

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-EXO-22-018 | ||
| Search for leptoquarks produced in lepton-quark collisions and coupling to $ \tau $ leptons | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 22 May 2023 | ||
| Abstract: A search for leptoquarks produced in lepton-quark collisions and coupling to $ \tau $ leptons is presented. It is based on a data set of proton-proton collision events recorded by the CMS detector at the LHC at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV and corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. The reconstructed final state consists of a jet, significant missing transverse momentum, and a $ \tau $ lepton reconstructed through its leptonic or hadronic decays. Limits are set on the leptoquark production cross section times branching fraction and interpreted as exclusions in the plane of the leptoquark mass and the coupling strength of the leptoquark-lepton-quark vertex. These results complement the constraints on the leptoquark-$ \tau $-b couplings set by previous searches in other production modes, while they are the first limits for leptoquark-$ \tau $-u, leptoquark-$ \tau $-d, and leptoquark-$ \tau $-s couplings. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, Submitted to PRL. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
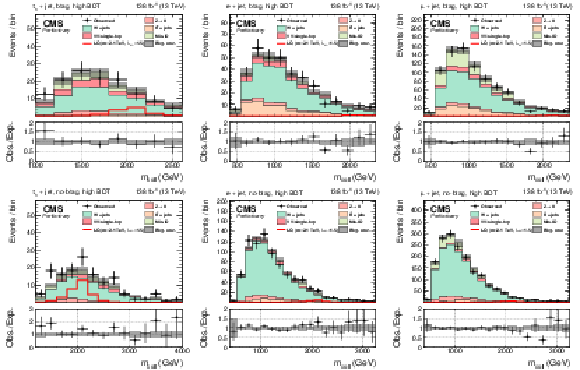
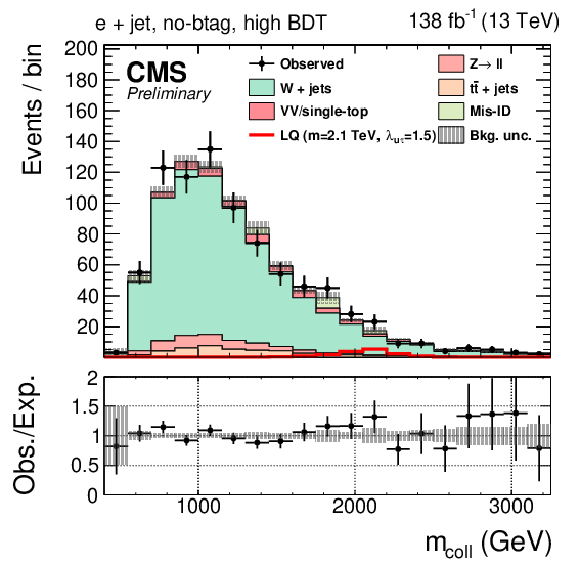
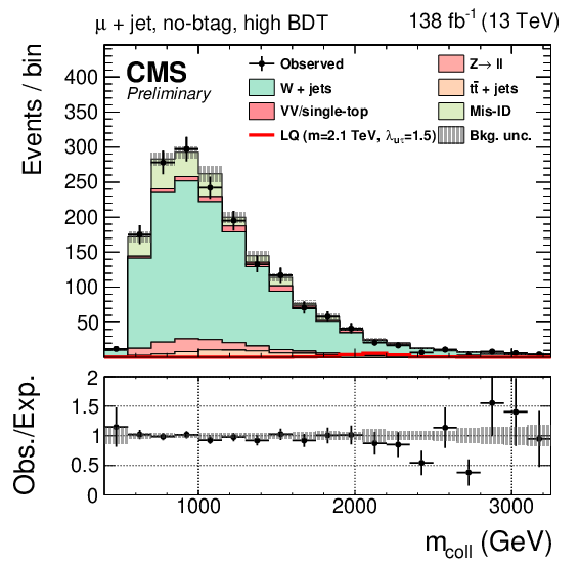
Figure 1:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
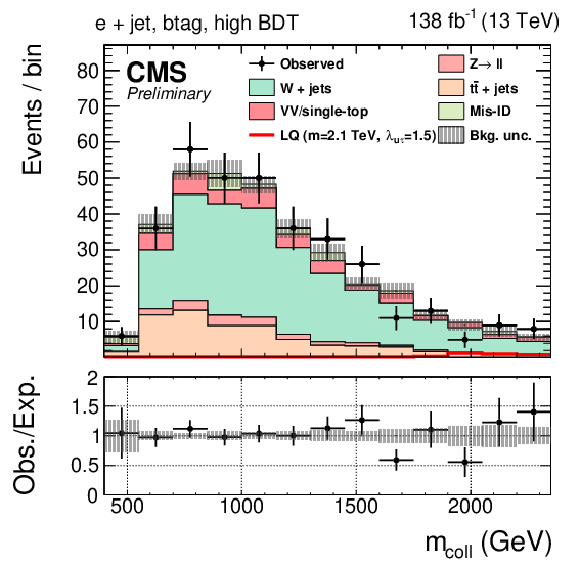
Figure 1-b:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
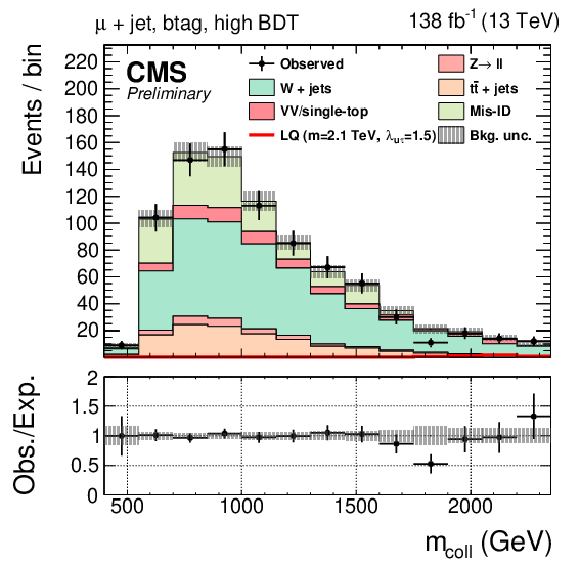
Figure 1-c:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
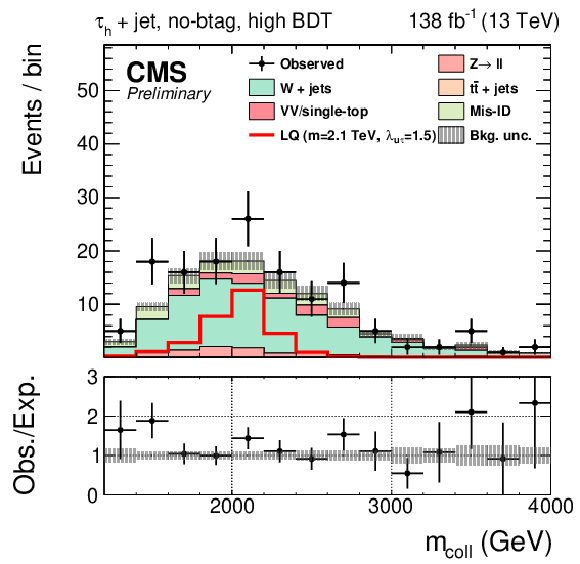
Figure 1-d:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-e:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-f:
Observed and expected distributions of the collinear mass in the $ \tau_\mathrm{h}$+jet (left), $ \mathrm{e}$+jet (center), and $ \mu$+jet (right) channels for the btag (top) and no-btag (bottom) categories with the highest BDT output requirements. The uncertainty band includes statistical and systematic uncertainties, and the background distributions are the results of the maximum likelihood fit. |
png pdf |
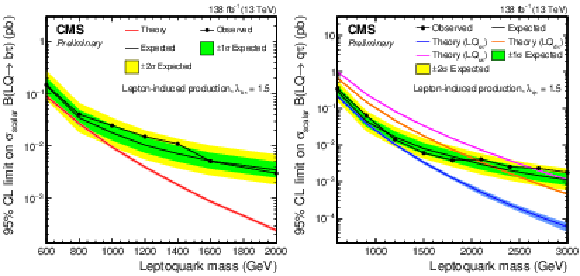
Figure 2:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the scalar lepton-induced LQ production cross section times branching fraction for a LQ coupling to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), or to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right), using $ \lambda= $ 1.5. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the scalar lepton-induced LQ production cross section times branching fraction for a LQ coupling to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), or to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right), using $ \lambda= $ 1.5. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the scalar lepton-induced LQ production cross section times branching fraction for a LQ coupling to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), or to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right), using $ \lambda= $ 1.5. |

png pdf |
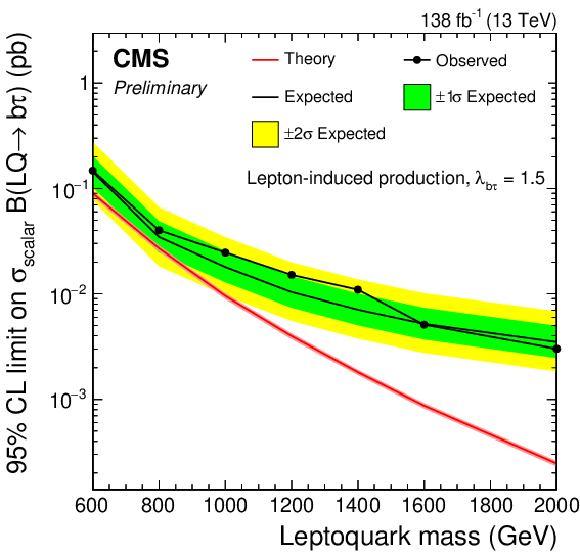
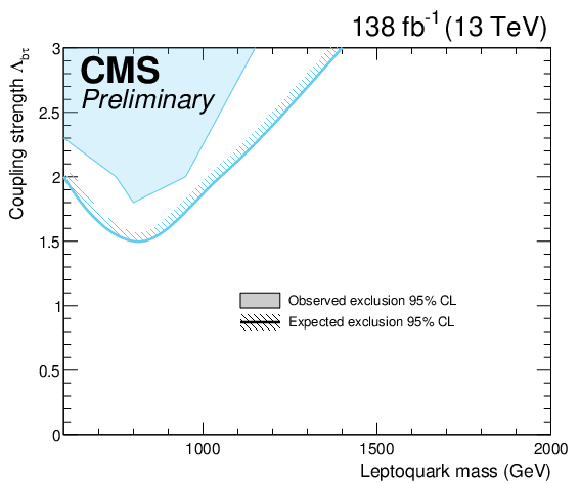
Figure 3:
Expected upper limit at 95% CL on the coupling strength $ \lambda $ of a scalar LQ to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), and to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right). |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Expected upper limit at 95% CL on the coupling strength $ \lambda $ of a scalar LQ to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), and to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right). |

png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Expected upper limit at 95% CL on the coupling strength $ \lambda $ of a scalar LQ to b quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (left), and to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons (right). |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
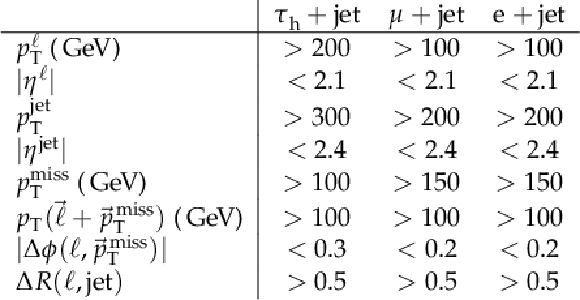
Table 1:
Selection criteria, where $ \ell $ stands for $ \tau_\mathrm{h} $, $ \mu $, or e, depending on the final state. |
| Summary |
| As a summary, a search for leptoquarks produced via lepton-induced production and coupling to $ \tau $ leptons has been performed for the first time, using data collected by the CMS detector in Run-2. The limits are competitive with those set using other production modes at high mass and coupling values for $ \mathrm{b}\tau $ couplings, while limits on the couplings of leptoquarks to light-flavor quarks and $ \tau $ leptons are set for the first time. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | J. C. Pati and A. Salam | Lepton number as the fourth color | (Jul, ) 275, 1974 PRD 1 (1974) 0 |
|
| 2 | H. Georgi and S. L. Glashow | Unity of all elementary-particle forces | (Feb, ) 438, 1974 PRL 3 (1974) 2 |
|
| 3 | S. Dimopoulos and L. Susskind | Mass without scalars | Nuclear Physics B 155 (1979) 237 | |
| 4 | S. Dimopoulos | Technicoloured signatures | Nuclear Physics B 168 (1980) 69 | |
| 5 | B. Schrempp and F. Schrempp | Light leptoquarks | Physics Letters B 153 (1985) 101 | |
| 6 | W. Buchmuller and D. Wyler | Constraints on SU(5)-type leptoquarks | Physics Letters B 177 (1986) 377 | |
| 7 | M. Tanaka and R. Watanabe | New physics in the weak interaction of $ \bar B\to D^{(*)}\tau\bar\nu $ | PRD 87 (2013) 034028 | 1212.1878 |
| 8 | S. Fajfer, J. F. Kamenik, I. Nisandzic, and J. Zupan | Implications of lepton flavor universality violations in B decays | PRL 109 (2012) 161801 | 1206.1872 |
| 9 | Y. Sakaki, M. Tanaka, A. Tayduganov, and R. Watanabe | Testing leptoquark models in $ \bar B \to D^{(*)} \tau \bar\nu $ | PRD 88 (2013) 094012 | 1309.0301 |
| 10 | M. Bauer and M. Neubert | Minimal leptoquark explanation for the $ R_{D^{(*)}} $, $ R_K $, and $ (g-2)_\mu $ anomalies | PRL 116 (2016) 141802 | 1511.01900 |
| 11 | L. Calibbi, A. Crivellin, and T. Ota | Effective field theory approach to $ b\to s\ell\ell^{(')} $, $ B\to K^{(*)}\nu\overline{\nu} $ and $ B\to D^{(*)}\tau\nu $ with third generation couplings | PRL 115 (2015) 181801 | 1506.02661 |
| 12 | M. Freytsis, Z. Ligeti, and J. T. Ruderman | Flavor models for $ \bar{B} \to D^{(*)} \tau \bar{\nu} $ | PRD 92 (2015) 054018 | 1506.08896 |
| 13 | S. Bhattacharya, S. Nandi, and S. K. Patra | Optimal-observable analysis of possible new physics in $ B\to D^{(\ast)}\tau\nu_{\tau} $ | PRD 93 (2016) 034011 | 1509.07259 |
| 14 | S. Fajfer and N. Ko \v s nik | Vector leptoquark resolution of $ R_K $ and $ R_{D^{(*)}} $ puzzles | PLB 755 (2016) 270 | 1511.06024 |
| 15 | B. Dumont, K. Nishiwaki, and R. Watanabe | Lhc constraints and prospects for $ S_1 $ scalar leptoquark explaining the $ \bar B \to D^{(*)} \tau \bar\nu $ anomaly | PRD 94 (2016) 034001 | 1603.05248 |
| 16 | D. Buttazzo, A. Greljo, G. Isidori, and D. Marzocca | B-physics anomalies: a guide to combined explanations | JHEP 11 (2017) 044 | 1706.07808 |
| 17 | J. Kumar, D. London, and R. Watanabe | Combined explanations of the $ b \to s \mu^+ \mu^- $ and $ b \to c \tau^- {\bar\nu} $ anomalies: a general model analysis | PRD 99 (2019) 015007 | 1806.07403 |
| 18 | A. Angelescu et al. | Single leptoquark solutions to the B-physics anomalies | PRD 104 (2021) 055017 | 2103.12504 |
| 19 | Belle Collaboration | Observation of $ B^0 \rightarrow D^{*-} \tau^+ \nu_\tau $ decay at Belle | PRL 99 (2007) 191807 | 0706.4429 |
| 20 | Belle Collaboration | Observation of $ B^+ \to \bar{D}^*0 \tau^+ \nu_\tau $ and evidence for $ B^+ \to \bar{D}^0 \tau^+ \nu_\tau $ at Belle | PRD 82 (2010) 072005 | 1005.2302 |
| 21 | BaBar Collaboration | Evidence for an excess of $ \bar{B} \to D^{(*)} \tau^-\bar{\nu}_\tau $ decays | PRL 109 (2012) 101802 | 1205.5442 |
| 22 | BaBar Collaboration | Measurement of an excess of $ \bar{B} \to D^{(*)}\tau^- \bar{\nu}_\tau $ decays and implications for charged higgs bosons | PRD 88 (2013) 072012 | 1303.0571 |
| 23 | LHCb Collaboration | Measurement of the ratio of branching fractions $ \mathcal{B}(\bar{B}^0 \to D^{*+}\tau^{-}\bar{\nu}_{\tau})/\mathcal{B}(\bar{B}^0 \to D^{*+}\mu^{-}\bar{\nu}_{\mu}) $ | PRL 115 (2015) 111803 | 1506.08614 |
| 24 | Belle Collaboration | Measurement of the branching ratio of $ \bar{B}^0 \rightarrow D^{*+} \tau^- \bar{\nu}_{\tau} $ relative to $ \bar{B}^0 \rightarrow D^{*+} \ell^- \bar{\nu}_{\ell} $ decays with a semileptonic tagging method | PRD 94 (2016) 072007 | 1607.07923 |
| 25 | Belle Collaboration | Measurement of the $ \tau $ lepton polarization and $ R(D^*) $ in the decay $ \bar{B} \rightarrow D^* \tau^- \bar{\nu}_\tau $ with one-prong hadronic $ \tau $ decays at Belle | PRD 97 (2018) 012004 | 1709.00129 |
| 26 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in $ pp $ collisions in final states with tau leptons, b-jets, and missing transverse momentum with the ATLAS detector | PRD 104 (2021) 112005 | 2108.07665 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a singly produced third-generation scalar leptoquark decaying to a $ \tau $ lepton and a bottom quark in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2018) 115 | CMS-EXO-17-029 1806.03472 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Search for singly and pair-produced leptoquarks coupling to third-generation fermions in proton-proton collisions at s=13 TeV | PLB 819 (2021) 136446 | CMS-EXO-19-015 2012.04178 |
| 29 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for pair production of third-generation scalar leptoquarks decaying into a top quark and a $ \tau $-lepton in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} $ = 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 06 (2021) 179 | 2101.11582 |
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | Searches for additional Higgs bosons and for vector leptoquarks in $ \tau\tau $ final states in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} $ = 13 TeV | Submitted to JHEP, 2022 | CMS-HIG-21-001 2208.02717 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in the $ \tau $ lepton plus missing transverse momentum final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt s $ = 13 TeV | Submitted to JHEP, 2022 | CMS-EXO-21-009 2212.12604 |
| 32 | V. Bertone, S. Carrazza, D. Pagani, and M. Zaro | On the impact of lepton PDFs | JHEP 11 (2015) 194 | 1508.07002 |
| 33 | A. Manohar, P. Nason, G. P. Salam, and G. Zanderighi | How bright is the proton? A precise determination of the photon parton distribution function | PRL 117 (2016) 242002 | 1607.04266 |
| 34 | NNPDF Collaboration | Illuminating the photon content of the proton within a global PDF analysis | SciPost Phys. 5 (2018) 008 | 1712.07053 |
| 35 | A. V. Manohar, P. Nason, G. P. Salam, and G. Zanderighi | The photon content of the proton | JHEP 12 (2017) 046 | 1708.01256 |
| 36 | L. Buonocore, P. Nason, F. Tramontano, and G. Zanderighi | Leptons in the proton | JHEP 08 (2020) 019 | 2005.06477 |
| 37 | L. Buonocore et al. | Lepton-quark collisions at the Large Hadron Collider | PRL 125 (2020) 231804 | 2005.06475 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13\,TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 41 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P10005 | CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 46 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of hadronic tau lepton decays using a deep neural network | JINST 17 (2022) P07023 | CMS-TAU-20-001 2201.08458 |
| 49 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 50 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 51 | J. M. Lindert et al. | Precise predictions for $ V+ $ jets dark matter backgrounds | EPJC 77 (2017) 829 | 1705.04664 |
| 52 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 53 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 54 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 55 | S. Alioli et al. | Jet pair production in POWHEG | JHEP 04 (2011) 081 | 1012.3380 |
| 56 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | NLO higgs boson production via gluon fusion matched with shower in POWHEG | JHEP 04 (2009) 002 | 0812.0578 |
| 57 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 58 | R. D. Ball et al. | Unbiased global determination of parton distributions and their uncertainties at NNLO and at LO | NPB 855 (2012) 153 | 1107.2652 |
| 59 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions with QED corrections | NPB 877 (2013) 290 | 1308.0598 |
| 60 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | EPJC 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 61 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4 --- a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 62 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P05011 | CMS-BTV-16-002 1712.07158 |
| 63 | E. Bols et al. | Jet flavour classification using DeepJet | JINST 15 (2020) P12012 | 2008.10519 |
| 64 | A. Höcker et al. | TMVA - Toolkit for multivariate data analysis | arXiv e-prints (March, ) physics/0703039, 2007 | physics/0703039 |
| 65 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 66 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 67 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 68 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 69 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: the $ \rm CL_s $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 70 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|