

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIG-25-014 | ||
| Combination of ATLAS and CMS searches for Higgs boson pair production at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | ||
| ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | ||
| 2025-10-30 | ||
| Abstract: This note presents a combination of searches for Higgs boson pair (HH) production performed by the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations using proton-proton collision data sets recorded at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV at the LHC Run 2, corresponding to integrated luminosities ranging between 126 and 140 fb$^{-1}$. The upper limit at the 95% confidence level on the total HH production cross section corresponds to 2.5 times the standard model (SM) prediction with an expected value of 1.7 (2.8) assuming the absence (presence) of the SM HH signal. The strength of the HH signal is measured to be 0.8 $ ^{+0.9}_{-0.7} $ relative to the SM prediction. The observed significance is found to be 1.1 standard deviations when 1.3 are expected for the SM HH signal. Constraints are set on the Higgs boson trilinear self-coupling and on the couplings of two Higgs bosons to two vector bosons, both normalized to the SM predictions and denoted as $ \kappa_\lambda $ and $ \kappa_{2\mathrm{V}} $, respectively. The observed individual constraints at the 95% confidence level are $ -$0.71 $ < \kappa_\lambda < $ 6.1 and 0.73 $ < \kappa_{2\mathrm{V}} < $ 1.3, while the expected constraints assuming the presence of the SM HH signal are $ -1.3 < \kappa_\lambda < $ 6.7 and 0.66 $ < \kappa_{2\mathrm{V}} < $ 1.4. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
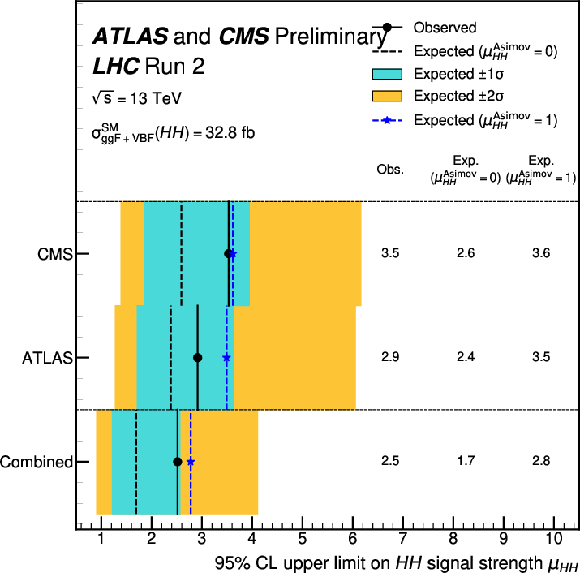
png pdf |
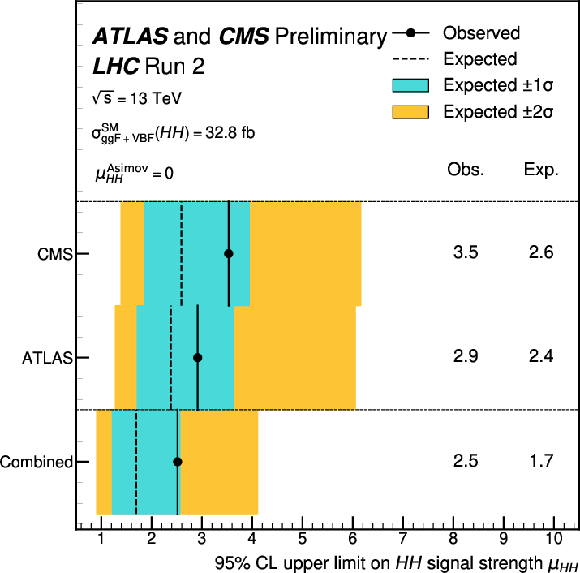
Figure 1:
Expected and observed 95% CL upper limits on the total HH signal strength, defined as the ratio of the measured cross section to the sum of the ggF and VBF HH SM production cross sections, for ATLAS, CMS, and the combination of both experiments. The median expected limits on $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ are obtained under the hypotheses of no HH signal ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov}= $ 0) or assuming the presence of the SM HH signal ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov}= $ 1). The $ \pm 1\sigma $ and $ \pm 2\sigma $ bands are computed under the $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov}= $ 0 hypothesis. |
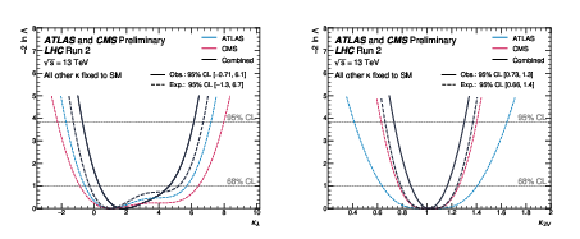
png pdf |
Figure 2:
Expected negative log-likelihood values as function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ (left) and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ (right) for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination, and observed values for the combination. The result is obtained fixing all the other couplings to their SM values. |
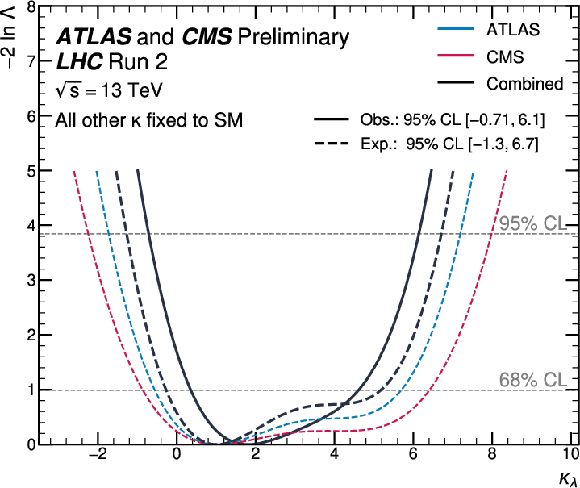
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
Expected negative log-likelihood values as function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ (left) and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ (right) for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination, and observed values for the combination. The result is obtained fixing all the other couplings to their SM values. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
Expected negative log-likelihood values as function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ (left) and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ (right) for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination, and observed values for the combination. The result is obtained fixing all the other couplings to their SM values. |
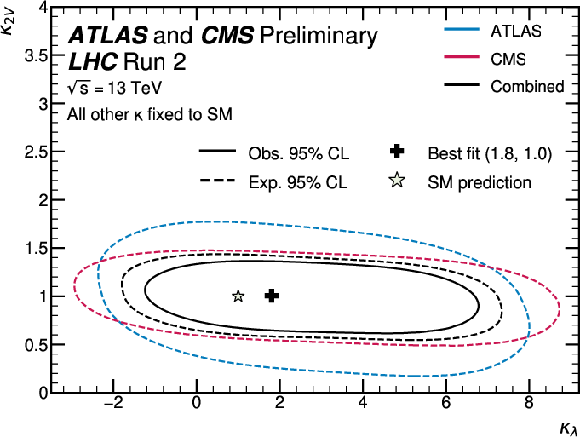
png pdf |
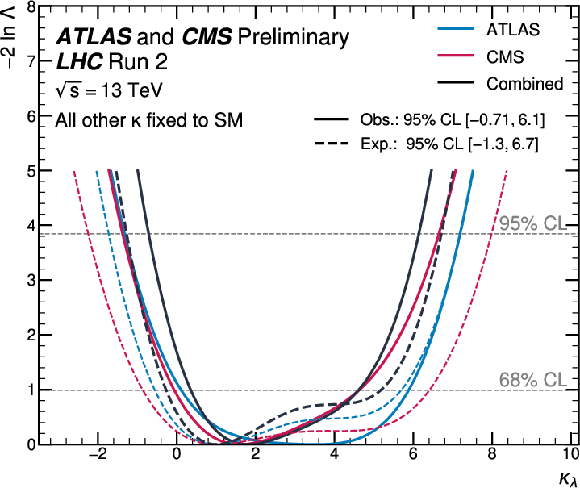
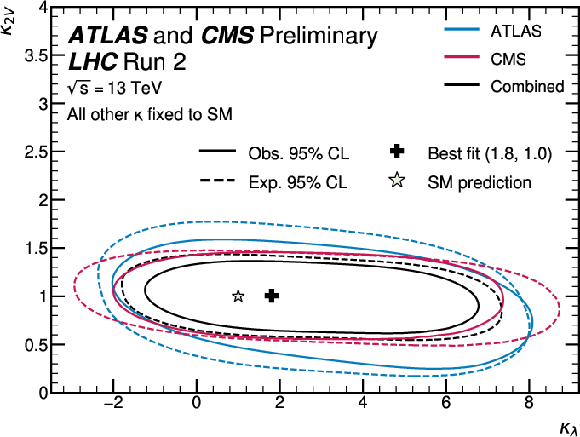
Figure 3:
Observed and expected 95% CL contours for the simultaneous scan of the profile likelihood as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $. The expected constraints from the individual experiments are also shown. All other Higgs boson couplings are fixed to their SM value. |
png pdf |
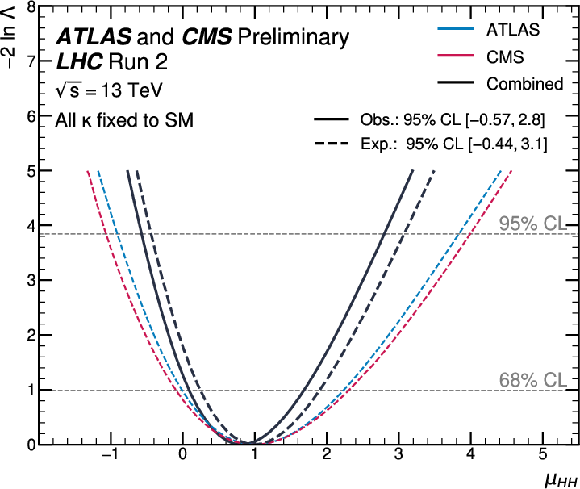
Figure 4:
Expected negative log-likelihood values as a function of the total signal strength parameter $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination. The observed value for the combination is also shown. All the couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values, but the overall ggF+VBF HH signal normalization is allowed to vary freely. |
png pdf |
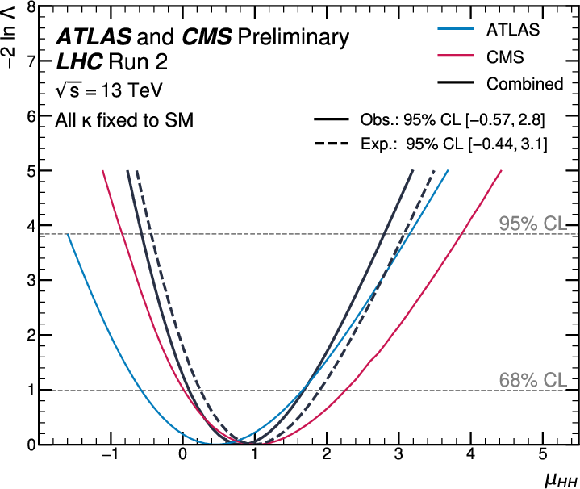
Figure 5:
Observed negative log-likelihood values as a function of the total signal strength parameter $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination. The expected value for the combination is also shown. All the couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values, but the overall ggF+VBF HH signal normalization is allowed to vary freely. |
png pdf |
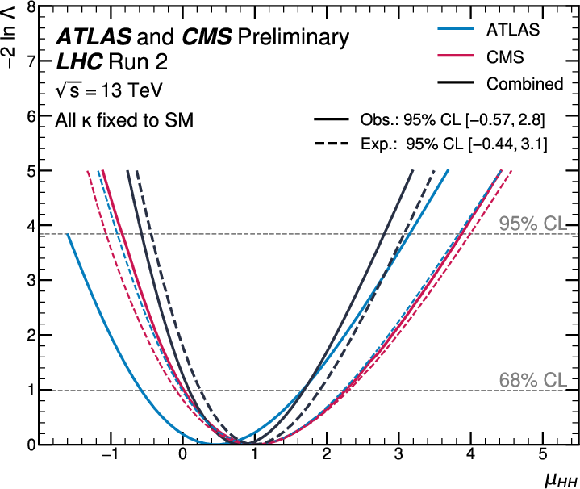
Figure 6:
Observed and expected negative log-likelihood values as a function of the total signal strength parameter $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $. All the couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values, but the overall ggF+VBF HH signal normalization is allowed to vary freely. |
png pdf |
Figure 7:
Observed and expected negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $. All the other couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values. |
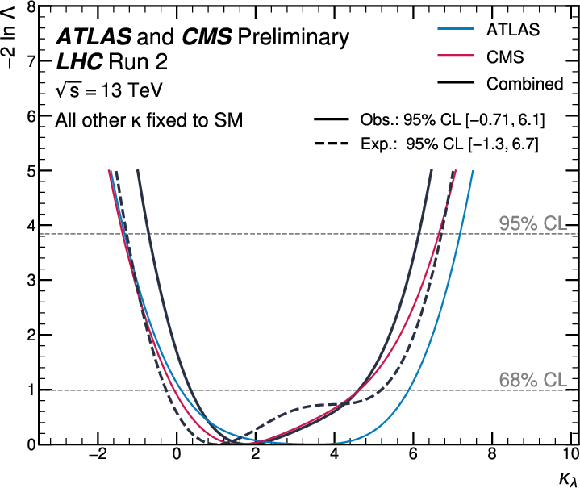
png pdf |
Figure 8:
Observed negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination, and expected value for the combination. All the other couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
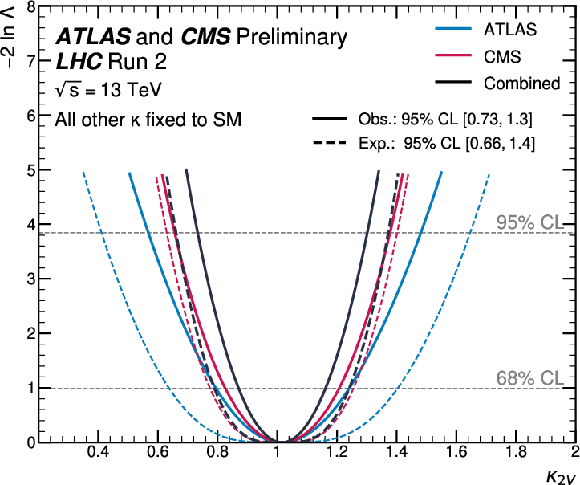
Figure 9:
Observed and expected negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $. All the other couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
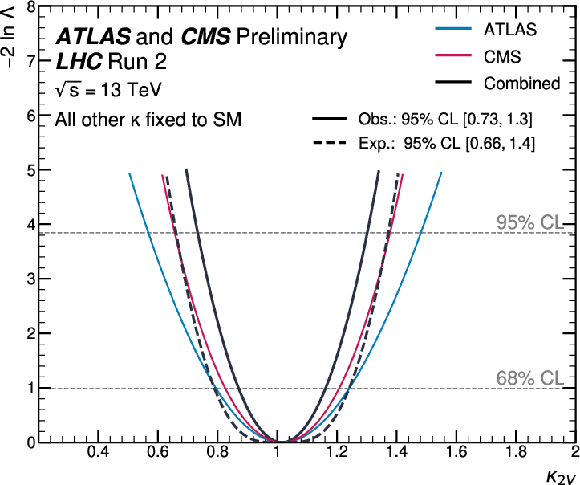
Figure 10:
Observed negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination, and expected value for the combination. All the other couplings are assumed to be fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
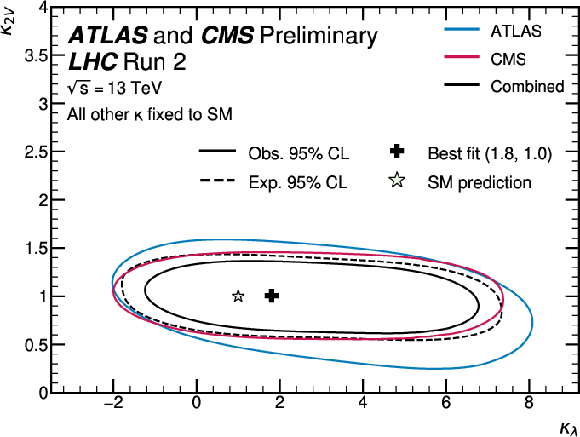
Figure 11:
Observed and expected 95% CL contours for a bidimensional likelihood scan in the $ (\kappa_\lambda, \kappa_{2\text{V}}) $ plane for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination. All other Higgs boson couplings are fixed to their SM value. |
png pdf |
Figure 12:
Observed 95% CL contours for a bidimensional likelihood scan in the $ (\kappa_\lambda, \kappa_{2\text{V}}) $ plane for ATLAS, CMS, and their combination. The expected contour from the combination is also shown. All other Higgs boson couplings are fixed to their SM value. |
png pdf |
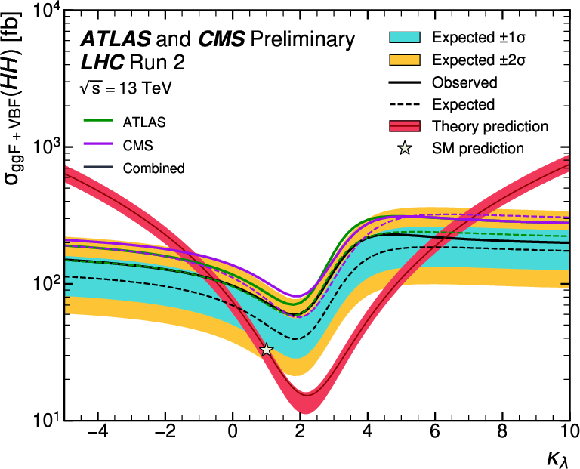
Figure 13:
Exclusion limit at the 95% confidence level on the total HH cross section as a function of the value of $ \kappa_\lambda $. The expected exclusion is computed assuming no HH signal is present ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov} = $ 0). The individual results by ATLAS and CMS are indicated by the green and purple lines, respectively. Dashed and solid lines denote respectively the expected median and the observed limits. The theoretical prediction, corresponding to the sum of the ggF and VBF HH cross sections, is shown in red. |
png pdf |
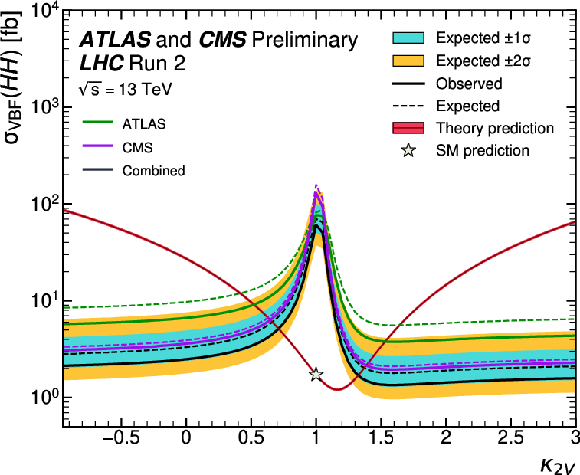
Figure 14:
Exclusion limit at the 95% confidence level on the total HH cross section as a function of the value of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $. The expected exclusion is computed assuming no HH signal is present ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov} = $ 0). The individual results by ATLAS and CMS are indicated by the green and purple lines, respectively. Dashed and solid lines denote respectively the expected median and the observed limits. The theoretical prediction, corresponding to the sum of the ggF and VBF HH cross sections, is shown in red. |
png pdf |
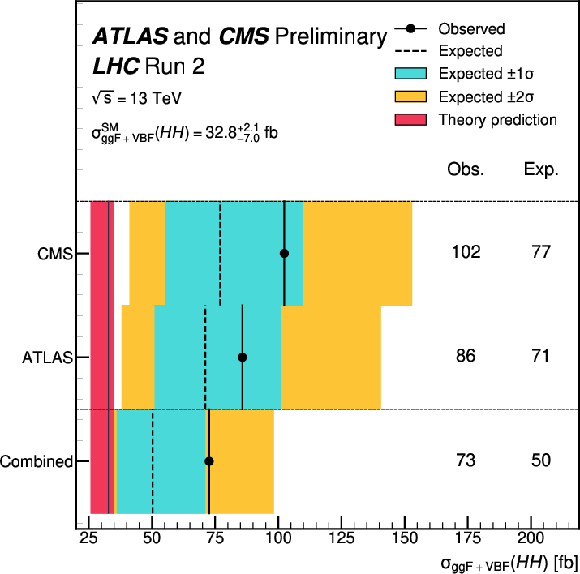
Figure 15:
Expected and observed 95% CL upper limits on the total HH signal strength, defined as the ratio of the measured cross section to the sum of the ggF and VBF HH SM production cross sections, for ATLAS, CMS, and the combination of both experiments. The expected limits on $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ are obtained assuming the absence of an HH signal ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov}= $ 0). |
png pdf |
Figure 16:
Expected and observed 95% CL upper limits on the total HH cross section, defined as the sum of the ggF and VBF HH SM production cross sections, for ATLAS, CMS, and the combination of both experiments. The expected limits on $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ are obtained assuming the absence of an HH signal ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{Asimov}= $ 0). The theoretical prediction is indicated in red. |
png pdf |
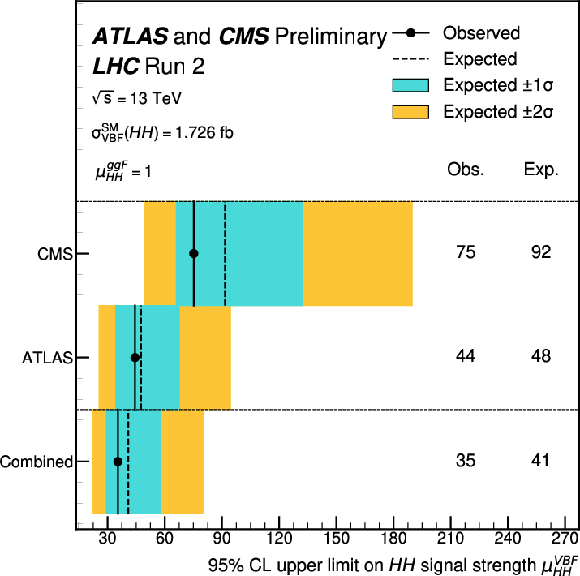
Figure 17:
Expected and observed 95% CL upper limits on the signal strength of the VBF HH production $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{VBF} $, defined as the ratio of the measured VBF HH cross section to the corresponding SM prediction, for ATLAS, CMS, and the combination of both experiments. The limits are obtained by fixing the ggF signal strength to the SM prediction ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{ggF} = $ 1). The expected limits assume the absence of the VBF HH signal. |
png pdf |
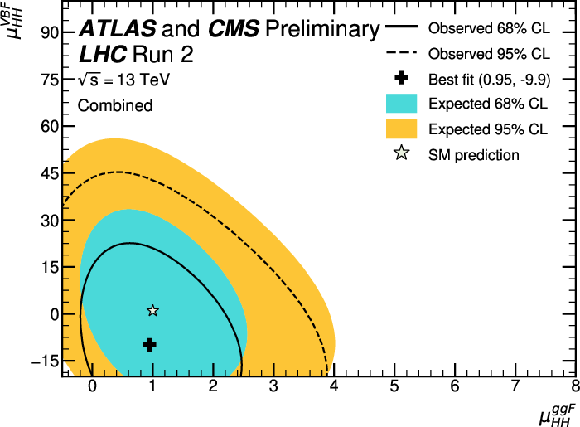
Figure 18:
Observed and expected 95% CL contours for a bidimensional likelihood scan where the individual signal strengths for the ggF ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{ggF} $) and VBF ($ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{VBF} $) HH production modes are allowed to vary independently. All Higgs boson couplings are fixed to their SM value. The likelihood function is not well defined in regions with large negative values of either $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{ggF} $ or $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{VBF} $, where the total prediction for the sum of signal and backgrounds can become negative in some categories of the input analyses. This region is therefore not shown. |
png pdf |
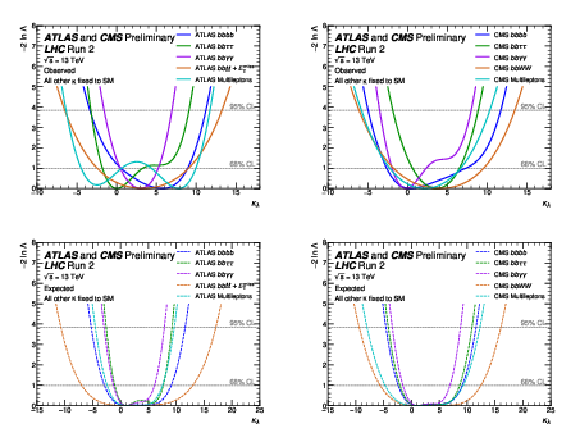
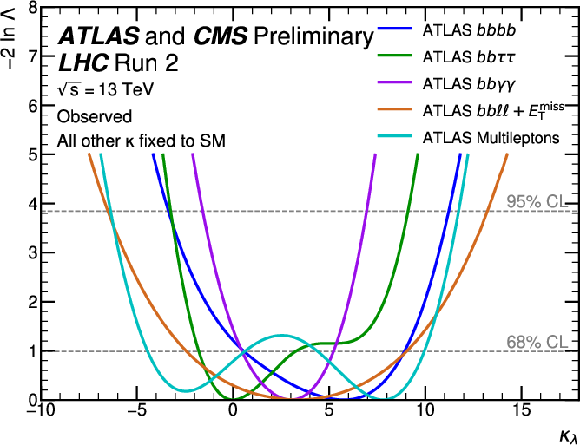
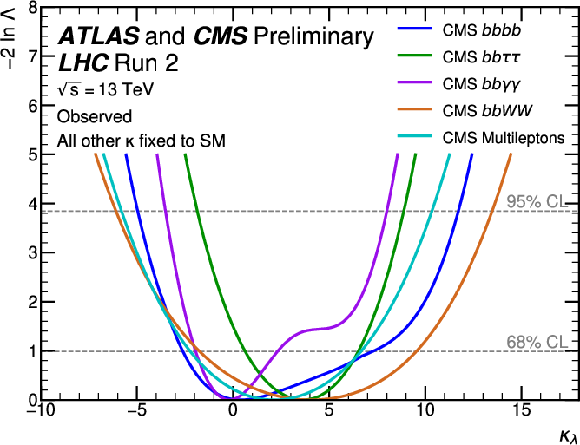
Figure 19:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
Figure 19-a:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
Figure 19-b:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |

png pdf |
Figure 19-c:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |

png pdf |
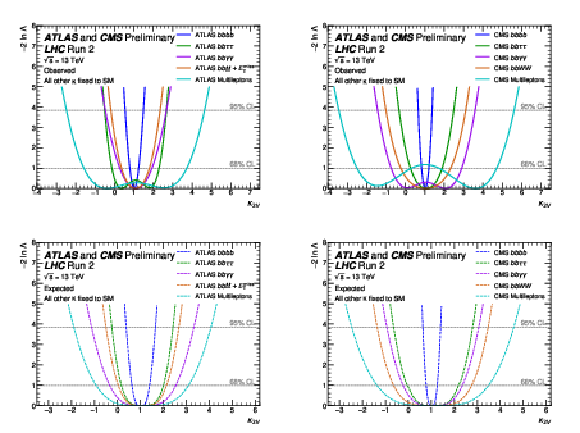
Figure 19-d:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_\lambda $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
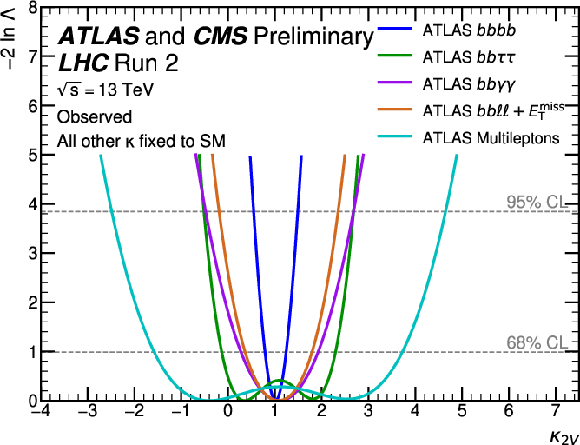
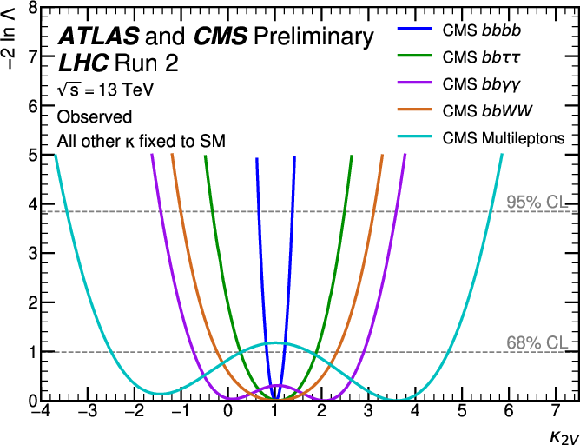
Figure 20:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
Figure 20-a:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
Figure 20-b:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
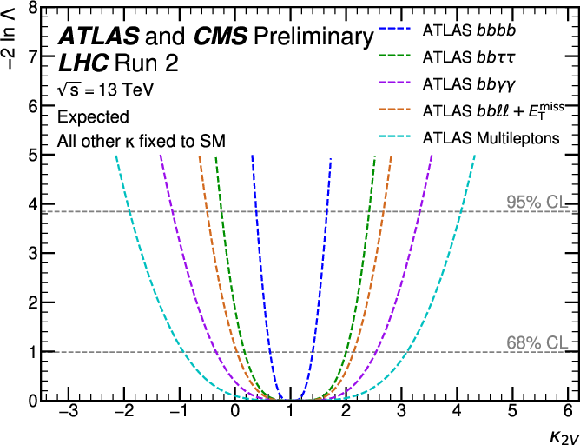
Figure 20-c:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
png pdf |
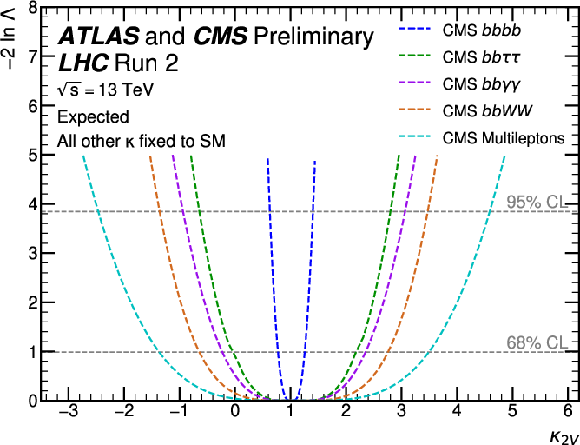
Figure 20-d:
Observed (top) and expected (bottom) negative log-likelihood values as a function of $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the input ATLAS (left) and CMS (right) analyses. All the other couplings are fixed to the SM values. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Summary of the observed and expected results from the individual input analyses considered, the single experiment combination, and the LHC combination presented in this work. The upper limit on $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}=\sigma_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}/\sigma_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}}^\text{SM} $ and the constraints on $ \kappa_\lambda $ and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ are reported. All values quoted are defined at the 95% CL. The expected limits on $ \mu_{\mathrm{H}\mathrm{H}} $ are computed assuming the absence of HH signal. The references indicate the original publication where the corresponding analyses are documented, and the results were recomputed following the modifications to input analyses described in the text. |
png pdf |
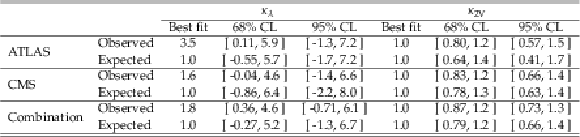
Table 2:
Best fit values, 68%, and 95% CL intervals obtained from the likelihood values as a function of the coupling modifiers for the trilinear Higgs boson self-coupling $ \kappa_\lambda $ and the quartic coupling between two Higgs bosons and two vector bosons $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ for the ATLAS and CMS experiments and their combination. Results for $ \kappa_\lambda $ and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ are computed from independent fits where all other Higgs boson couplings are set to their SM value. |
| Summary |
| In summary, this note presents the first combination of ATLAS and CMS searches for Higgs boson pair (HH) production. The searches are performed using the LHC Run 2 data set with integrated luminosities ranging between 126 and 140 fb$ ^{-1} $. The upper limit at the 95% confidence level on the total HH cross section, defined as the sum of the ggF and VBF production modes, corresponds to 2.5 times the SM prediction, compared to an expected value of 1.7 (2.8) in the absence (presence) of SM HH production. The best fit signal strength, defined as the ratio of the measured cross section to the SM prediction, is observed to be 0.8 $ ^{+0.9}_{-0.7} $, corresponding to a significance of 1.1 standard deviations. The observed 95% confidence level constraints on the $ \kappa_\lambda $ and $ \kappa_{2\text{V}} $ coupling modifiers are $ -$0.71 $ < \kappa_\lambda < $ 6.1 ($ -$1.3 $ < \kappa_\lambda < $ 6.7 expected) and 0.73 $ < \kappa_{2\text{V}} < $ 1.3 (0.66 $ < \kappa_{2\text{V}} < $ 1.4 expected). The results are compatible within their uncertainties with the SM predictions and provide the most comprehensive and most sensitive results on HH production to date. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | S. L. Glashow | Partial-symmetries of weak interactions | NP 22 (1961) 579 | |
| 2 | F. Englert and R. Brout | Broken Symmetry and the Mass of Gauge Vector Mesons | PRL 13 (1964) 321--323 | |
| 3 | P. W. Higgs | Broken symmetries, massless particles and gauge fields | PL 12 (1964) 132 | |
| 4 | P. W. Higgs | Broken Symmetries and the Masses of Gauge Bosons | PRL 13 (1964) 508--509 | |
| 5 | G. S. Guralnik, C. R. Hagen, and T. W. B. Kibble | Global Conservation Laws and Massless Particles | PRL 13 (1964) 585--587 | |
| 6 | S. Weinberg | A model of leptons | PRL 19 (1967) 1264 | |
| 7 | A. Salam | Weak and electromagnetic interactions | in Elementary particle physics: relativistic groups and analyticity, N. Svartholm, ed., p. 367. Almqvist \& Wiksell, Stockholm, 1968. Proceedings of the eighth Nobel symposium | |
| 8 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1--29 | 1207.7214 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a New Boson at a Mass of 125 GeV with the CMS Experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30--61 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a New Boson with Mass Near 125 GeV in $ pp $ Collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2013) 081 | CMS-HIG-12-036 1303.4571 |
| 11 | ATLAS Collaboration | A detailed map of Higgs boson interactions by the ATLAS experiment ten years after the discovery | Nature 607 (2022) 52--59 | 2207.00092 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | A portrait of the Higgs boson by the CMS experiment ten years after the discovery. | Nature 607 (2022) 60--68 | CMS-HIG-22-001 2207.00043 |
| 13 | S. Dawson, S. Dittmaier, and M. Spira | Neutral Higgs boson pair production at hadron colliders: QCD corrections | PRD 58 (1998) 115012 | hep-ph/9805244 |
| 14 | S. Borowka et al. | Higgs Boson Pair Production in Gluon Fusion at Next-to-Leading Order with Full Top-Quark Mass Dependence | PRL 117 (2016) 012001 | 1604.06447 |
| 15 | J. Baglio et al. | Gluon fusion into Higgs pairs at NLO QCD and the top mass scheme | EPJC 79 (2019) 459 | 1811.05692 |
| 16 | D. de Florian and J. Mazzitelli | Higgs Boson Pair Production at Next-to-Next-to-Leading Order in QCD | PRL 111 (2013) 201801 | 1309.6594 |
| 17 | D. Y. Shao, C. S. Li, H. T. Li, and J. Wang | Threshold resummation effects in Higgs boson pair production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2013) 169 | 1301.1245 |
| 18 | D. de Florian and J. Mazzitelli | Higgs pair production at next-to-next-to-leading logarithmic accuracy at the LHC | JHEP 09 (2015) 053 | 1505.07122 |
| 19 | M. Grazzini et al. | Higgs boson pair production at NNLO with top quark mass effects | JHEP 05 (2018) 059 | 1803.02463 |
| 20 | J. Baglio et al. | $ gg\to HH $: Combined uncertainties | PRD 103 (2021) 056002 | 2008.11626 |
| 21 | J. Baglio et al. | The measurement of the Higgs self-coupling at the LHC: theoretical status | JHEP 04 (2013) 151 | 1212.5581 |
| 22 | R. Frederix et al. | Higgs pair production at the LHC with NLO and parton-shower effects | PLB 732 (2014) 142--149 | 1401.7340 |
| 23 | L.-S. Ling et al. | NNLO QCD corrections to Higgs pair production via vector boson fusion at hadron colliders | PRD 89 (2014) 073001 | 1401.7754 |
| 24 | F. A. Dreyer and A. Karlberg | Fully differential Vector-Boson Fusion Higgs Pair Production at Next-to-Next-to-Leading Order | PRD 99 (2019) 074028 | 1811.07918 |
| 25 | F. A. Dreyer and A. Karlberg | Vector-Boson Fusion Higgs Pair Production at N$ ^3 $LO | PRD 98 (2018) 114016 | 1811.07906 |
| 26 | F. A. Dreyer, A. Karlberg, J.-N. Lang, and M. Pellen | Precise predictions for double-Higgs production via vector-boson fusion | EPJC 80 (2020) 1037 | 2005.13341 |
| 27 | PDF4LHC Working Group Collaboration | The PDF4LHC21 combination of global PDF fits for the LHC Run III | JPG 49 (2022) 080501 | 2203.05506 |
| 28 | F. Bishara, R. Contino, and J. Rojo | Higgs pair production in vector-boson fusion at the LHC and beyond | EPJC 77 (2017) 481 | 1611.03860 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Higgs boson pair production in the four b quark final state in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 129 (2022) 081802 | CMS-HIG-20-005 2202.09617 |
| 30 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for nonresonant pair production of Higgs bosons in the $b\bar{b}b\bar{b}$ final state in $pp$ collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 108 (2023) 052003 | 2301.03212 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Nonresonant Pair Production of Highly Energetic Higgs Bosons Decaying to Bottom Quarks | PRL 131 (2023) 041803 | 2205.06667 |
| 32 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for pair production of boosted Higgs bosons via vector-boson fusion in the $b\bar{b}b\bar{b}$ final state using $pp$ collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 858 (2024) 139007 | 2404.17193 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Search for nonresonant Higgs boson pair production in final state with two bottom quarks and two tau leptons in proton-proton collisions at s=13 TeV | PLB 842 (2023) 137531 | CMS-HIG-20-010 2206.09401 |
| 34 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the non-resonant production of Higgs boson pairs via gluon fusion and vector-boson fusion in the $b\bar{b} \tau^+\tau^-$ final state in proton--proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 110 (2024) 032012 | 2404.12660 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Search for nonresonant Higgs boson pair production in final states with two bottom quarks and two photons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 2103 (2021) 257 | CMS-HIG-19-018 2011.12373 |
| 36 | ATLAS Collaboration | Studies of new Higgs boson interactions through nonresonant $HH$ production in the $b\bar{b}\gamma\gamma$ final state in $pp$ collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 01 (2024) 066 | 2310.12301 |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Higgs boson pair production in the $b\bar{b}W^+W^-$ decay mode in proton--proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2024) 293 | CMS-HIG-21-005 2403.09430 |
| 38 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for non-resonant Higgs boson pair production in the $2b + 2\ell + E_{\mathrm{T}}^{\text{miss}}$ final state in $pp$ collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 02 (2024) 037 | 2310.11286 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Higgs boson pairs decaying to WW*WW*, WW*$ \tau\tau $, and $ \tau\tau\tau\tau $ in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 07 (2023) 095 | CMS-HIG-21-002 2206.10268 |
| 40 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for non-resonant Higgs boson pair production in final states with leptons, taus, and photons in $pp$ collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 08 (2024) 164 | 2405.20040 |
| 41 | ATLAS Collaboration | Combination of Searches for Higgs Boson Pair Production in pp Collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS Detector | PRL 133 (2024) 101801 | 2406.09971 |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | Combination of searches for nonresonant Higgs boson pair production in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-HIG-20-011 2510.07527 |
|
| 43 | ATLAS Collaboration | The ATLAS Experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider | JINST 3 (2008) S08003 | |
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS Experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | |
| 45 | J. Butterworth et al. | PDF4LHC recommendations for LHC Run II | JPG 43 (2016) 023001 | 1510.03865 |
| 46 | G. Heinrich et al. | NLO predictions for Higgs boson pair production with full top quark mass dependence matched to parton showers | JHEP 08 (2017) 088 | 1703.09252 |
| 47 | G. Heinrich et al. | Probing the trilinear Higgs boson coupling in di-Higgs production at NLO QCD including parton shower effects | JHEP 06 (2019) 066 | 1903.08137 |
| 48 | G. Heinrich, J. Lang, and L. Scyboz | Erratum to: SMEFT predictions for gg →hh at full NLO QCD and truncation uncertainties | JHEP 2023 (2023) 86 | |
| 49 | E. Bagnaschi, G. Degrassi, and R. Grober | Higgs boson pair production at NLO in the POWHEG approach and the top quark mass uncertainties | EPJC 83 (2023) 1054 | 2309.10525 |
| 50 | G. Degrassi, P. P. Giardino, F. Maltoni, and D. Pagani | Probing the Higgs self coupling via single Higgs production at the LHC | JHEP 12 (2016) 080 | 1607.04251 |
| 51 | F. Maltoni, D. Pagani, A. Shivaji, and X. Zhao | Trilinear Higgs coupling determination via single-Higgs differential measurements at the LHC | EPJC 77 (2017) 887 | 1709.08649 |
| 52 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC 71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 53 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIM A 434 (1999) 435--443 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 54 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The $ CL_s $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693--2704 | |
| 55 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS statistical analysis and combination tool: Combine | Comput. Softw. Big Sci. 8 (2024) 19 | CMS-CAT-23-001 2404.06614 |
| 56 | Wouter Verkerke and David Kirkby | The RooFit toolkit for data modeling | link | |
| 57 | L. Moneta et al. | The RooStats Project | 1009.1003 | |
| 58 | ROOT Collaboration | HistFactory: A tool for creating statistical models for use with RooFit and RooStats | technical report, New York U., New York, 2012 link |
|
| 59 | S. Manzoni et al. | Taming a leading theoretical uncertainty in HH measurements via accurate simulations for $ \textrm{b}\overline{\textrm{b}}\textrm{H} $ production | JHEP 09 (2023) 179 | 2307.09992 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|