

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-BTV-12-001 ; CERN-PH-EP-2012-262 | ||
| Identification of b-quark jets with the CMS experiment | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 19 November 2012 | ||
| J. Instrum. 8 (2013) P04013 | ||
| Abstract: At the Large Hadron Collider, the identification of jets originating from b quarks is important for searches for new physics and for measurements of standard model processes. A variety of algorithms has been developed by CMS to select b-quark jets based on variables such as the impact parameters of charged-particle tracks, the properties of reconstructed decay vertices, and the presence or absence of a lepton, or combinations thereof. The performance of these algorithms has been measured using data from proton-proton collisions at the LHC and compared with expectations based on simulation. The data used in this study were recorded in 2011 at $\sqrt{s}$ = 7 TeV for a total integrated luminosity of 5.0 inverse femtobarns. The efficiency for tagging b-quark jets has been measured in events from multijet and t-quark pair production. CMS has achieved a b-jet tagging efficiency of 85% for a light-parton misidentification probability of 10%. For analyses requiring higher purity, a misidentification probability of only 1.5% has been achieved, for a 70% b-jet tagging efficiency. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:1211.4462 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
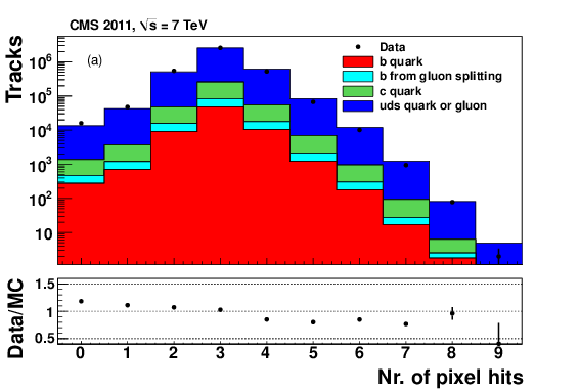
png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
|
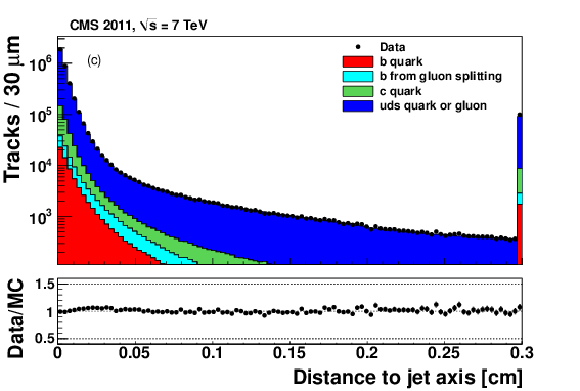
png pdf |
Figure 1-c:
|
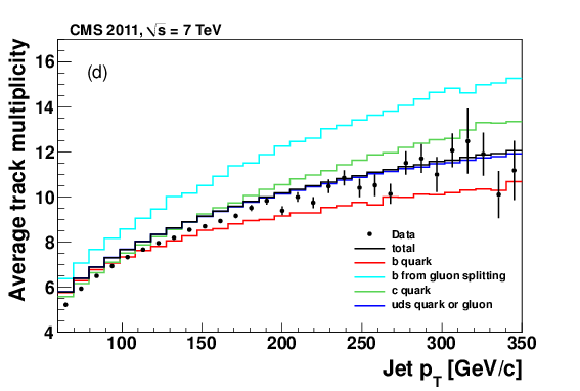
png pdf |
Figure 1-d:
|
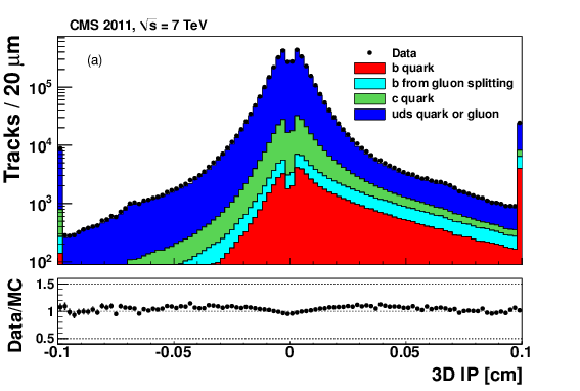
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
|
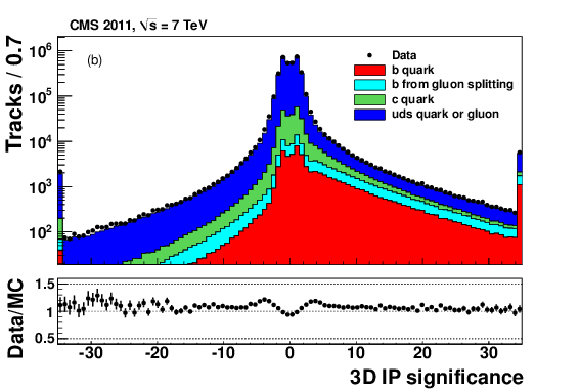
png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
|
png pdf |
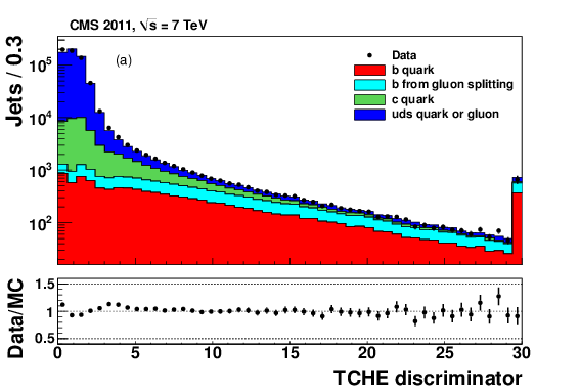
Figure 3-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
|
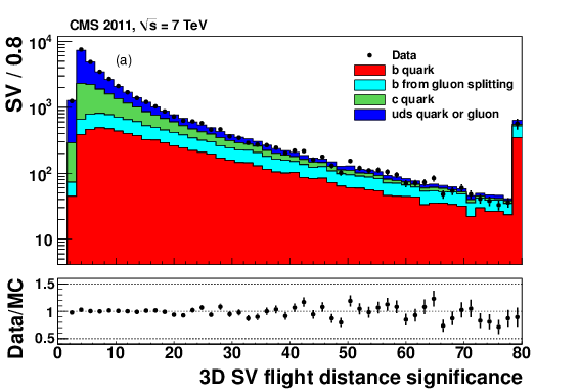
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
|
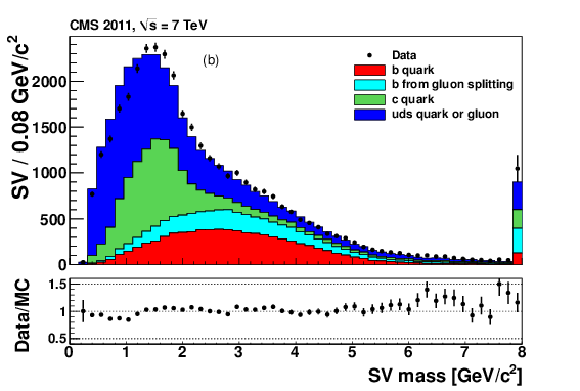
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
|

png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
|
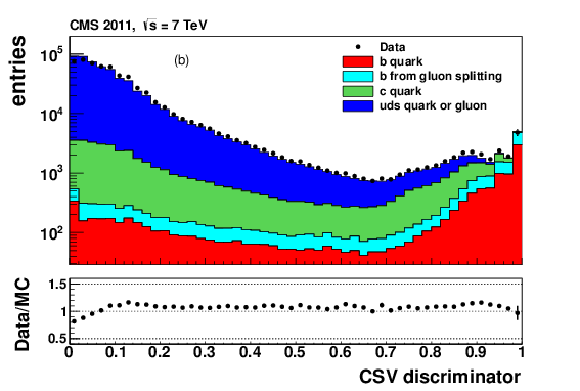
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
|
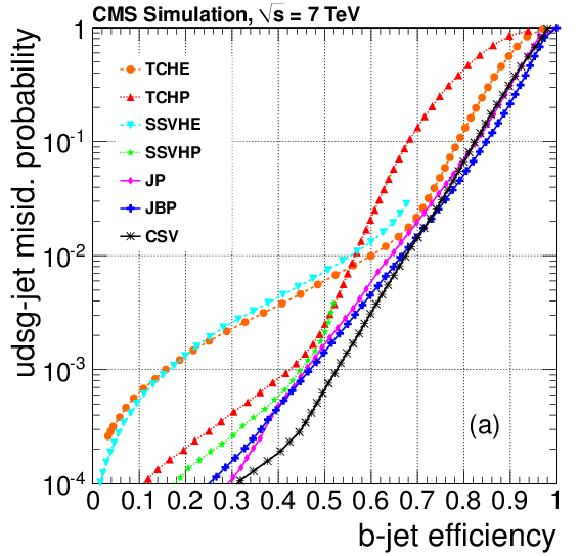
png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
|
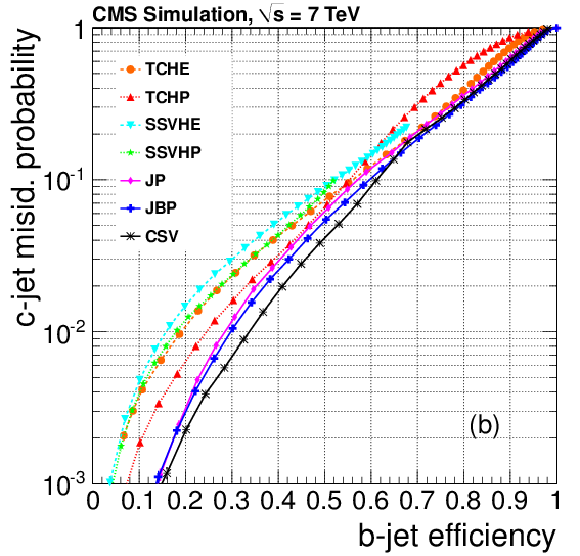
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
|
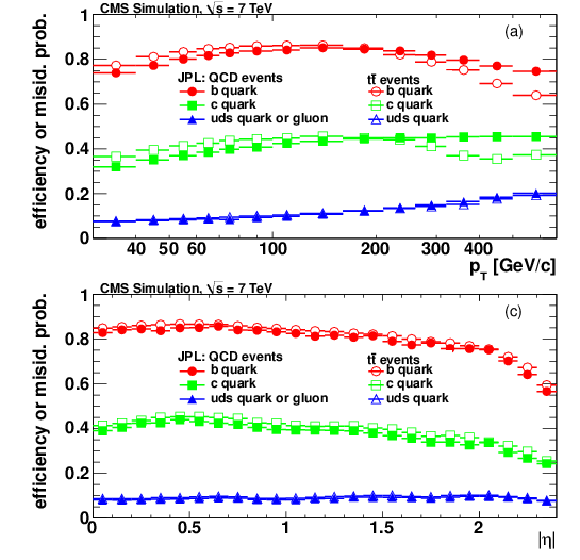
png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
|
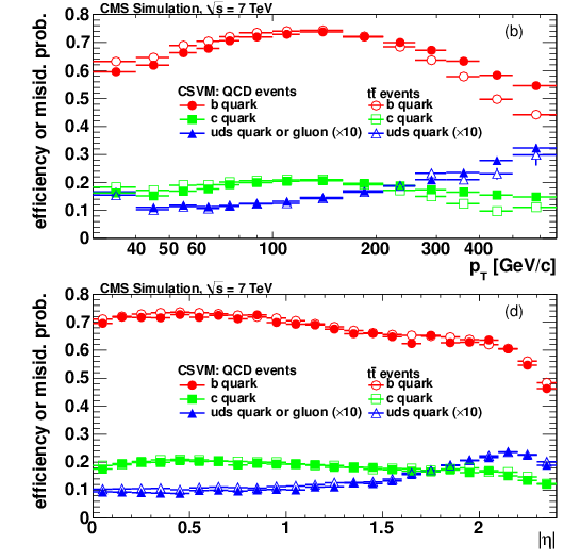
png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
|
png pdf |
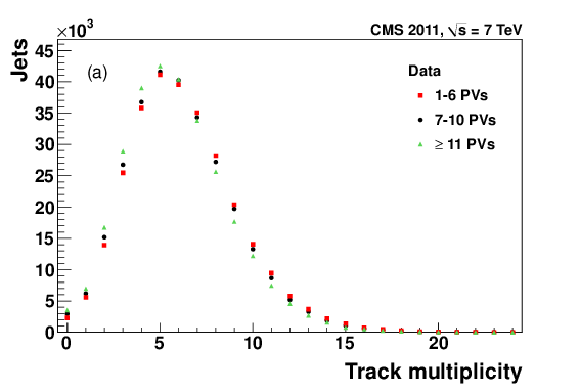
Figure 8-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 8-b:
|
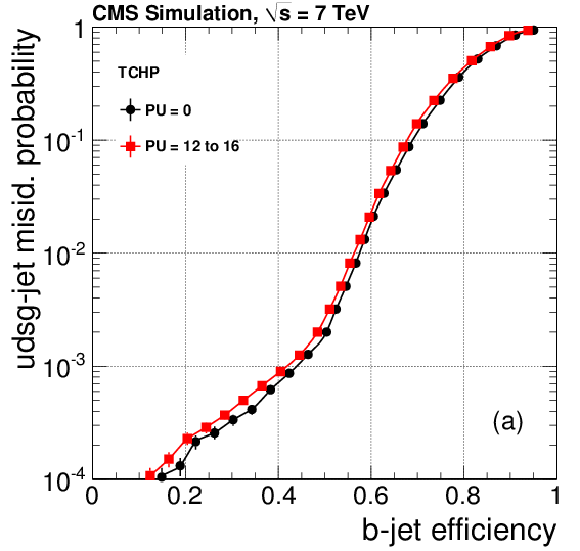
png pdf |
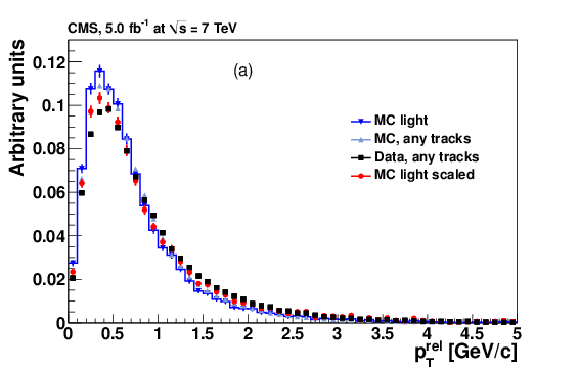
Figure 9-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 9-b:
|
png pdf |
Figure 10-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 10-b:
|
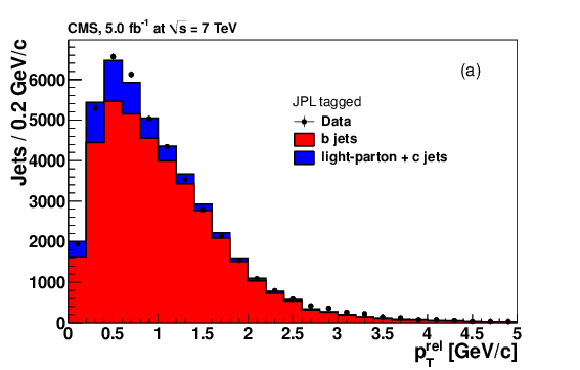
png pdf |
Figure 11-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 11-b:
|
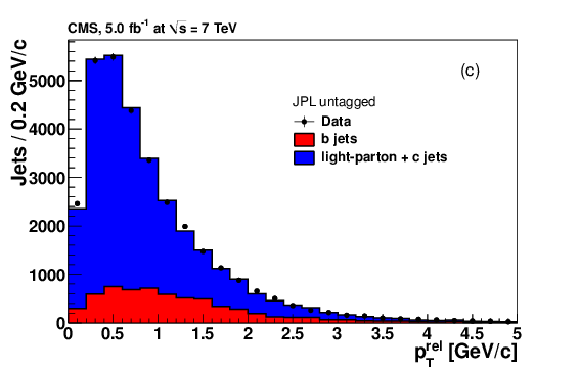
png pdf |
Figure 11-c:
|

png pdf |
Figure 11-d:
|
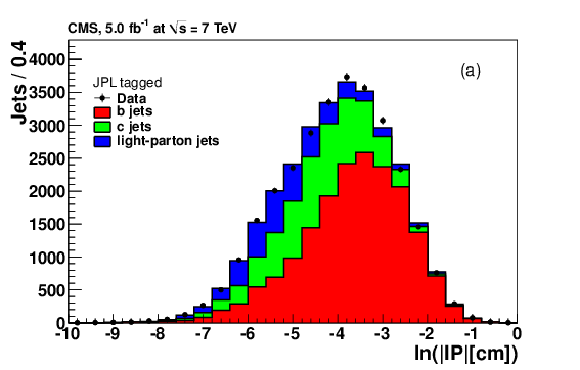
png pdf |
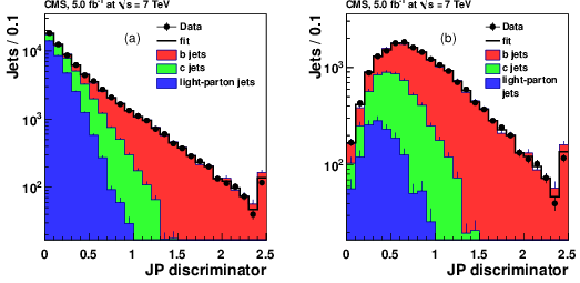
Figure 12-a:
|
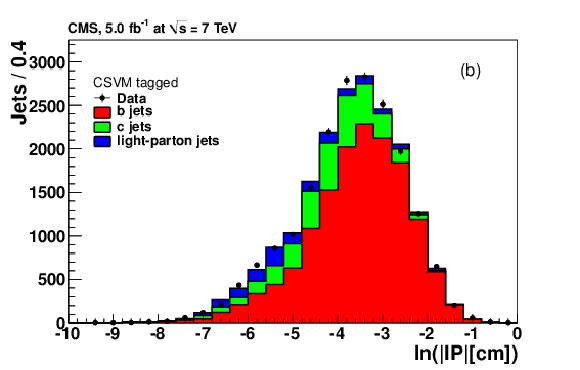
png pdf |
Figure 12-b:
|
png pdf |
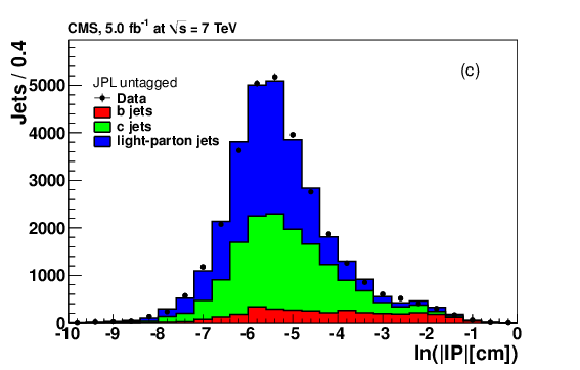
Figure 12-c:
|
png pdf |
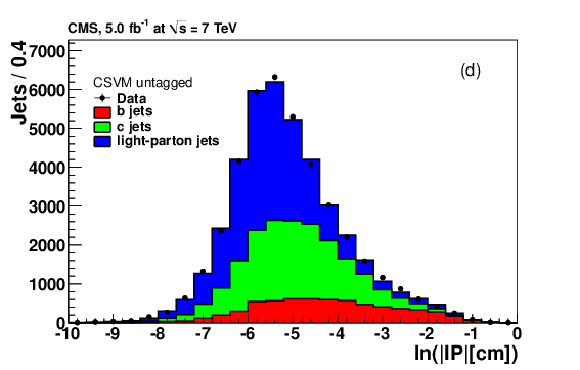
Figure 12-d:
|
png pdf |
Figure 13-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 13-b:
|
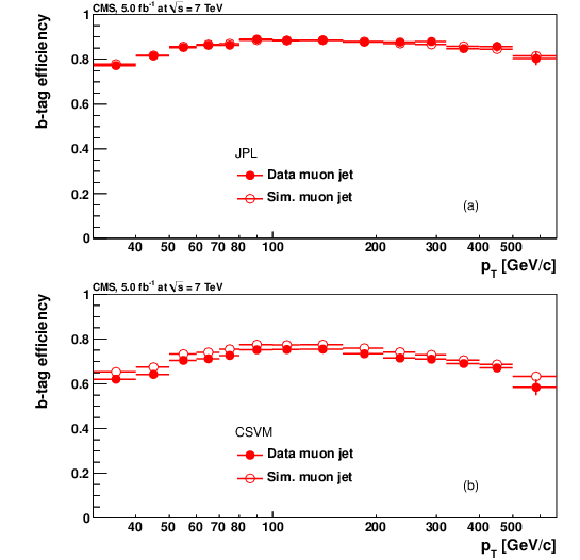
png pdf |
Figure 14:
|
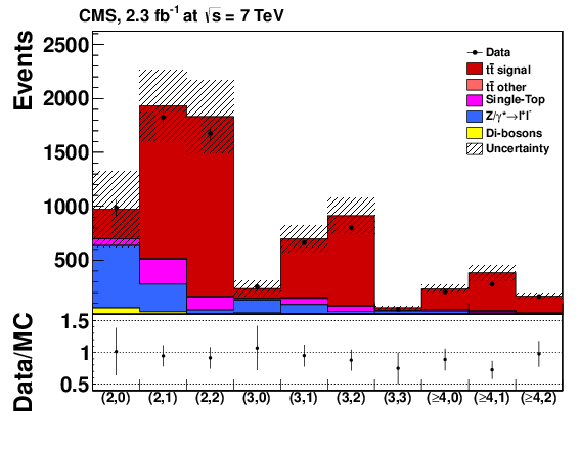
png pdf |
Figure 15:
|
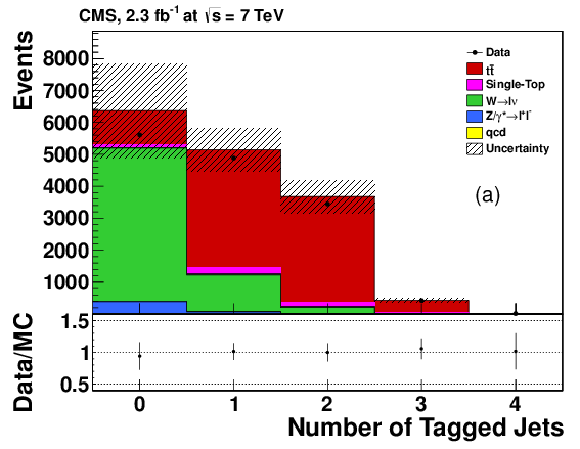
png pdf |
Figure 16-a:
|

png pdf |
Figure 16-b:
|
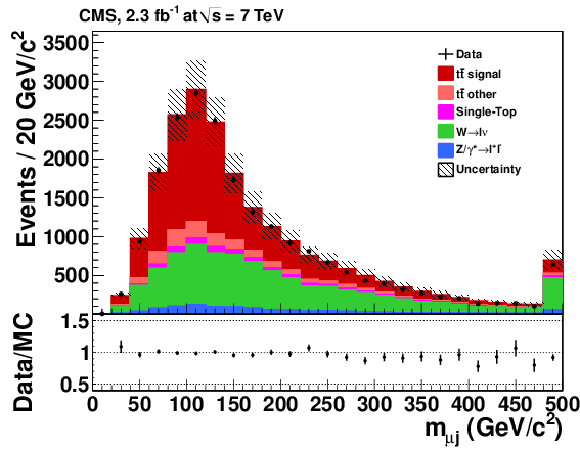
png pdf |
Figure 17:
|
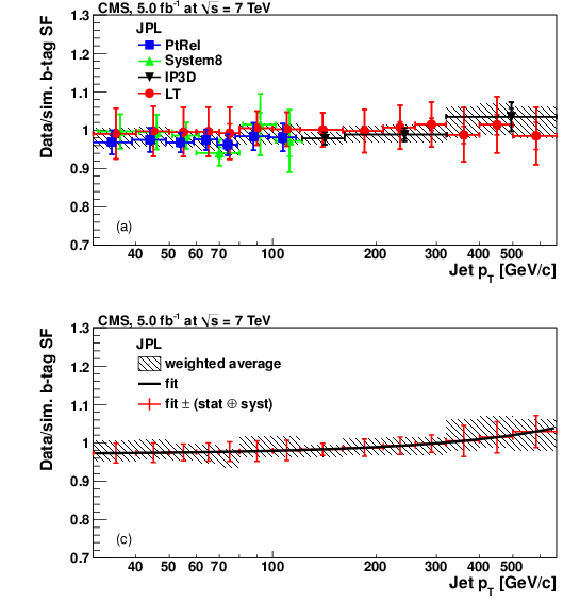
png pdf |
Figure 18-a:
|
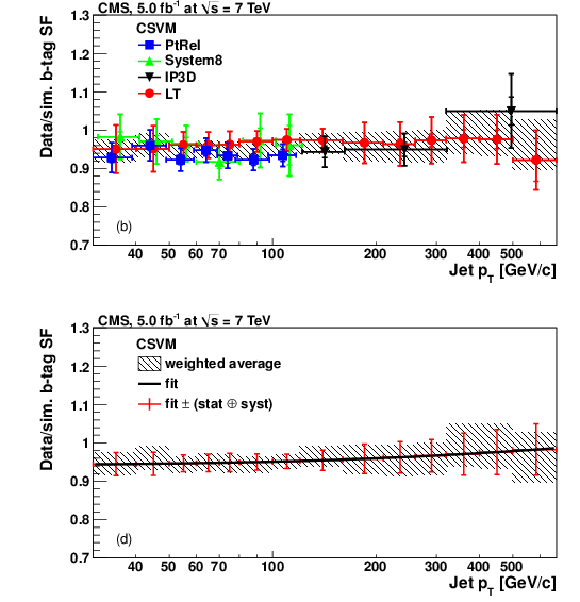
png pdf |
Figure 18-b:
|

png pdf |
Figure 19-a:
|
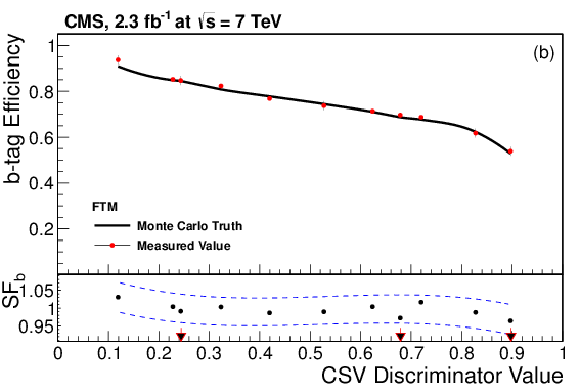
png pdf |
Figure 19-b:
|

png pdf |
Figure 19-c:
|
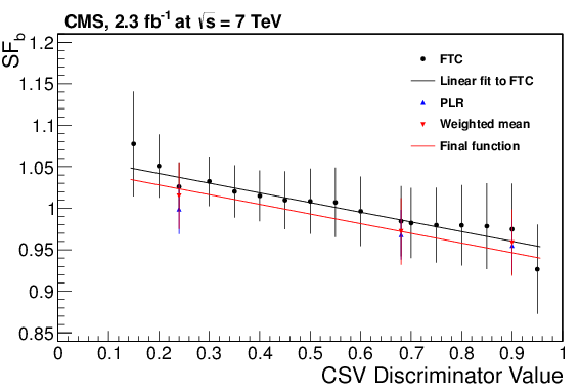
png pdf |
Figure 20:
|

png pdf |
Figure 21-a:
|
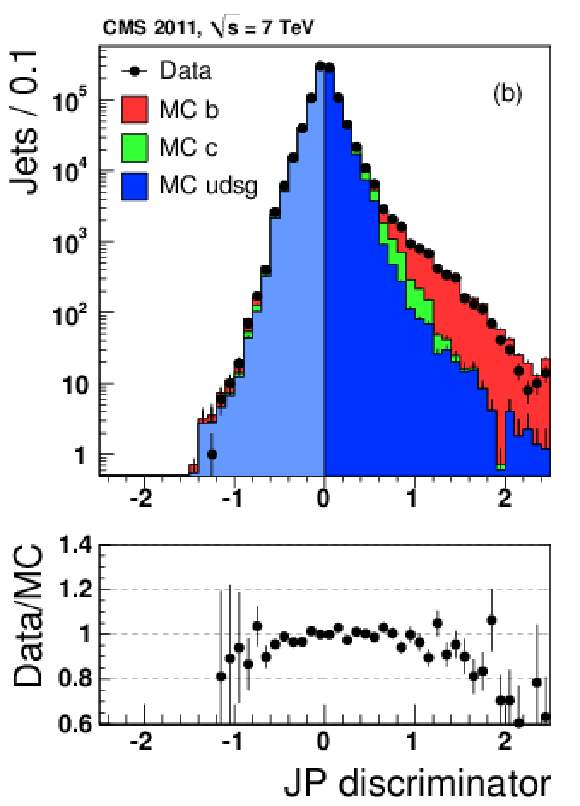
png pdf |
Figure 21-b:
|

png pdf |
Figure 21-c:
|
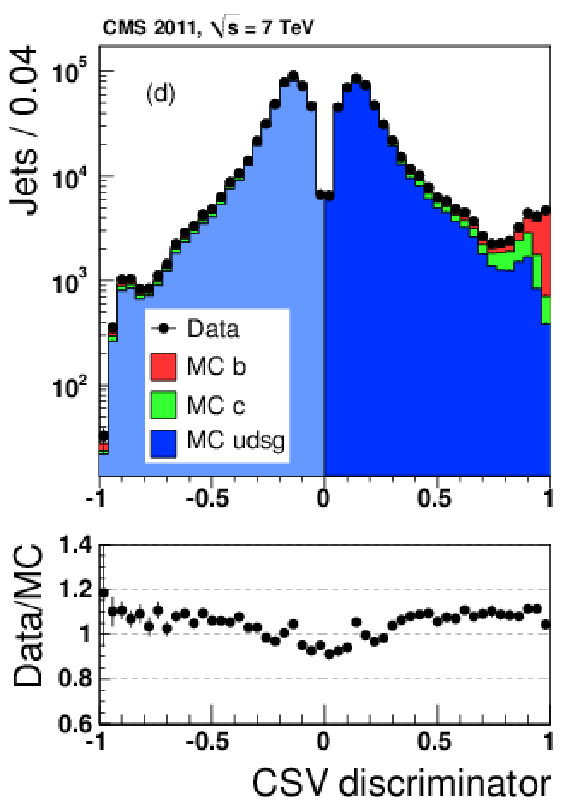
png pdf |
Figure 21-d:
|
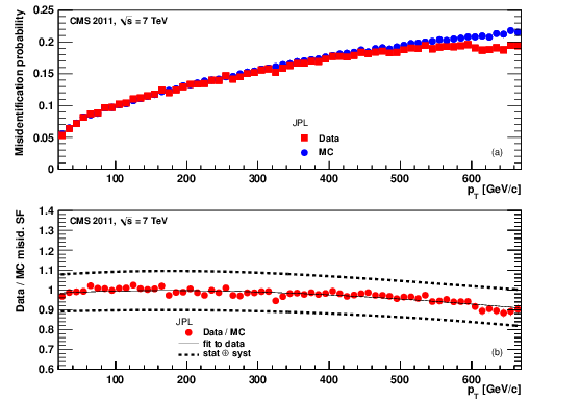
png pdf |
Figure 22:
|
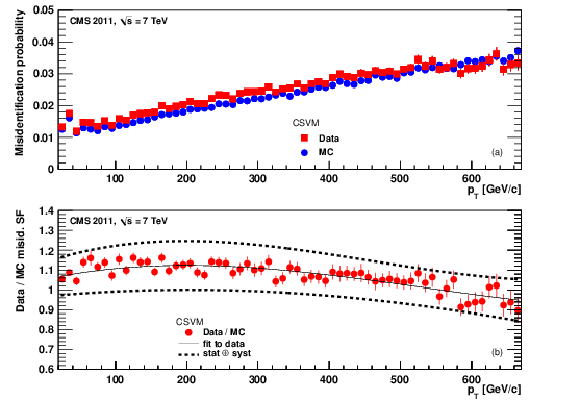
png pdf |
Figure 23:
|

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|