB 747 (2015) 265 | 1502.07652 |
| 28 | PHENIX Collaboration | Measurements of elliptic and triangular flow in high-multiplicity $ ^{3} $He$ + $Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 115 (2015) 142301 | 1507.06273 |
| 29 | K. Dusling and R. Venugopalan | Comparison of the color glass condensate to dihadron correlations in proton-proton and proton-nucleus collisions | PRD 87 (2013) 094034 | 1302.7018 |
| 30 | K. Dusling, M. Mace, and R. Venugopalan | Multiparticle collectivity from initial state correlations in high energy proton-nucleus collisions | PRL 120 (2018) 042002 | 1705.00745 |
| 31 | L. He et al. | Anisotropic parton escape is the dominant source of azimuthal anisotropy in transport models | PLB 753 (2016) 506--510 | 1502.05572 |
| 32 | ALICE Collaboration | Anisotropic flow fluctuations of charged and identified hadrons in Pb-Pb collisions with the ALICE detector | NP A 1005 (2021) 121997. 4 p | |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Probing charm quark dynamics via multiparticle azimuthal correlations in 5.02 TeV PbPb collisions | CMS-PAS-HIN-20-001 | CMS-PAS-HIN-20-001 |
| 34 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 36 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4--a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) 01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Charged-particle nuclear modification factors in PbPb and pPb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\mathrm{N}\;\mathrm{N}}}= $ 5.02 TeV | JHEP 04 (2017) 039 | CMS-HIN-15-015 1611.01664 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement using 2016 proton-nucleus collisions at nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy of 8.16 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-002 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-002 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Multiplicity and transverse momentum dependence of two- and four-particle correlations in $ \mathrm{pPb}\ $ and $ \mathrm{PpPb}\ $ collisions | PLB 724 (2013) 213 | CMS-HIN-13-002 1305.0609 |
| 41 | CMS Collaboration | Particle--flow event reconstruction in CMS and performance for jets, taus, and $E_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{miss}}$ | CDS | |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | Commissioning of the particle-flow reconstruction in minimum-bias and jet events from $ {\mathrm{p}}{\mathrm{p}} $ collisions at 7 TeV | CMS-PAS-PFT-10-002 | |
| 43 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_t $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 44 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 45 | O. Kodolova, I. Vardanian, A. Nikitenko, and A. Oulianov | The performance of the jet identification and reconstruction in heavy ions collisions with CMS detector | EPJC 50 (2007) 117 | |
| 46 | CMS Collaboration | Observation and studies of jet quenching in PbPb collisions at nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy = 2.76 TeV | PRC 84 (2011) 024906 | CMS-HIN-10-004 1102.1957 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | Strange Particle Production in $ pp $ Collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 0.9 and 7 TeV | JHEP 05 (2011) 064 | CMS-QCD-10-007 1102.4282 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Long-range two-particle correlations of strange hadrons with charged particles in pPb and PbPb collisions at LHC energies | PLB 742 (2015) 200 | CMS-HIN-14-002 1409.3392 |
| 49 | Particle Data Group Collaboration | Review of Particle Physics | PRD 98 (2018) 030001 | |
| 50 | A. Hoecker et al. | Tmva - toolkit for multivariate data analysis | 2007 | |
| 51 | CMS Collaboration | Multiplicity and rapidity dependence of strange hadron production in pp, pPb, and PbPb collisions at the LHC | PLB 768 (2017) 103 | CMS-HIN-15-006 1605.06699 |
| 52 | CMS Collaboration | Pseudorapidity and transverse momentum dependence of flow harmonics in pPb and PbPb collisions | PRC 98 (2018) 044902 | CMS-HIN-15-008 1710.07864 |
| 53 | CMS Collaboration | Azimuthal anisotropy of charged particles with transverse momentum up to 100 GeV/ c in PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt {s}_{{NN}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 776 (2018) 195--216 | CMS-HIN-15-014 1702.00630 |
| 54 | A. Bilandzic, R. Snellings, and S. Voloshin | Flow analysis with cumulants: Direct calculations | PRC 83 (2011) 044913 | 1010.0233 |
| 55 | A. Bilandzic et al. | Generic framework for anisotropic flow analyses with multiparticle azimuthal correlations | PRC 89 (2014) 064904 | 1312.3572 |
| 56 | N. Borghini, P. M. Dinh, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Flow analysis from multiparticle azimuthal correlations | PRC 64 (2001) 054901 | nucl-th/0105040 |
| 57 | CMS Collaboration | Comparing transverse momentum balance of b jet pairs in pp and PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\mathrm{NN}}}= $ 5.02 TeV | JHEP 03 (2018) 181 | CMS-HIN-16-005 1802.00707 |
| 58 | W. Zhao, H.-j. Xu, and H. Song | Collective flow in 2.76 A TeV and 5.02 A TeV Pb+Pb collisions | EPJC 77 (2017) 645 | 1703.10792 |
| 59 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for transverse momentum and pseudorapidity dependent event plane fluctuations in PbPb and pPb collisions | PRC 92 (2015) 034911 | CMS-HIN-14-012 1503.01692 |
| 60 | PHOBOS Collaboration | Importance of correlations and fluctuations on the initial source eccentricity in high-energy nucleus-nucleus collisions | PRC 77 (2008) 014906 | 0711.3724 |
| 61 | J.-Y. Ollitrault, A. M. Poskanzer, and S. A. Voloshin | Effect of flow fluctuations and nonflow on elliptic flow methods | PRC 80 (2009) 014904 | 0904.2315 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|