

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-HIG-16-015 ; CERN-EP-2016-292 | ||
| Search for light bosons in decays of the 125 GeV Higgs boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 8 January 2017 | ||
| JHEP 10 (2017) 076 | ||
| Abstract: A search is presented for decays beyond the standard model of the 125 GeV Higgs bosons to a pair of light bosons, based on models with extended scalar sectors. Light boson masses between 5 and 62.5 GeV are probed in final states containing four $\tau$ leptons, two muons and two b quarks, or two muons and two $\tau$ leptons. The results are from data in proton-proton collisions corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$, accumulated by the CMS experiment at the LHC at a center-of-mass energy of 8 TeV. No evidence for such exotic decays is found in the data. Upper limits are set on the product of the cross section and branching fraction for several signal processes. The results are also compared to predictions of two-Higgs-doublet models, including those with an additional scalar singlet. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:1701.02032 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
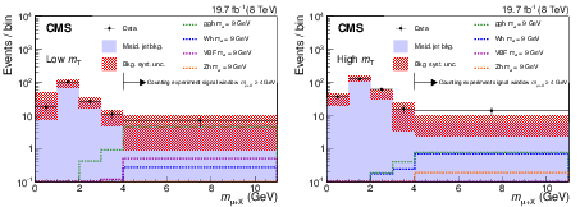
Figure 1:
Comparison, for the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 4\tau $ search, of $m_{\mu +\text {X}}$ distributions for data (black markers) and the misidentified jet background estimate (solid histogram) in the low-$ {m_\mathrm {T}} $ (left) and high-$ {m_\mathrm {T}} $ (right) bins. Predicted signal distributions (dotted lines) for each of the four Higgs boson production mechanisms are also shown; the distributions are normalized to an integrated luminosity of the data sample of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$, assuming SM Higgs boson production cross sections and $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h}\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^{2}( \mathrm {a} \to \tau ^+\tau ^-) = $ 0.1. The last bin on the right contains all the events with $m_{\mu +\text {X}}\geq $ 4 GeV, which correspond to the numbers reported in Table 3. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Comparison, for the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 4\tau $ search, of $m_{\mu +\text {X}}$ distributions for data (black markers) and the misidentified jet background estimate (solid histogram) in the low-$ {m_\mathrm {T}} $ bin. Predicted signal distributions (dotted lines) for each of the four Higgs boson production mechanisms are also shown; the distributions are normalized to an integrated luminosity of the data sample of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$, assuming SM Higgs boson production cross sections and $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h}\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^{2}( \mathrm {a} \to \tau ^+\tau ^-) = $ 0.1. The last bin on the right contains all the events with $m_{\mu +\text {X}}\geq $ 4 GeV, which correspond to the numbers reported in Table 3. |
png pdf |
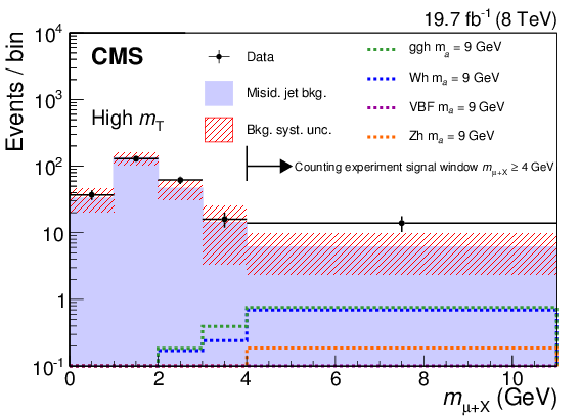
Figure 1-b:
Comparison, for the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 4\tau $ search, of $m_{\mu +\text {X}}$ distributions for data (black markers) and the misidentified jet background estimate (solid histogram) in the high-$ {m_\mathrm {T}} $ bin. Predicted signal distributions (dotted lines) for each of the four Higgs boson production mechanisms are also shown; the distributions are normalized to an integrated luminosity of the data sample of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$, assuming SM Higgs boson production cross sections and $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h}\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^{2}( \mathrm {a} \to \tau ^+\tau ^-) = $ 0.1. The last bin on the right contains all the events with $m_{\mu +\text {X}}\geq $ 4 GeV, which correspond to the numbers reported in Table 3. |
png pdf |
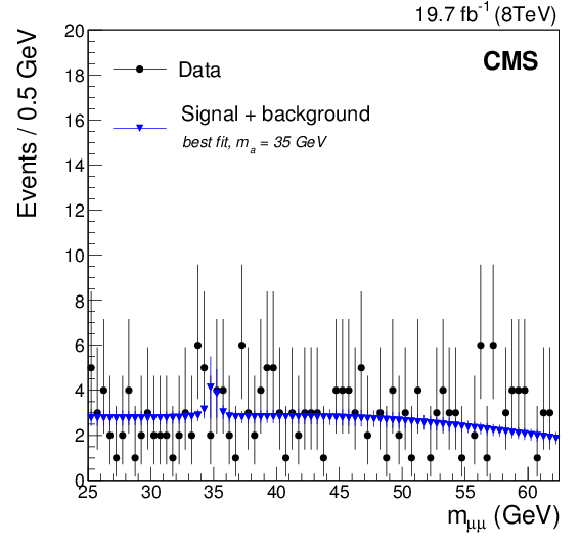
Figure 2:
The best fit to the data for a signal-plus-background model with $ m_{ \mathrm {a} } =$ 35 GeV, including profiling of the uncertainties, in the search for $ mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ events. |
png pdf |
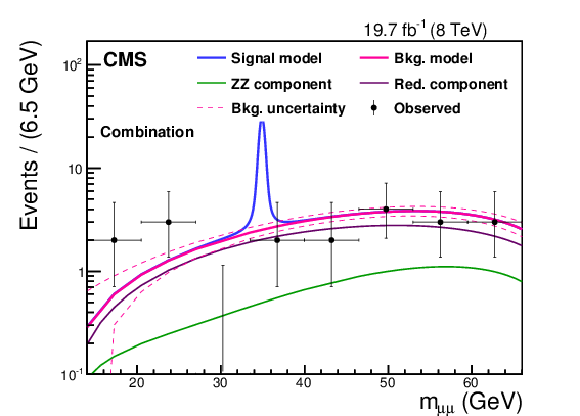
Figure 3:
Background and signal ($ m_{ \mathrm {a} } = $ 35 GeV) models, scaled to their expected yields, for the combination of all final states in the search for $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\tau $ decays. The two components of the background model, ZZ and reducible processes, are drawn. The signal sample is scaled with $\sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }$ as predicted in the SM, assuming $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) = $ 10%, and considering decays of the pseudoscalar $ \mathrm {a} $ boson to leptons only ($\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow {\tau ^{+}}{\tau ^{-}})+\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \mu ^+\mu ^-)+\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \mathrm {e} ^+\mathrm {e} ^-) = 1$) using Eq.(\ref {eq:2hdm}). The results are shown after a simultaneous maximum likelihood fit in all five channels that takes into account the systematic uncertainties described in Section 6. |
png pdf |
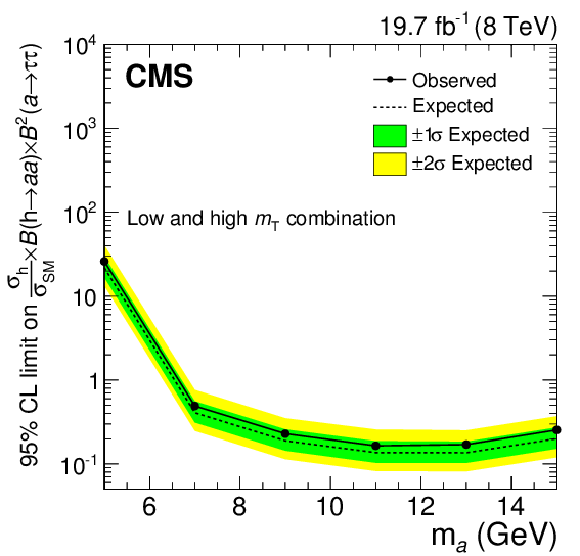
Figure 4:
Observed 95% CL limits on the branching fraction $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^{2}( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \tau ^{+}\tau ^{-})$ assuming SM h production rates, compared to expected limits for pseudoscalar mass points between 5 and 15 GeV. |
png pdf |
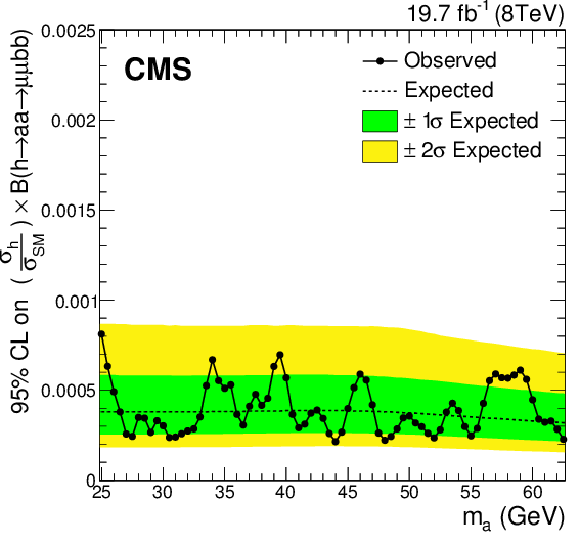
Figure 5:
Observed and expected upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( { \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } )$. |
png pdf |
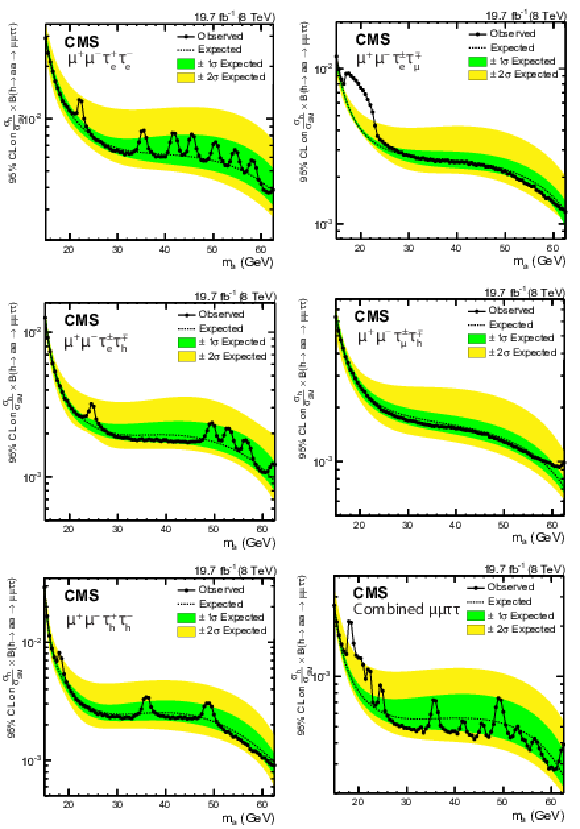
Figure 6:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau_\mathrm {e}^+\tau_\mathrm {e}^-$ (top left), $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau _{e}^\pm \tau _{\mu }^\mp $ (top right), $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau_\mathrm {e}^\pm \tau _{\rm {h}}^\mp $ (center left), $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau _{\mu }^\pm {\tau _{\rm h}}^\mp $ (center right), and $\mu ^+\mu ^-{\tau _{\rm h}}^+{\tau _{\rm h}}^-$ (bottom left) final states, and for the combination of these five final states (bottom right). None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |
png pdf |
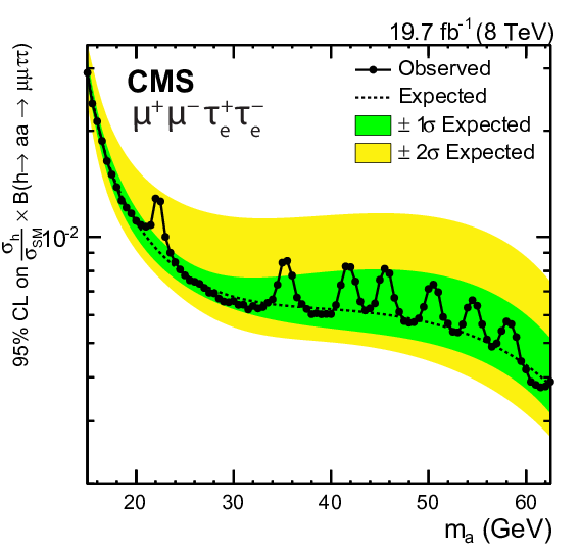
Figure 6-a:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau_\mathrm {e}^+\tau_\mathrm {e}^-$ final state. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |

png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau _{e}^\pm \tau _{\mu }^\mp $ final state. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |
png pdf |
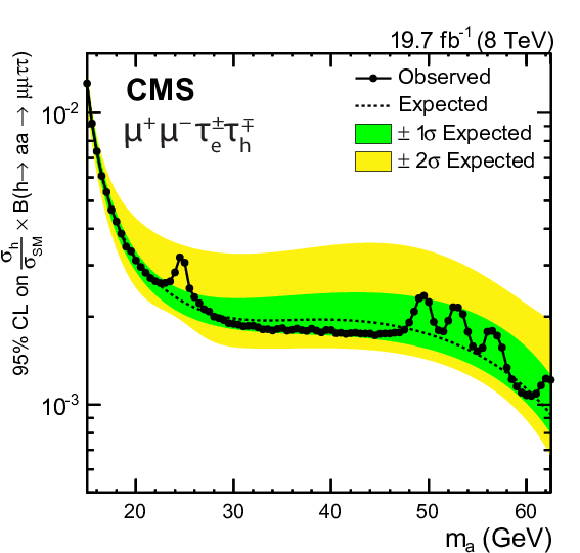
Figure 6-c:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau_\mathrm {e}^\pm \tau _{\rm {h}}^\mp $ final state. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |
png pdf |
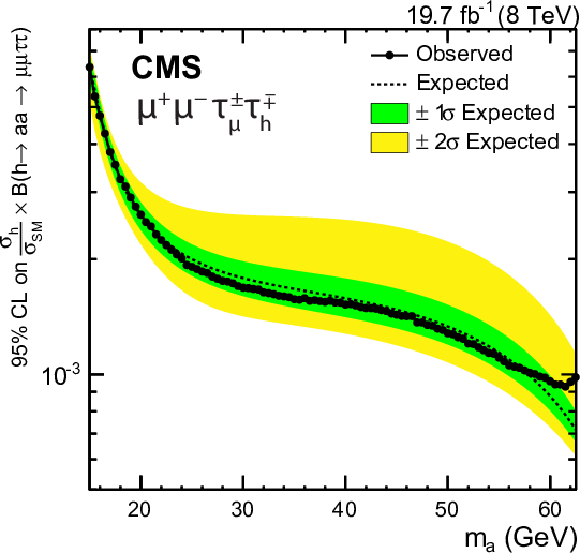
Figure 6-d:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-\tau _{\mu }^\pm {\tau _{\rm h}}^\mp $ final state. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |

png pdf |
Figure 6-e:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ in the $\mu ^+\mu ^-{\tau _{\rm h}}^+{\tau _{\rm h}}^-$ final state. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |
png pdf |
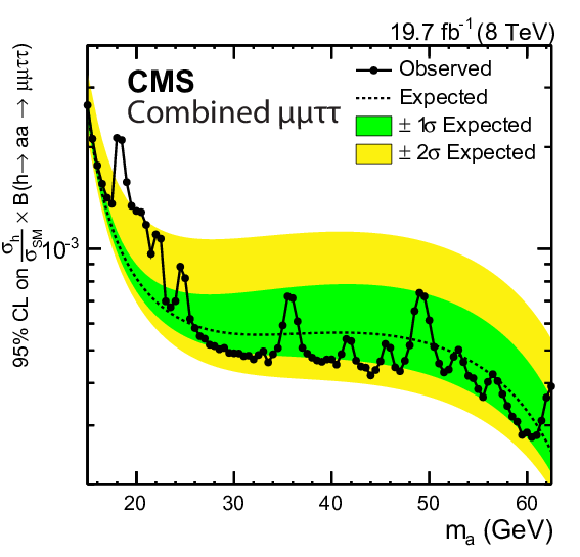
Figure 6-f:
Expected and observed upper limits at 95% CL on the h boson production normalized to the SM prediction times $\mathcal {B}( {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } )$ for the combination of the five final states. None of the event excesses exceed two standard deviations in global significance. |
png pdf |
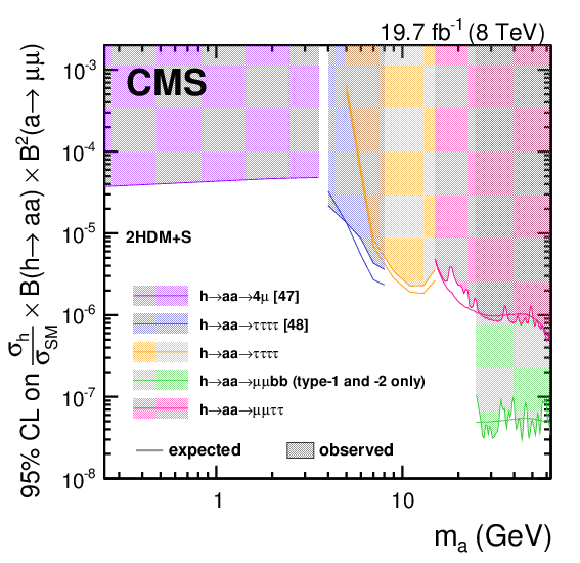
Figure 7:
Expected and observed 95% CL exclusion limits on $({\sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }}/{\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^2( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \mu ^+\mu ^-)$ for various exotic h boson decay searches performed with data collected at 8 TeV with the CMS detector, assuming that the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to muons, $\tau $ leptons and b quarks follow Eqs.(1)-(2). This assumption implies that the limit shown for $ { \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ is valid only in type-1 and -2 2HDM+S. |
png pdf |
Figure 8:
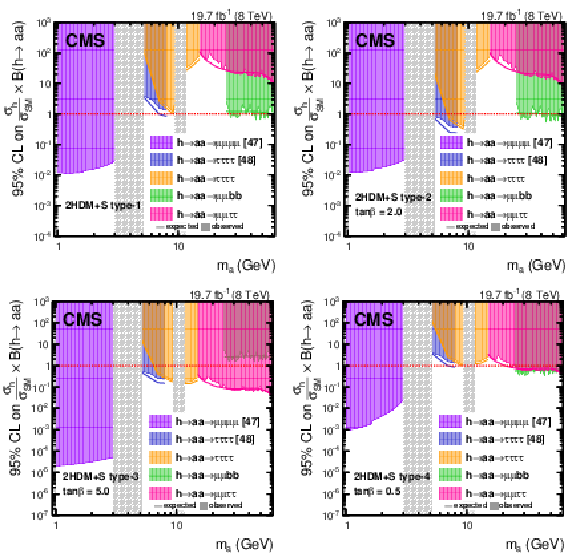
Expected and observed 95% CL limits on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in 2HDM+S type-1 (top left), type-2 with $\tan\beta =$ 2 (top right), type-3 with $\tan\beta =$ 5 (bottom left), and type-4 with $\tan\beta =$ 0.5 (bottom right). Limits are shown as a function of the mass of the light boson, $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} $. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following a model described in Ref. [8]. Grey shaded regions correspond to regions where theoretical predictions for the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are not reliable. |
png pdf |
Figure 8-a:
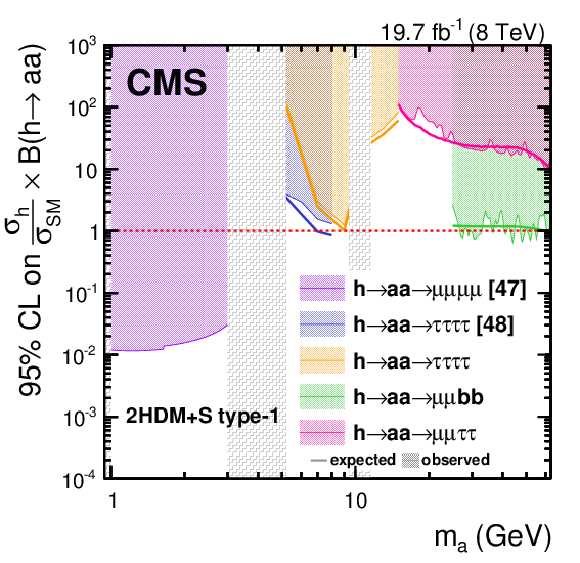
Expected and observed 95% CL limits on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in 2HDM+S type-1. Limits are shown as a function of the mass of the light boson, $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} $. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following a model described in Ref. [8]. Grey shaded regions correspond to regions where theoretical predictions for the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are not reliable. |

png pdf |
Figure 8-b:
Expected and observed 95% CL limits on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in type-2 with $\tan\beta =$ 2. Limits are shown as a function of the mass of the light boson, $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} $. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following a model described in Ref. [8]. Grey shaded regions correspond to regions where theoretical predictions for the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are not reliable. |

png pdf |
Figure 8-c:
Expected and observed 95% CL limits on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in type-3 with $\tan\beta =$ 5. Limits are shown as a function of the mass of the light boson, $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} $. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following a model described in Ref. [8]. Grey shaded regions correspond to regions where theoretical predictions for the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are not reliable. |

png pdf |
Figure 8-d:
Expected and observed 95% CL limits on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}}) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in type-4 with $\tan\beta =$ 0.5. Limits are shown as a function of the mass of the light boson, $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} $. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following a model described in Ref. [8]. Grey shaded regions correspond to regions where theoretical predictions for the branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are not reliable. |
png pdf |
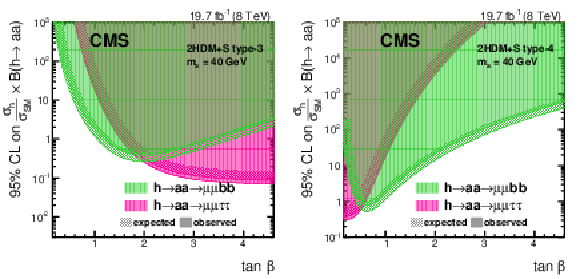
Figure 9:
The 95% CL limit on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}} ) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in 2HDM+S type-3 (left) and type-4 (right) for different $\tan\beta $ values, for the $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\tau $ and $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ analyses at $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} =$ 40 GeV. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following the prescriptions in Ref. [8]. |
png pdf |
Figure 9-a:
The 95% CL limit on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}} ) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in 2HDM+S type-3 for different $\tan\beta $ values, for the $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\tau $ and $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ analyses at $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} =$ 40 GeV. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following the prescriptions in Ref. [8]. |
png pdf |
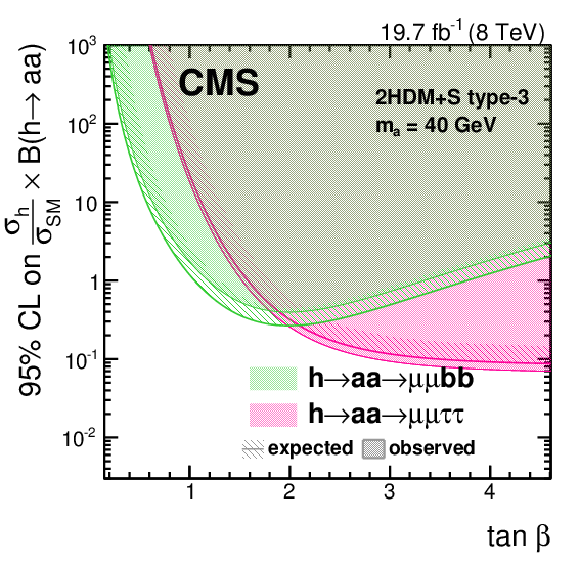
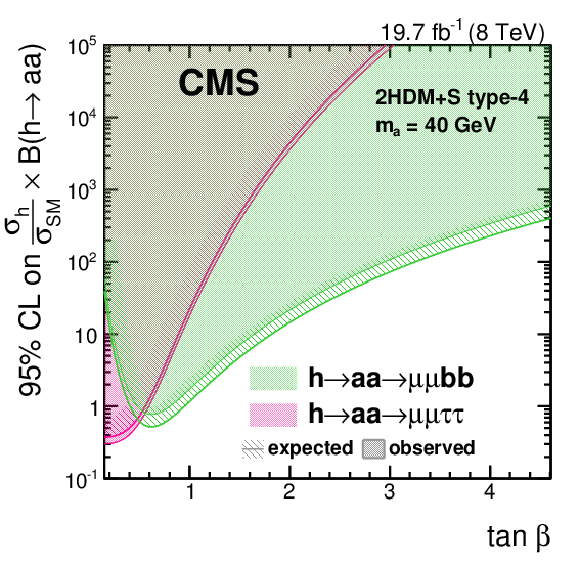
Figure 9-b:
The 95% CL limit on $( \sigma _{ \mathrm {h} }/\sigma _{\textrm {SM}} ) \mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )$ in 2HDM+S and type-4 for different $\tan\beta $ values, for the $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\tau $ and $ { \mathrm {h} }\to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ analyses at $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} =$ 40 GeV. The branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson to SM particles are computed following the prescriptions in Ref. [8]. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Doublets to which the different types of fermions couple in the four types of 2HDM without FCNC at lowest order. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Ratio of the Yukawa couplings of the pseudoscalar boson a of the 2HDM relative to those of the Higgs boson of the SM, in the four types of 2HDM without FCNC at lowest order. |
png pdf |
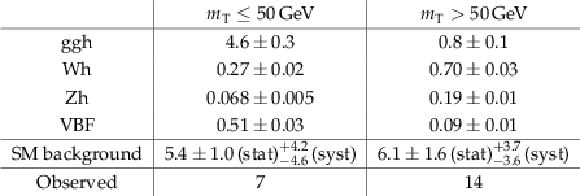
Table 3:
Expected signal yields for the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 4\tau $ process for a representative pseudoscalar mass of 9 GeV, in both $ m_\mathrm {T} $ bins, assuming SM cross sections and $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) \mathcal {B}^{2}( \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \tau ^{+}\tau ^{-})=$ 0.1, in the context of the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 4\tau $ search. Expected background yields as well as observed numbers of events are also quoted. Only the statistical uncertainty is given for signal yields. |
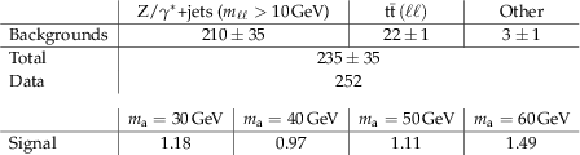
png pdf |
Table 4:
Expected signal and background yields, together with the number of observed events, for the $ \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \to 2\mu 2\mathrm{ b } $ search, in the range 20 $ \leq {m_{\mu \mu }} \leq $ 70 GeV. Signal yields are evaluated assuming $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \rightarrow \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} )= $ 10% and $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} \rightarrow \mu ^+\mu ^- \mathrm{ b } \overline{ \mathrm{ b } })= 1.7\times 10^{-3}$, with the latter obtained in the context of type-3 2HDM+S with $\tan\beta =$ 2. |
png pdf |
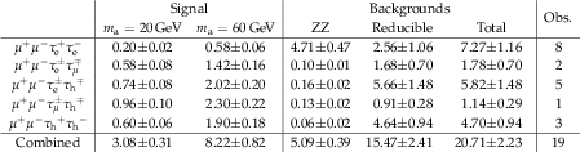
Table 5:
Expected and observed yields in the search for $ { \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau $ decays. The signal samples are scaled with the production cross section for the SM h boson, assuming $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {h} \to \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} ) = 10%$ and considering decays of the pseudoscalar $ \mathrm {a} $ boson to leptons only. Background yields are obtained after a maximum likelihood fit to observed data, taking into account the systematic uncertainties detailed in Section 6. |

png pdf |
Table 6:
Sources of systematic uncertainties, and their effects on process yields, for the three different searches. Ranges for the $ {{ \mathrm {h} }\to { \mathrm {a} \mathrm {a} }\to 2\mu 2\tau } $ search correspond to different final states. |

png pdf |
Table 7:
Branching fractions of the pseudoscalar boson a to muons, $\tau $ leptons, and b quarks, in the four 2HDM+S scenarios considered in Fig. 8, as a function of the light boson mass. The branching fraction $\mathcal {B}( \mathrm {a} \to \mathrm{b} \overline{ \mathrm{ b } } )$ is not indicated in the mass range $ {m_{ \mathrm {a} }} \in $ [5,15] GeV because it is not used to interpret the results. |
| Summary |
| Searches for the decay of the SM-like Higgs boson to pairs of light scalar particles have been performed using 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ of pp collisions at a center-of-mass energy of 8 TeV, collected by the CMS experiment at the LHC, in final states with $\tau$ leptons, muons, or b quark jets. Such signatures are motivated in light of the non-negligible branching fraction provided in recent experimental constraints for non-SM ${{\mathrm{h}}} $ decays. The data were found to be compatible with SM predictions. Whereas indirect measurements from the combination of data collected by the ATLAS and CMS collaborations at the LHC at 8 TeV center-of-mass energy set an upper limit of 34% on branching fraction of the Higgs boson to BSM, direct limits provide complementarity and improve the sensitivity to the 2HDM+S models for particular scenarios and pseudoscalar masses. Upper limits at 95% CL on $({\sigma_{{{\mathrm{h}}} }}/{\sigma_{\textrm{SM}}}) \, \mathcal{B}({{\mathrm{h}}} \rightarrow {\mathrm{a}} {\mathrm{a}} )$, assuming SM production of the 125 GeV Higgs boson, are as low as 17, 16, and 4%, and have been determined for the ${{{{\mathrm{h}}} }\to{{\mathrm{a}} {\mathrm{a}} }\to4\tau} $, ${{{{\mathrm{h}}} }\to{{\mathrm{a}} {\mathrm{a}} }\to2\mu2\mathrm{ b }} $, and ${{{{\mathrm{h}}} }\to{{\mathrm{a}} {\mathrm{a}} }\to2\mu2\tau} $ analyses, respectively. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1 | 1207.7214 |
| 2 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 3 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson with mass near 125 GeV in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2013) 081 | CMS-HIG-12-036 1303.4571 |
| 4 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Measurements of the Higgs boson production and decay rates and constraints on its couplings from a combined ATLAS and CMS analysis of the LHC $ pp $ collision data at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 08 (2016) 45 | 1606.02266 |
| 5 | CMS Collaboration | Precise determination of the mass of the Higgs boson and tests of compatibility of its couplings with the standard model predictions using proton collisions at 7 and 8 TeV | EPJC 75 (2015) 212 | CMS-HIG-14-009 1412.8662 |
| 6 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurements of the Higgs boson production and decay rates and coupling strengths using $ pp $ collision data at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 and 8 TeV in the ATLAS experiment | EPJC 76 (2016) 6 | 1507.04548 |
| 7 | ATLAS Collaboration | Constraints on new phenomena via Higgs boson couplings and invisible decays with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 11 (2015) 206 | 1509.00672 |
| 8 | D. Curtin et al. | Exotic decays of the 125 GeV Higgs boson | PRD 90 (2014) 075004 | 1312.4992 |
| 9 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Combined measurement of the Higgs boson mass in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 and 8 TeV with the ATLAS and CMS experiments | PRL 114 (2015) 191803 | 1503.07589 |
| 10 | M. E. Peskin | Comparison of LHC and ILC capabilities for Higgs boson coupling measurements | 1207.2516 | |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Projected performance of an upgraded CMS detector at the LHC and HL-LHC: contribution to the Snowmass process | 1307.7135 | |
| 12 | ATLAS Collaboration | Physics at a high-luminosity LHC with ATLAS | 1307.7292 | |
| 13 | R. Dermisek and J. F. Gunion | Escaping the large fine tuning and little hierarchy problems in the next to minimal supersymmetric model and $ h \rightarrow aa $ decays | PRL 95 (2005) 041801 | hep-ph/0502105 |
| 14 | R. Dermisek and J. F. Gunion | The NMSSM close to the R-symmetry limit and naturalness in $ h \rightarrow aa $ decays for $ m_a < 2 m_b $ | PRD 75 (2007) 075019 | hep-ph/0611142 |
| 15 | S. Chang, R. Dermisek, J. F. Gunion, and N. Weiner | Nonstandard Higgs boson decays | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 58 (2008) 75 | 0801.4554 |
| 16 | C. Englert, T. Plehn, D. Zerwas, and P. M. Zerwas | Exploring the Higgs portal | PLB 703 (2011) 298 | 1106.3097 |
| 17 | T. D. Lee | A theory of spontaneous T violation | PRD 8 (1973) 1226 | |
| 18 | N. G. Deshpande and E. Ma | Pattern of symmetry breaking with two higgs doublets | PRD 18 (1978) 2574 | |
| 19 | N. G. Deshpande and E. Ma | The fermion mass scale and possible effects of higgs bosons on experimental observables | NPB 161 (1979) 493 | |
| 20 | J. F. Gunion, H. E. Haber, G. L. Kane, and S. Dawson | The Higgs hunter's guide | volume 80 of Frontiers in Physics Perseus Books | |
| 21 | G. C. Branco et al. | Theory and phenomenology of two-Higgs-doublet models | Phys. Rep. 516 (2012) 1 | 1106.0034 |
| 22 | P. Fayet | Supergauge invariant extension of the Higgs mechanism and a model for the electron and its neutrino | NPB 90 (1975) 104 | |
| 23 | P. Fayet | Spontaneously broken supersymmetric theories of weak, electromagnetic and strong interactions | PLB 69 (1977) 489 | |
| 24 | J. E. Kim and H. P. Nilles | The $ \mu $-problem and the strong CP-problem | PLB 138 (1984) 150 | |
| 25 | U. Ellwanger, C. Hugonie, and A. M. Teixeira | The next-to-minimal supersymmetric standard model | Phys. Rep. 496 (2010) 1 | 0910.1785 |
| 26 | J. Bernon, J. F. Gunion, Y. Jiang, and S. Kraml | Light Higgs bosons in two-Higgs-doublet models | PRD 91 (2015) 075019 | 1412.3385 |
| 27 | R. D. Peccei and H. R. Quinn | CP conservation in the presence of instantons | PRL 38 (1977) 1440 | |
| 28 | R. D. Peccei and H. R. Quinn | Constraints imposed by CP conservation in the presence of instantons | PRD 16 (1977) 1791 | |
| 29 | P. Fayet | Supersymmetry and weak, electromagnetic and strong interactions | PLB 64 (1976) 159 | |
| 30 | S. Heinemeyer, O. Stal, and G. Weiglein | Interpreting the LHC Higgs search results in the MSSM | PLB 710 (2012) 201 | 1112.3026 |
| 31 | A. Celis, V. Ilisie, and A. Pich | LHC constraints on two-Higgs doublet models | JHEP 07 (2013) 053 | 1302.4022 |
| 32 | B. Grinstein and P. Uttayarat | Carving out parameter space in type-II two Higgs doublets model | JHEP 06 (2013) 094 | 1304.0028 |
| 33 | B. Coleppa, F. Kling, and S. Su | Constraining type-II 2HDM in light of LHC Higgs searches | JHEP 01 (2014) 161 | 1305.0002 |
| 34 | C.-Y. Chen, S. Dawson, and M. Sher | Heavy Higgs searches and constraints on two Higgs doublet models | PRD 88 (2013) 015018 | 1305.1624 |
| 35 | N. Craig, J. Galloway, and S. Thomas | Searching for signs of the second Higgs doublet | 1305.2424 | |
| 36 | L. Wang and X.-F. Han | Status of the aligned two-Higgs-doublet model confronted with the Higgs data | JHEP 04 (2014) 128 | 1312.4759 |
| 37 | J. Baglio, O. Eberhardt, U. Nierste, and M. Wiebusch | Benchmarks for Higgs pair production and heavy Higgs searches in the two-Higgs-doublet model of type II | PRD 90 (2014) 015008 | 1403.1264 |
| 38 | B. Dumont, J. F. Gunion, Y. Jiang, and S. Kraml | Constraints on and future prospects for two-Higgs-doublet models in light of the LHC Higgs signal | PRD 90 (2015) 035021 | 1405.3584 |
| 39 | S. F. King, M. Muehlleitner, R. Nevzorov, and K. Walz | Natural NMSSM Higgs bosons | NPB 870 (2013) 323 | 1211.5074 |
| 40 | J. Cao et al. | A light Higgs scalar in the NMSSM confronted with the latest LHC Higgs data | JHEP 11 (2013) 018 | 1309.4939 |
| 41 | N. D. Christensen, T. Han, Z. Liu, and S. Su | Low-mass Higgs bosons in the NMSSM and their LHC implications | JHEP 08 (2013) 019 | 1303.2113 |
| 42 | D. G. Cerdeno, P. Ghosh, and C. B. Park | Probing the two light Higgs scenario in the NMSSM with a low-mass pseudoscalar | JHEP 06 (2013) 031 | 1301.1325 |
| 43 | G. Chalons and F. Domingo | Analysis of the Higgs potentials for two doublets and a singlet | PRD 86 (2012) 115024 | 1209.6235 |
| 44 | A. Ahriche, A. Arhrib, and S. Nasri | Higgs phenomenology in the two-singlet model | JHEP 02 (2014) 042 | 1309.5615 |
| 45 | J. Bernon et al. | Scrutinizing the alignment limit in two-Higgs-doublet models: $ m_\textrm{h} = $ 125 GeV | PRD 92 (2015) 075004 | 1507.00933 |
| 46 | A. Djouadi | The anatomy of electro-weak symmetry breaking. I: the Higgs boson in the standard model | Phys. Rep. 457 (2008) 1 | hep-ph/0503172 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | A search for pair production of new light bosons decaying into muons | PLB 752 (2016) 146 | CMS-HIG-13-010 1506.00424 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a very light NMSSM Higgs boson produced in decays of the 125 GeV scalar boson and decaying into tau leptons in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JHEP 01 (2016) 079 | CMS-HIG-14-019 1510.06534 |
| 49 | D0 Collaboration | Search for NMSSM Higgs bosons in the $ h \rightarrow aa \rightarrow \mu\mu\mu\mu $, $ \mu\mu\tau\tau $ channels using $ p \bar{p} $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 1.96 TeV | PRL 103 (2009) 061801 | 0905.3381 |
| 50 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for Higgs bosons decaying to $ aa $ in the $ \mu\mu\tau\tau $ final state in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS experiment | PRD 92 (2015) 052002 | 1505.01609 |
| 51 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a light pseudoscalar Higgs boson in the dimuon decay channel in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | PRL 109 (2012) 121801 | CMS-HIG-12-004 1206.6326 |
| 52 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a low-mass pseudoscalar Higgs boson produced in association with a $ \mathrm{b\bar{b}} $ pair in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | PLB 758 (2016) 296 | CMS-HIG-14-033 1511.03610 |
| 53 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 54 | J. Alwall et al. | MadGraph 5: going beyond | JHEP 06 (2011) 128 | 1106.0522 |
| 55 | T. Sjostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Z. Skands | PYTHIA 6.4 physics and manual | JHEP 05 (2006) 026 | hep-ph/0603175 |
| 56 | Z. W\cas | TAUOLA the library for $ \tau $ lepton decay, and KKMC/KORALB/KORALZ/... status report | NPPS 98 (2001) 96 | hep-ph/0011305 |
| 57 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | NLO single-top production matched with shower in POWHEG: $ s $- and $ t $-channel contributions | JHEP 09 (2009) 111 | 0907.4076 |
| 58 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 59 | E. Re | Single-top $ Wt $-channel production matched with parton showers using the POWHEG method | EPJC 71 (2011) 1547 | 1009.2450 |
| 60 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 61 | J. Pumplin et al. | New generation of parton distributions with uncertainties from global QCD analysis | JHEP 07 (2002) 012 | hep-ph/0201195 |
| 62 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4---a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 63 | GEANT4 Collaboration | Geant4 developments and applications | IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53 (2006) 270 | |
| 64 | CMS Collaboration | Particle--flow event reconstruction in CMS and performance for jets, taus, and $ E_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{miss}} $ | CMS-PAS-PFT-09-001 | |
| 65 | CMS Collaboration | Commissioning of the particle--flow event reconstruction with the first LHC collisions recorded in the CMS detector | CDS | |
| 66 | K. Rose | Deterministic annealing for clustering, compression, classification, regression and related optimisation problems | Proceedings of the IEEE 86 (1998) 2210 | |
| 67 | W. Waltenberger, R. Fruhwirth, and P. Vanlaer | Adaptive vertex fitting | JPG 34 (2007) N343 | |
| 68 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of CMS muon reconstruction in pp collision events at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JINST 7 (2012) P10002 | CMS-MUO-10-004 1206.4071 |
| 69 | H. Voss, A. Hocker, J. Stelzer, and F. Tegenfeldt | TMVA, the toolkit for multivariate data analysis with ROOT | in XIth International Workshop on Advanced Computing and Analysis Techniques in Physics Research (ACAT), p. 40 2007 | physics/0703039 |
| 70 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of electron reconstruction and selection with the CMS detector in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P06005 | CMS-EGM-13-001 1502.02701 |
| 71 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_t $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 72 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 73 | M. Cacciari and G. P. Salam | Dispelling the $ N^{3} $ myth for the $ k_t $ jet-finder | PLB 641 (2006) 57 | hep-ph/0512210 |
| 74 | CMS Collaboration | Determination of jet energy calibration and transverse momentum resolution in CMS | JINST 6 (2011) P11002 | CMS-JME-10-011 1107.4277 |
| 75 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of b-quark jets with the CMS experiment | JINST 8 (2013) P04013 | CMS-BTV-12-001 1211.4462 |
| 76 | CMS Collaboration | Reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ lepton decays to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ at CMS | JINST 11 (2016) P01019 | CMS-TAU-14-001 1510.07488 |
| 77 | CMS Collaboration | Missing transverse energy performance of the CMS detector | JINST 6 (2011) P09001 | CMS-JME-10-009 1106.5048 |
| 78 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of MET reconstruction in CMS | J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 587 (2015) 012006 | |
| 79 | P. M. Ferreira, J. F. Gunion, H. E. Haber, and R. Santos | Probing wrong-sign Yukawa couplings at the LHC and a future linear collider | PRD 89 (2014) 115003 | 1403.4736 |
| 80 | D. Curtin, R. Essig, and Y.-M. Zhong | Uncovering light scalars with exotic Higgs decays to $ b\overline{b}{\mu}^{+}{\mu}^{-} $ | JHEP 06 (2015) 025 | 1412.4779 |
| 81 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 1. Inclusive observables | 1101.0593 | |
| 82 | NIST | ``NIST Digital library of mathematical functions'' | Release 1.0.12 of 2016-09-09 | |
| 83 | M. J. Oreglia | A study of the reactions $\psi' \to \gamma\gamma \psi$ | PhD thesis, Stanford University, 1980 SLAC Report SLAC-R-236, see Appendix D | |
| 84 | P. D. Dauncey, M. Kenzie, N. Wardle, and G. J. Davies | Handling uncertainties in background shapes: the discrete profiling method | JINST 10 (2015) P04015 | 1408.6865 |
| 85 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of the diphoton decay of the Higgs boson and measurement of its properties | EPJC 74 (2014) 3076 | CMS-HIG-13-001 1407.0558 |
| 86 | L. Bianchini, J. Conway, E. K. Friis, and C. Veelken | Reconstruction of the Higgs mass in H$ \to \tau\tau $ events by dynamical likelihood techniques | J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 513 (2014) 022035 | |
| 87 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Vector boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2011) 018 | 1105.0020 |
| 88 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of inclusive W and Z cross sections in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2011) 080 | CMS-EWK-10-002 1012.2466 |
| 89 | S. Alekhin et al. | The PDF4LHC Working Group interim report | 1101.0536 | |
| 90 | M. Botje et al. | The PDF4LHC Working Group interim recommendations | 1101.0538 | |
| 91 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the inelastic proton-proton cross section at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | PLB 722 (2013) 5 | CMS-FWD-11-001 1210.6718 |
| 92 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 3. Higgs properties | 1307.1347 | |
| 93 | LHC Higgs Combination Group | Procedure for the LHC Higgs boson search combination in Summer 2011 | CMS-NOTE-2011-005 | |
| 94 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 95 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIMA 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 96 | A. L. Read | Modified frequentist analysis of search results (the $ {CL}_s $ method) | CERN-OPEN-2000-005, CERN | |
| 97 | E. Gross and O. Vitells | Trial factors or the look elsewhere effect in high energy physics | EPJC 70 (2010) 525 | 1005.1891 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|