

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-EXO-24-030 | ||
| Search for soft unclustered energy patterns in association with a W boson in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 27 March 2025 | ||
| Abstract: A search for soft unclustered energy patterns (SUEPs) produced in association with a W boson is presented. The analysis is based on proton-proton collision data corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $, collected between 2016 and 2018 with the CMS detector at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV. Final states containing a W boson candidate and a high multiplicity of soft tracks are explored for the first time. Upper limits are set on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures & Tables | Summary | Additional Figures | References | CMS Publications |
|---|
| Figures | |
png pdf |
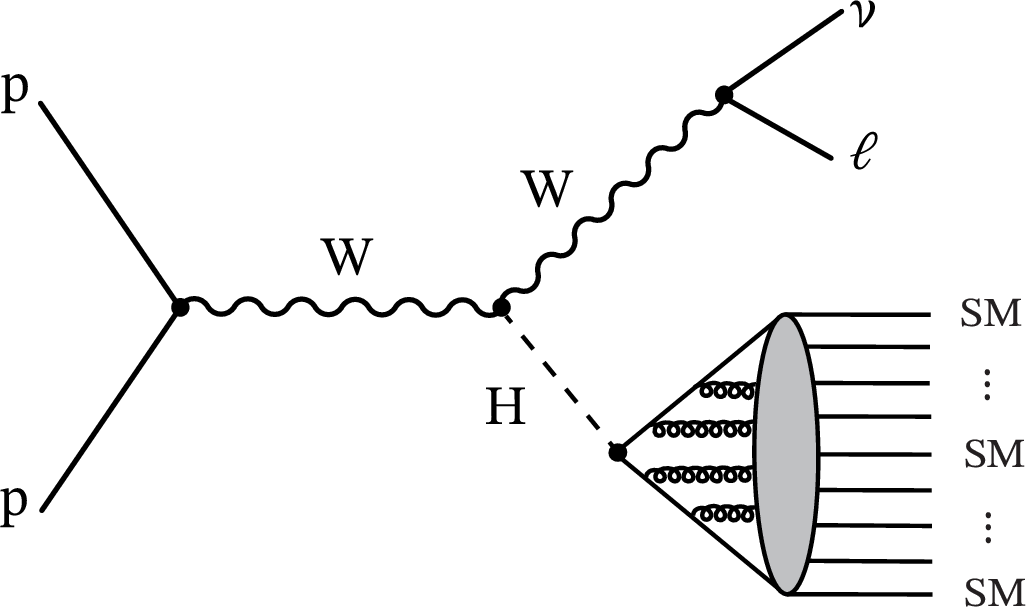
Figure 1:
A schematic Feynman diagram of a Higgs boson decaying to a SUEP shower, produced in association with a leptonically decaying W boson. |
png pdf |
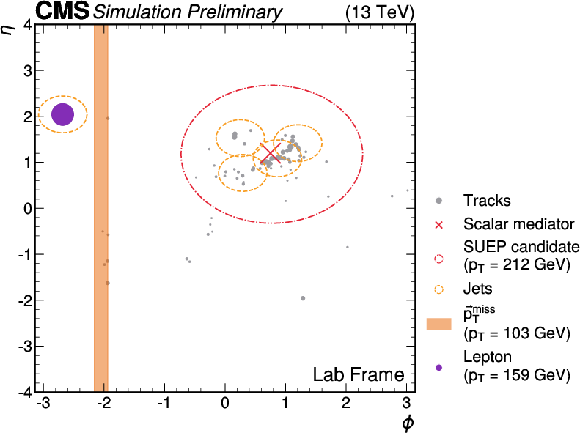
Figure 2:
Display of a representative simulated signal event ($ m_{\phi}=T_{\text{D}}= $ 2 GeV, $ m_{\mathrm{A}'}= $ 1 GeV) in the lab frame as a function of pseudorapidity $ \eta $ and azimuthal angle $ \phi $, showing the Higgs boson decaying to a SUEP shower, which is reconstructed as a cluster of charged tracks recoiling against a W boson and $ p_{\mathrm{T}}^\text{miss} $. The size of each dot is scaled based on the $ p_{\mathrm{T}} $ of the corresponding track. |
png pdf |
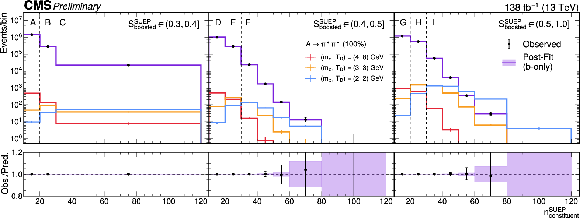
Figure 3:
The observed and fitted distributions of the number of constituents in the SUEP candidate in all regions of the SR, and the distributions from several representative signal hypotheses. |
png pdf |
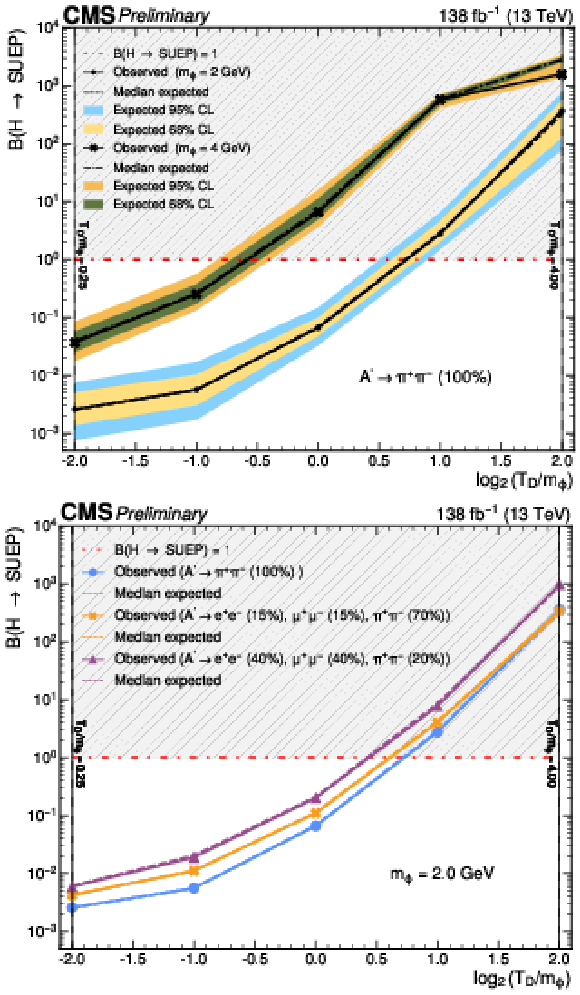
Figure 4:
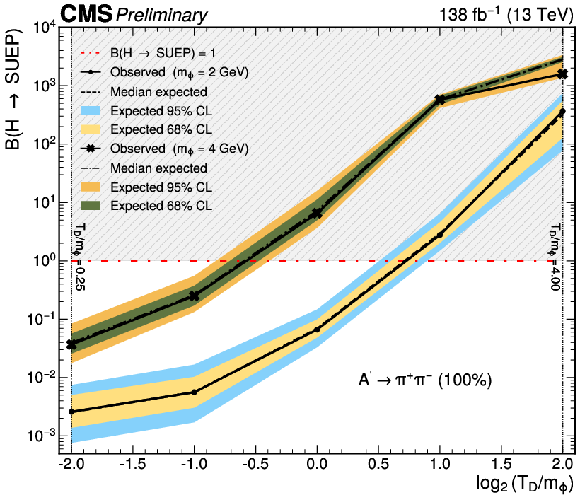
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP for several different signal models are shown as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $. Upper: two representative $ m_{\phi} $ values, 2 and 4 GeV, with fully hadronic A' decays ($ \mathrm{A}' \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%) are shown. Lower: comparison of the limits for the three different final-state flavor compositions considered in this search, which correspond to the different values of $ m_{\mathrm{A}'} $, for $ m_{\phi} = $ 2 GeV. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP for several different signal models are shown as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $. Upper: two representative $ m_{\phi} $ values, 2 and 4 GeV, with fully hadronic A' decays ($ \mathrm{A}' \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%) are shown. Lower: comparison of the limits for the three different final-state flavor compositions considered in this search, which correspond to the different values of $ m_{\mathrm{A}'} $, for $ m_{\phi} = $ 2 GeV. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |

png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP for several different signal models are shown as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $. Upper: two representative $ m_{\phi} $ values, 2 and 4 GeV, with fully hadronic A' decays ($ \mathrm{A}' \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%) are shown. Lower: comparison of the limits for the three different final-state flavor compositions considered in this search, which correspond to the different values of $ m_{\mathrm{A}'} $, for $ m_{\phi} = $ 2 GeV. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |
png pdf |
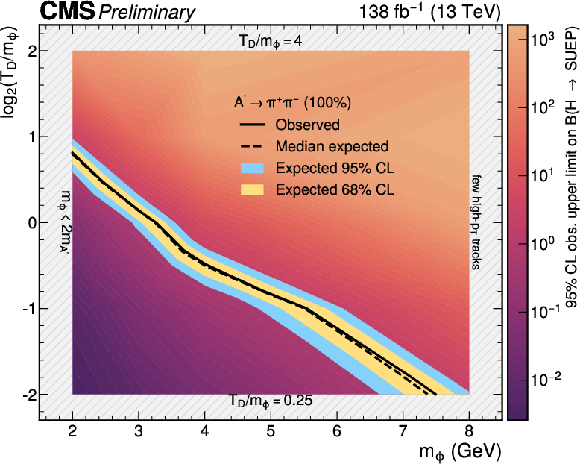
Figure 5:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching ratio for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP are shown as a function of $ m_{\phi} $ and $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $, with $ m_{\mathrm{A}'}= $ 1.0 GeV ($ \mathrm{A}' \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B}=$ 100%). The values between explicitly simulated signal models are determined via logarithmic interpolation. The contour at which the observed (median expected) upper limit on the branching fraction equals unity is shown as a solid (dotted) black line. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
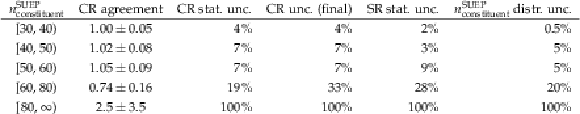
Table 1:
For each bin in the SER, the prediction-observation agreement in the CR is shown, along with the nominal statistical uncertainty in the CR prediction, the final uncertainty accounting for the slightly larger disagreement in the fourth bin, the statistical uncertainty in the SR, and the final value of the uncertainty in the $ n_{\text{constituent}}^{\text{SUEP}} $ distribution. |
| Summary |
| In summary, this note presents the first search for soft unclustered energy patterns (SUEPs) produced in association with a W boson. Data corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $ are used, collected with triggers requiring a single muon or electron and reconstructed with the full offline processing. This strategy preferentially selects events with a W boson recoiling against a SUEP candidate cluster of many low-momentum, isotropically-distributed charged particles. The number of tracks and the associated sphericity of the SUEP candidate are used to discriminate between the signal and the background from standard model processes, whose contributions are estimated from data. Limits are placed on the most SUEP-like hidden valley scenarios with highly isotropic dark showers arising from a 125 GeV Higgs boson and producing a large multiplicity of tracks. |
| Additional Figures | |
png pdf |
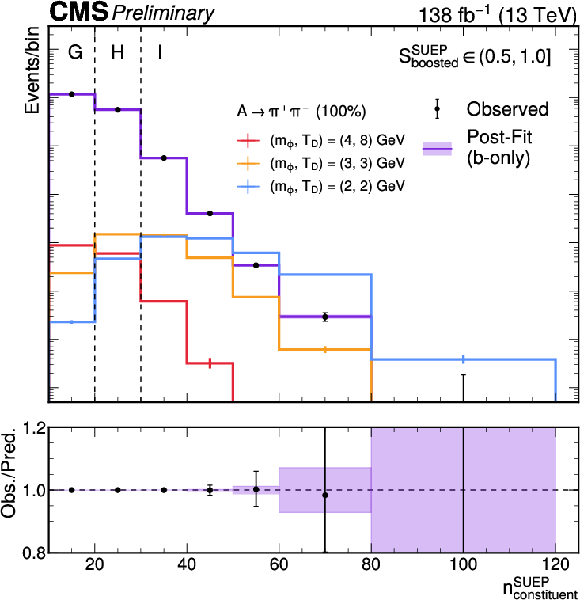
Additional Figure 1:
The observed and fitted distributions of the number of constituents in the SUEP candidate in regions G, H, and I of the SR, and the distributions from several representative signal hypotheses. |
png pdf |
Additional Figure 2:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching ratio for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP as a function of $ m_{\phi} $ and $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $, with $ m_{\text{A}^{\prime}} = $ 0.5 GeV ($ \text{A}^{\prime} \to \mathrm{e}^+\mathrm{e}^-, \mu^{+}\mu^{-}, \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 40, 40, 20%). The values between explicitly simulated signal models are determined via logarithmic interpolation. The contour at which the observed (median expected) upper limit on the branching fraction equals unity is shown as a solid (dotted) black line. |
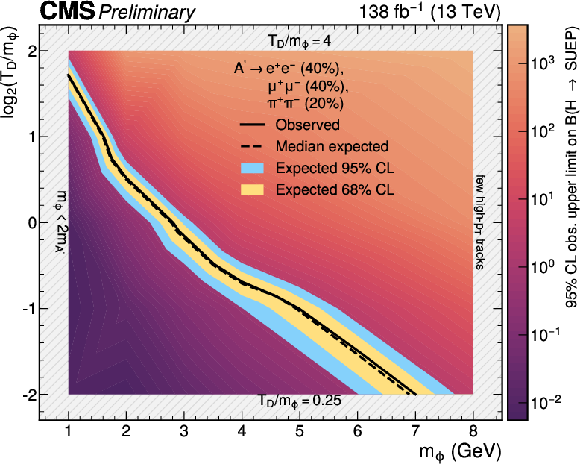
png pdf |
Additional Figure 3:
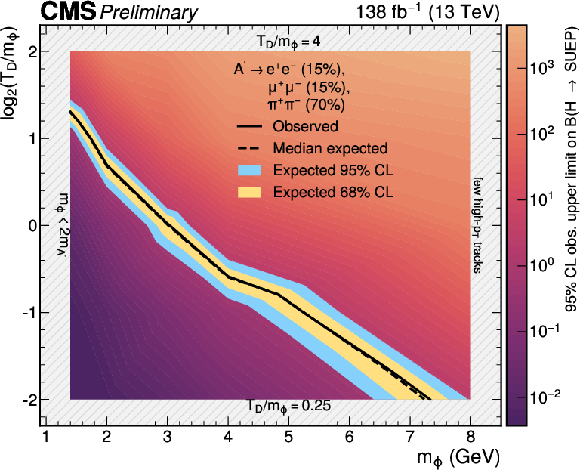
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching ratio for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP as a function of $ m_{\phi} $ and $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $, with $ m_{\text{A}^{\prime}} = $ 0.7 GeV ($ \text{A}^{\prime} \to \mathrm{e}^+\mathrm{e}^-, \mu^{+}\mu^{-},\pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 15,15, 70%). The values between explicitly simulated signal models are determined via logarithmic interpolation. The contour at which the observed (median expected) upper limit on the branching fraction equals unity is shown as a solid (dotted) black line. |
png pdf |
Additional Figure 4:
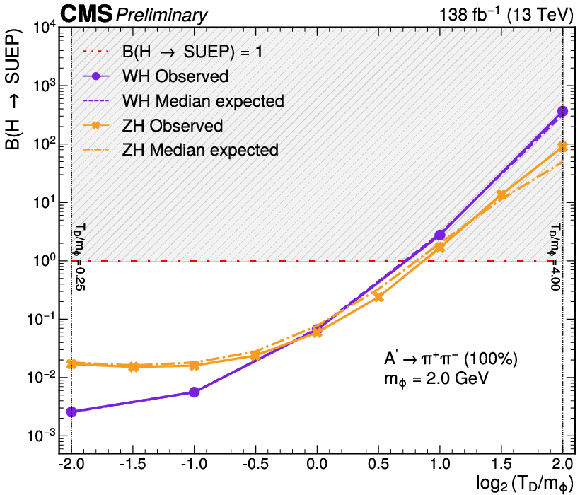
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP when produced in associated with a W boson (this search) and a Z boson (CMS-PAS-EXO-23-003) as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $ for a representative model with $ m_{\phi} = $ 2 GeV and $ \text{A}^{\prime} \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |
png pdf |
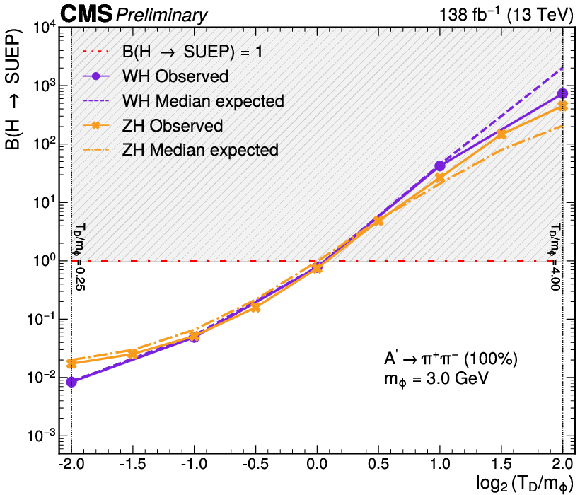
Additional Figure 5:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP when produced in associated with a W boson (this search) and a Z boson (CMS-PAS-EXO-23-003) as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $ for a representative model with $ m_{\phi} = $ 3 GeV and $ \text{A}^{\prime} \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |
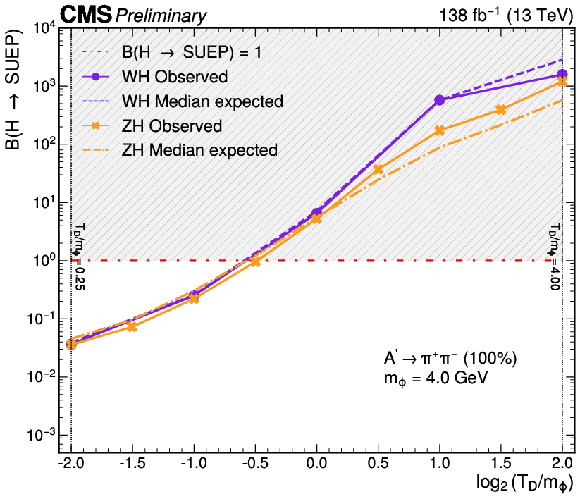
png pdf |
Additional Figure 6:
The 95% CL exclusion limits on the branching fraction for the Higgs boson decay to a SUEP when produced in associated with a W boson (this search) and a Z boson (CMS-PAS-EXO-23-003) as a function of $ \log_{2} (T_{\text{D}}/m_{\phi}) $ for a representative model with $ m_{\phi} = $ 4 GeV and $ \text{A}^{\prime} \to \pi^{+}\pi^{-} $ with $ \mathcal{B} = $ 100%. The horizontal dash-dotted lines represent a Higgs boson mediator with 100% branching fraction to a SUEP; above each line, the region with a branching fraction greater than unity is shaded to indicate it as physically forbidden. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | M. Cvetic, P. Langacker, and G. Shiu | Phenomenology of a three family standard like string model | PRD 66 (2002) 066004 | hep-ph/0205252 |
| 2 | Z. Chacko, H.-S. Goh, and R. Harnik | The twin Higgs: Natural electroweak breaking from mirror symmetry | PRL 96 (2006) 231802 | hep-ph/0506256 |
| 3 | M. J. Strassler and K. M. Zurek | Echoes of a hidden valley at hadron colliders | PLB 651 (2007) 374 | hep-ph/0604261 |
| 4 | T. Hur, D.-W. Jung, P. Ko, and J. Y. Lee | Electroweak symmetry breaking and cold dark matter from strongly interacting hidden sector | PLB 696 (2011) 262 | 0709.1218 |
| 5 | S. A. Abel et al. | Kinetic mixing of the photon with hidden U(1)s in string phenomenology | JHEP 07 (2008) 124 | 0803.1449 |
| 6 | Y. Bai and P. Schwaller | Scale of dark QCD | PRD 89 (2014) 063522 | 1306.4676 |
| 7 | M. J. Strassler | Why unparticle models with mass gaps are examples of hidden valleys | 0801.0629 | |
| 8 | S. Knapen, S. Pagan Griso, M. Papucci, and D. J. Robinson | Triggering soft bombs at the LHC | JHEP 08 (2017) 076 | 1612.00850 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Search for soft unclustered energy patterns in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | PRL 133 (2024) 191902 | CMS-EXO-23-002 2403.05311 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | Search for soft unclustered energy patterns in association with a Z boson in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2025 | CMS-PAS-EXO-23-003 |
| 11 | P. Schwaller, D. Stolarski, and A. Weiler | Emerging jets | JHEP 05 (2015) 059 | 1502.05409 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Search for dark QCD with emerging jets in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2024) 142 | CMS-EXO-22-015 2403.01556 |
| 13 | T. Cohen, M. Lisanti, and H. K. Lou | Semivisible jets: Dark matter undercover at the LHC | PRL 115 (2015) 171804 | 1503.00009 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonant production of strongly coupled dark matter in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | JHEP 06 (2022) 156 | CMS-EXO-19-020 2112.11125 |
| 15 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 16 | S. Knapen, J. Shelton, and D. Xu | Perturbative benchmark models for a dark shower search program | PRD 103 (2021) 115013 | 2103.01238 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 18 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | EPJC 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 19 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT 4---a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 20 | J. Barron et al. | Unsupervised hadronic SUEP at the LHC | JHEP 12 (2021) 129 | 2107.12379 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS high-level trigger during LHC run 2 | JINST 19 (2024) P11021 | CMS-TRG-19-001 2410.17038 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Technical proposal for the Phase-II upgrade of the Compact Muon Solenoid | CMS Technical Proposal CERN-LHCC-2015-010, CMS-TDR-15-02, 2015 CDS |
|
| 30 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_{\mathrm{T}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 31 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 34 | D. Bertolini, P. Harris, M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup per particle identification | JHEP 10 (2014) 059 | 1407.6013 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 36 | C. Cesarotti, M. Reece, and M. J. Strassler | The efficacy of event isotropy as an event shape observable | JHEP 07 (2021) 215 | 2011.06599 |
| 37 | S. Choi and H. Oh | Improved extrapolation methods of data-driven background estimations in high energy physics | EPJC 81 (2021) 643 | 1906.10831 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Precision luminosity measurement in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV in 2015 and 2016 at CMS | EPJC 81 (2021) 800 | CMS-LUM-17-003 2104.01927 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2018 CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | CMS Physics Analysis Summary, 2019 CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 41 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the primary Lund jet plane density in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 05 (2024) 116 | CMS-SMP-22-007 2312.16343 |
| 42 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 4. Deciphering the nature of the Higgs sector | CERN Report CERN-2017-002-M, 2016 link |
1610.07922 |
| 43 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 44 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The $ \text{CL}_\text{s} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|