

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-SUS-23-007 | ||
| Search for an explanation to the muon anomalous magnetic moment through the non-resonant production of two additional Higgs bosons | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 4 December 2023 | ||
| Abstract: A search is presented for the production of two additional Higgs bosons from an off-shell Z boson, where both additional particles decay to $ \tau $ lepton pairs. This is performed with a data sample collected with the CMS detector from proton-proton collisions at the LHC at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb$ ^{-1} $. This is motivated by the Type X ("lepton-specific") two Higgs doublet model which could explain the tension between the experimental and theoretical values of the muon anomalous magnetic moment. No deviation away from the standard model background is observed. Exclusion contours are placed on the Type X two Higgs doublet model alignment scenario, and the model as an explanation for the muon anomalous magnetic moment measurements is ruled out. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; Physics Briefing ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
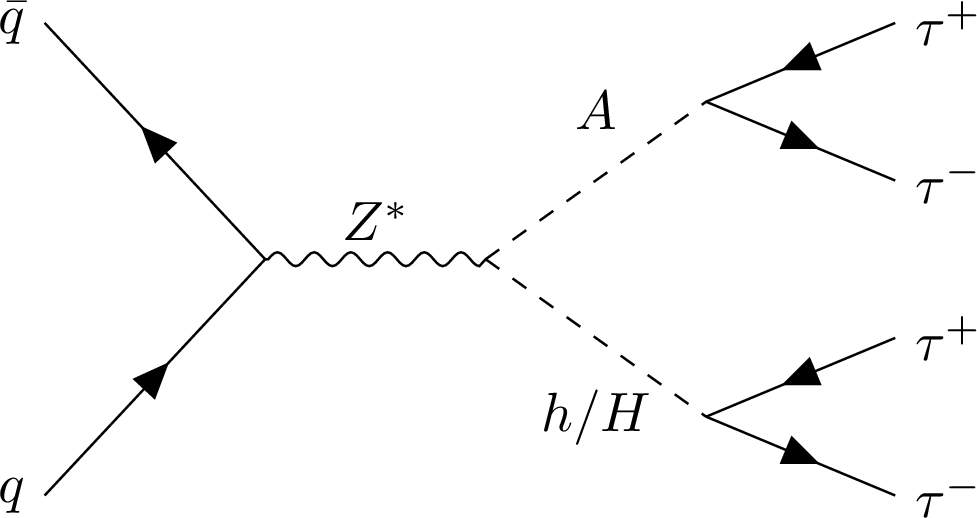
Figure 1:
Feynman diagram for the production of two additional neutral Higgs bosons from an off-shell Z boson and their decay to $ \tau $ leptons. |
png pdf |
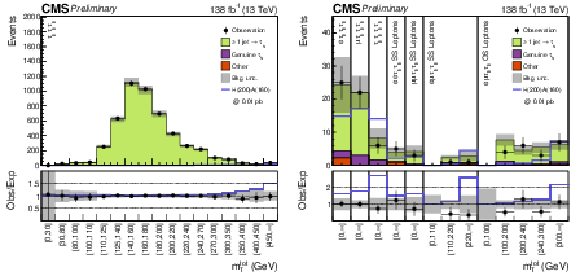
Figure 2:
Distributions of the discriminating variable $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{tot}} $ after a background-only fit to the data. The $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channel (left) and the $ \mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $, $ \mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ and $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channels, as well $ \mathrm{e}\mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mu\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS and $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ OS leptons categories are shown (right). The background uncertainty represents the combined statistical and systematical uncertainties. An example signal with mass hypotheses $ m_{\phi} = $ 200 GeV and $ m_{\mathrm{A}} = $ 160 GeV scaled to 0.01 pb is shown as a blue line for illustrative purposes. |
png pdf |
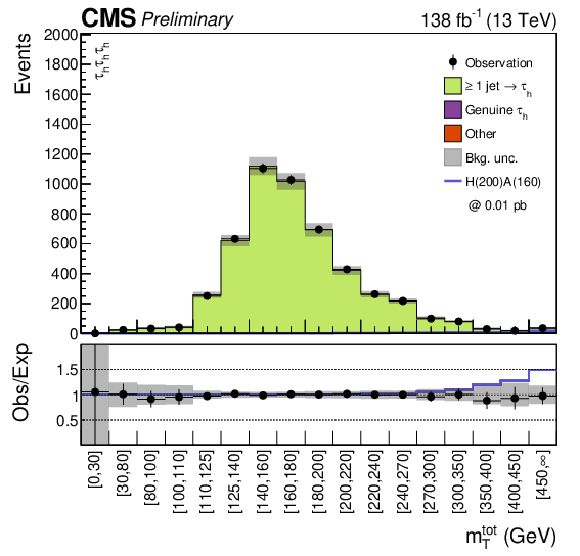
Figure 2-a:
Distributions of the discriminating variable $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{tot}} $ after a background-only fit to the data. The $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channel (left) and the $ \mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $, $ \mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ and $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channels, as well $ \mathrm{e}\mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mu\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS and $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ OS leptons categories are shown (right). The background uncertainty represents the combined statistical and systematical uncertainties. An example signal with mass hypotheses $ m_{\phi} = $ 200 GeV and $ m_{\mathrm{A}} = $ 160 GeV scaled to 0.01 pb is shown as a blue line for illustrative purposes. |
png pdf |
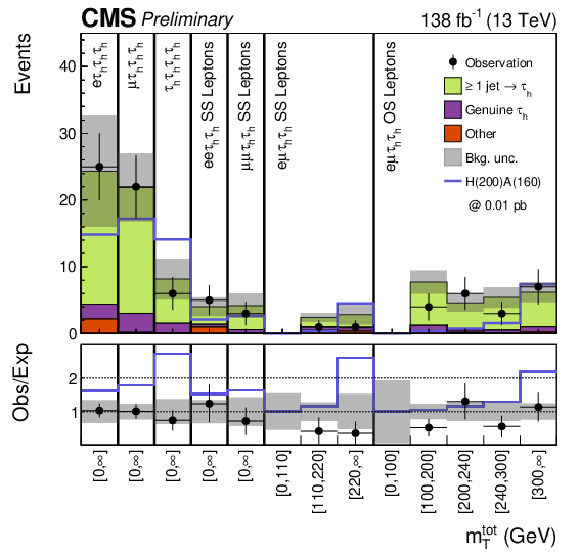
Figure 2-b:
Distributions of the discriminating variable $ m_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{tot}} $ after a background-only fit to the data. The $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channel (left) and the $ \mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $, $ \mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ and $ \tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ channels, as well $ \mathrm{e}\mathrm{e}\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mu\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS, $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ SS and $ \mathrm{e}\mu\tau_\mathrm{h}\tau_\mathrm{h} $ OS leptons categories are shown (right). The background uncertainty represents the combined statistical and systematical uncertainties. An example signal with mass hypotheses $ m_{\phi} = $ 200 GeV and $ m_{\mathrm{A}} = $ 160 GeV scaled to 0.01 pb is shown as a blue line for illustrative purposes. |
png pdf |
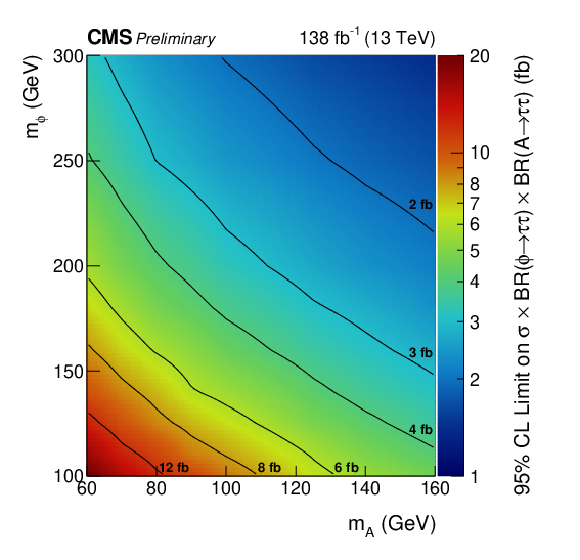
Figure 3:
Observed 95% CL upper limits on the product of the cross section and branching fractions for the decay into $ \tau $ leptons for the production of two additional Higgs bosons produced via an off-shell Z boson. |
png pdf |
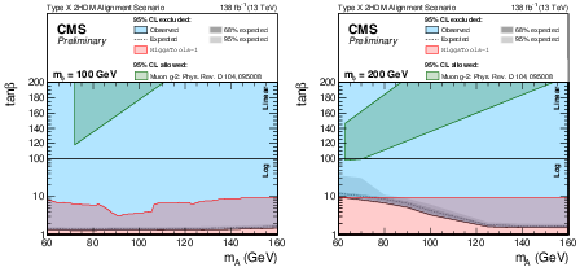
Figure 4:
Observed and expected 95% CL exclusion contours on the Type X 2HDM alignment scenario for $ m_{\phi} $ hypotheses of 100 (left) and 200 (right) GeV. The y-axis scales logarithmically below 100 and linearly above 100. The dashed line represents the expected median, the dark and bright grey bands correspond to the central 68% and 95% expected intervals and the blue area highlights the parameter space that has been observed to be excluded. Constraints from previous searches, obtained by HIGGSTOOLS-1 [54], are shown in red. The allowed regions for an explanation of the muon anomalous magnetic moment, as detailed in Ref. [9], are shown in green. |
png pdf |
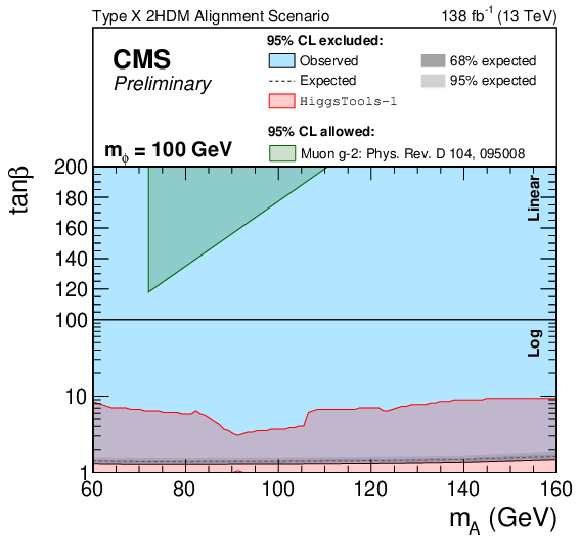
Figure 4-a:
Observed and expected 95% CL exclusion contours on the Type X 2HDM alignment scenario for $ m_{\phi} $ hypotheses of 100 (left) and 200 (right) GeV. The y-axis scales logarithmically below 100 and linearly above 100. The dashed line represents the expected median, the dark and bright grey bands correspond to the central 68% and 95% expected intervals and the blue area highlights the parameter space that has been observed to be excluded. Constraints from previous searches, obtained by HIGGSTOOLS-1 [54], are shown in red. The allowed regions for an explanation of the muon anomalous magnetic moment, as detailed in Ref. [9], are shown in green. |
png pdf |
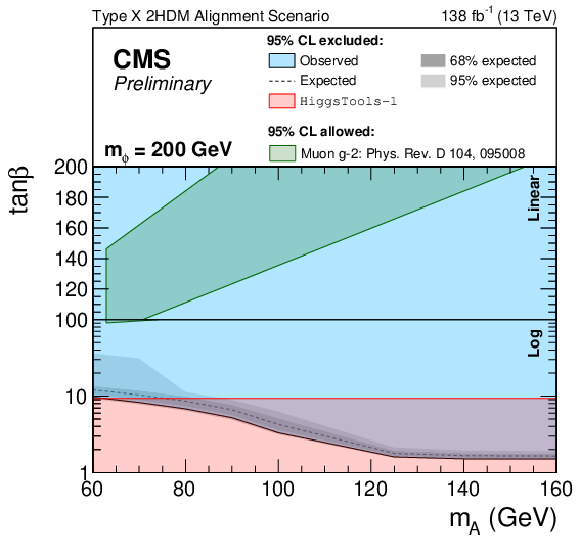
Figure 4-b:
Observed and expected 95% CL exclusion contours on the Type X 2HDM alignment scenario for $ m_{\phi} $ hypotheses of 100 (left) and 200 (right) GeV. The y-axis scales logarithmically below 100 and linearly above 100. The dashed line represents the expected median, the dark and bright grey bands correspond to the central 68% and 95% expected intervals and the blue area highlights the parameter space that has been observed to be excluded. Constraints from previous searches, obtained by HIGGSTOOLS-1 [54], are shown in red. The allowed regions for an explanation of the muon anomalous magnetic moment, as detailed in Ref. [9], are shown in green. |
| Summary |
| A search has been presented for additional Higgs bosons produced via off-shell Z bosons, that decay into $ \tau $ leptons in proton-proton collisions at the LHC, using a data sample collected with the CMS detector at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV. A good agreement between the background-only fit and the data is observed. Upper limits on the production cross sections multiplied by branching fractions range from 1.4 fb at $ m_{\mathrm{A}} = $ 160 GeV and $ m_{\phi} = $ 300 GeV to 20 fb at $ m_{\mathrm{A}} = $ 60 GeV and $ m_{\phi} = $ 100 GeV. The data, combined with the constraints from previous searches, exclude the majority of the Type X 2HDM phase space within this mass range. These limits rule out this model as an explanation for the muon anomalous magnetic moment, as described in Ref. [9]. Therefore, the deviation found in Refs. [1,2,3] likely originates from an alternative source. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | Muon g-2 Collaboration | Final Report of the Muon E821 Anomalous Magnetic Moment Measurement at BNL | PRD 73 (2006) 072003 | hep-ex/0602035 |
| 2 | Muon g-2 Collaboration | Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.46 ppm | no.~14, 141801, 2021 PRL 126 (2021) |
2104.03281 |
| 3 | Muon g-2 Collaboration | Measurement of the Positive Muon Anomalous Magnetic Moment to 0.20 ppm | no.~16, 161802, 2023 PRL 131 (2023) |
2308.06230 |
| 4 | T. Aoyama et al. | The anomalous magnetic moment of the muon in the Standard Model | Phys. Rept. 887 (2020) 1 | 2006.04822 |
| 5 | S. Borsanyi et al. | Leading hadronic contribution to the muon magnetic moment from lattice QCD | no.~7857, 51, 2021 Nature 593 (2021) |
2002.12347 |
| 6 | M. Carena and H. E. Haber | Higgs Boson Theory and Phenomenology | Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 50 (2003) 63 | hep-ph/0208209 |
| 7 | V. Ilisie | New Barr-Zee contributions to $ (g{-}2)_{\mu} $ in two-Higgs-doublet models | JHEP 04 (2015) 077 | 1502.04199 |
| 8 | N. Ghosh and J. Lahiri | Revisiting a generalized two-Higgs-doublet model in light of the muon anomaly and lepton flavor violating decays at the HL-LHC | no.~5, 055009, 2021 PRD 103 (2021) |
2010.03590 |
| 9 | A. Jueid, J. Kim, S. Lee, and J. Song | Type-X two-Higgs-doublet model in light of the muon $g{-}2$: Confronting Higgs boson and collider data | no.~9, 095008, 2021 PRD 104 (2021) |
2104.10175 |
| 10 | P. M. Ferreira, B. L. Gonçalves, F. R. Joaquim, and M. Sher | $(g {-} 2) _{\mu} $ in the 2HDM and slightly beyond: An updated view | no.~5, 053008, 2021 PRD 104 (2021) |
2104.03367 |
| 11 | T. Abe, R. Sato, and K. Yagyu | Lepton-specific two Higgs doublet model as a solution of muon g \ensuremath- 2 anomaly | JHEP 07 (2015) 064 | 1504.07059 |
| 12 | A. Broggio et al. | Limiting two-Higgs-doublet models | JHEP 11 (2014) 058 | 1409.3199 |
| 13 | E. J. Chun, Z. Kang, M. Takeuchi, and Y.-L. S. Tsai | LHC $\tau$-rich tests of lepton-specific 2HDM for $(g {-} 2) _{\mu} $ | JHEP 11 (2015) 099 | 1507.08067 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Electron and photon reconstruction and identification with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 16 (2021) P05014 | CMS-EGM-17-001 2012.06888 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | no.~10, P5, 2018 JINST 13 (2018) |
CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Jet energy scale and resolution in the CMS experiment in pp collisions at 8 TeV | JINST 12 (2017) P02014 | CMS-JME-13-004 1607.03663 |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of missing transverse momentum reconstruction in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV using the CMS detector | JINST 14 (2019) P07004 | CMS-JME-17-001 1903.06078 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of hadronic tau lepton decays using a deep neural network | JINST 17 (2022) P07023 | CMS-TAU-20-001 2201.08458 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | Identification of heavy-flavour jets with the CMS detector in pp collisions at 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P05011 | CMS-BTV-16-002 1712.07158 |
| 26 | E. Bols et al. | Jet flavour classification using DeepJet | JINST 15 (2020) P12012 | 2008.10519 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the $ \mathrm{Z}\gamma^{*} \to \tau\tau $ cross section in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV and validation of $ \tau $ lepton analysis techniques | no.~9, 708, 2018 EPJC 78 (2018) |
CMS-HIG-15-007 1801.03535 |
| 28 | A. Rogozhnikov | Reweighting with Boosted Decision Trees | no.~1, 01, 2016 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 762 (2016) |
1608.05806 |
| 29 | J. Alwall et al. | MadGraph 5: Going beyond | JHEP 06 (2011) 128 | 1106.0522 |
| 30 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 31 | R. Frederix and S. Frixione | Merging meets matching in MC@NLO | JHEP 12 (2012) 061 | 1209.6215 |
| 32 | J. Alwall et al. | Comparative study of various algorithms for the merging of parton showers and matrix elements in hadronic collisions | EPJC 53 (2008) 473 | 0706.2569 |
| 33 | S. Alioli, S.-O. Moch, and P. Uwer | Hadronic top-quark pair-production with one jet and parton showering | JHEP 01 (2012) 137 | 1110.5251 |
| 34 | R. Frederix, E. Re, and P. Torrielli | Single-top $ t $-channel hadroproduction in the four-flavour scheme with POWHEG and aMC@NLO | JHEP 09 (2012) 130 | 1207.5391 |
| 35 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 36 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 37 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 38 | T. Je \v z o and P. Nason | On the treatment of resonances in next-to-leading order calculations matched to a parton shower | JHEP 12 (2015) 065 | 1509.09071 |
| 39 | K. Melnikov and F. Petriello | Electroweak gauge boson production at hadron colliders through $ \mathcal{O}(\alpha_\text{s}^{2}) $ | PRD 74 (2006) 114017 | hep-ph/0609070 |
| 40 | M. Czakon and A. Mitov | Top++: A program for the calculation of the top-pair cross-section at hadron colliders | Comput. Phys. Commun. 185 (2014) 2930 | 1112.5675 |
| 41 | N. Kidonakis | Top quark production | in Helmholtz International Summer School on Physics of Heavy Quarks and Hadrons, 2014 link |
1311.0283 |
| 42 | J. M. Campbell, R. K. Ellis, and C. Williams | Vector boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2011) 018 | 1105.0020 |
| 43 | T. Gehrmann et al. | $ \mathrm{W^+}\mathrm{W^-} $ production at hadron colliders in next to next to leading order QCD | PRL 113 (2014) 212001 | 1408.5243 |
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of production cross sections of the Higgs boson in the four-lepton final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | no.~6, 488, 2021 EPJC 81 (2021) |
CMS-HIG-19-001 2103.04956 |
| 45 | M. Krause, M. Mühlleitner, and M. Spira | 2HDECAY - A program for the calculation of electroweak one-loop corrections to Higgs decays in the Two-Higgs-Doublet Model including state-of-the-art QCD corrections | Comput. Phys. Commun. 246 (2020) 106852 | 1810.00768 |
| 46 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions from high-precision collider data | EPJC 77 (2017) 663 | 1706.00428 |
| 47 | T. Sjöstrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | Comput. Phys. Commun. 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Extraction and validation of a new set of CMS PYTHIA8 tunes from underlying-event measurements | EPJC 80 (2020) 4 | CMS-GEN-17-001 1903.12179 |
| 49 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT 4---a simulation toolkit | NIM A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 50 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of inclusive W and Z cross sections in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2011) 080 | CMS-EWK-10-002 1012.2466 |
| 51 | CMS Collaboration | Searches for additional Higgs bosons and for vector leptoquarks in $ \tau\tau $ final states in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} $ = 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2023) 073 | CMS-HIG-21-001 2208.02717 |
| 52 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 53 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The CL$ _{\text{s}} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 54 | H. Bahl et al. | HiggsTools: BSM scalar phenomenology with new versions of HiggsBounds and HiggsSignals | Comput. Phys. Commun. 291 (2023) 108803 | 2210.09332 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|