

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIG-18-006 | ||
| Search for a pseudoscalar boson in the mass range from 4 to 15 GeV produced in decays of the 125 GeV Higgs boson in the final states with two muons and two nearby tracks at $\sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| March 2019 | ||
| Abstract: A search is presented for pairs of light pseudoscalar bosons, in the mass range between 4 and 15 GeV, produced in decay of the 125 GeV Higgs boson. The decay mode where one light boson decays into $\tau$ leptons, while the other one decays into a pair of $\tau$ leptons or muons, is considered. The search is based on proton-proton collision data collected by the CMS experiment at a centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV and corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 35.9 fb$^{-1}$. No significant excess of events above the standard model background expectation obtained from control regions in data is observed. The 95% confidence level observed (expected) upper limits on the signal production cross section times branching fraction into the 4$\tau$ final state, relative to the standard model Higgs boson production cross section are set between 0.022 (0.027) and 0.23 (0.19) in the probed mass range. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, PLB 800 (2019) 135087. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
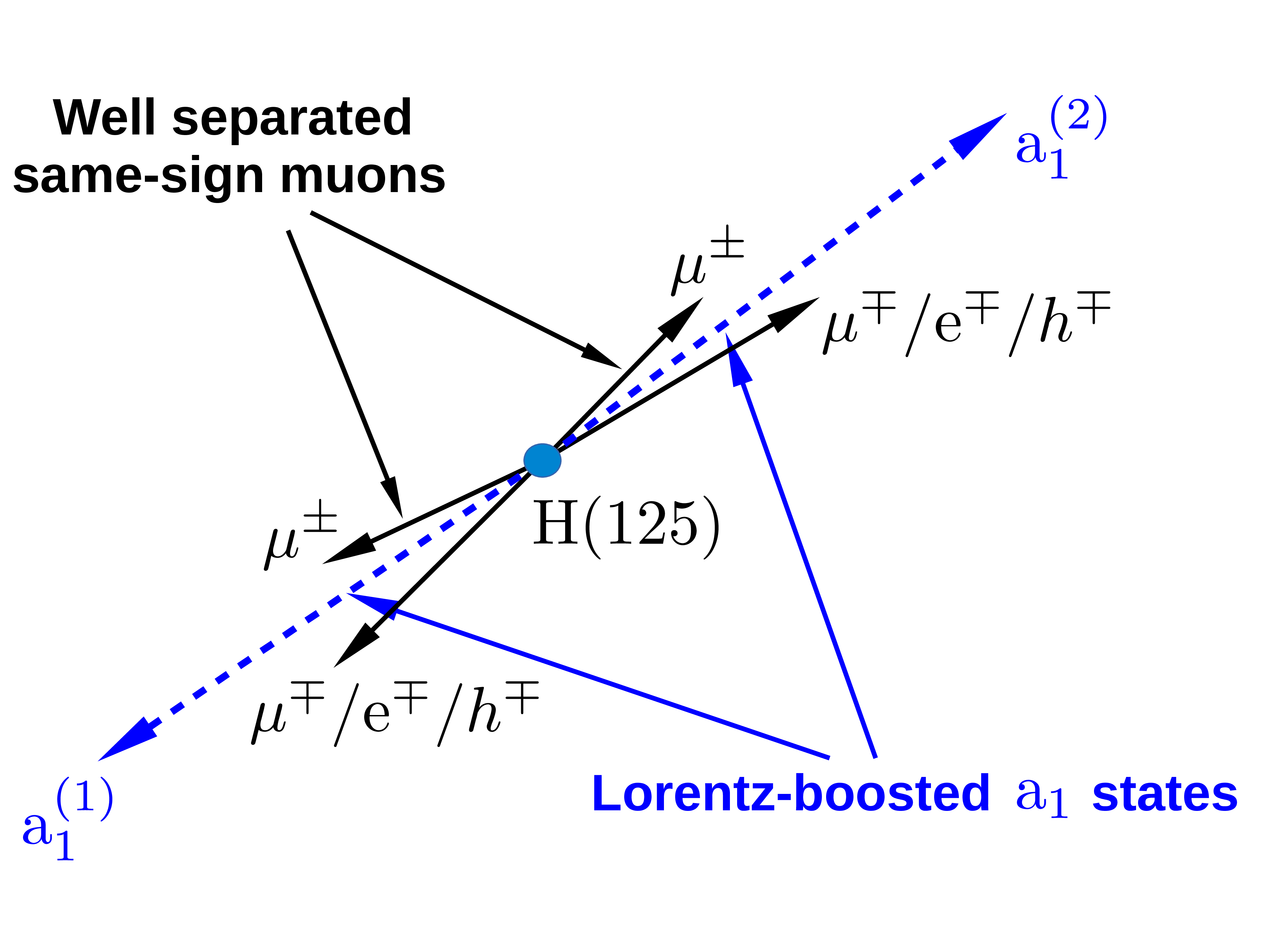
Figure 1:
Illustration of the signal topology. The H(125) decays into two $ {\mathrm {a}_1}$ bosons, where one decays into a pair of $ {\tau}$ leptons, while the other one decays into a pair of muons or a pair of $ {\tau}$ leptons. The analyzed final state consists of one muon and an oppositely charged track in each $ {\mathrm {a}_1}$ decay leg. |
png pdf |
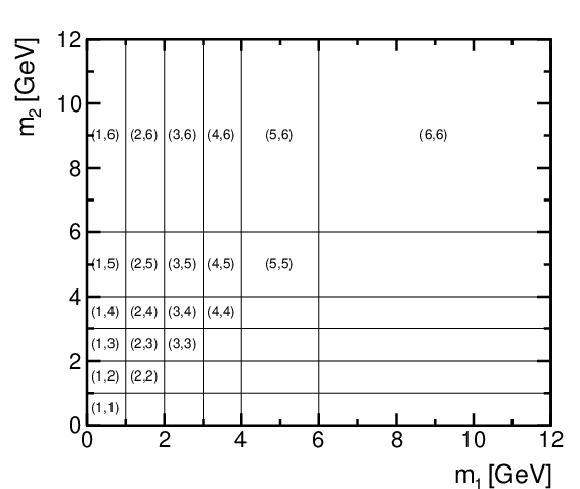
Figure 2:
Binning of the 2D ($m_1$, $m_2$) distribution. The last bin is an overflow bin and includes also masses up to 15 GeV, while values in parentheses are given in GeV. |
png pdf |
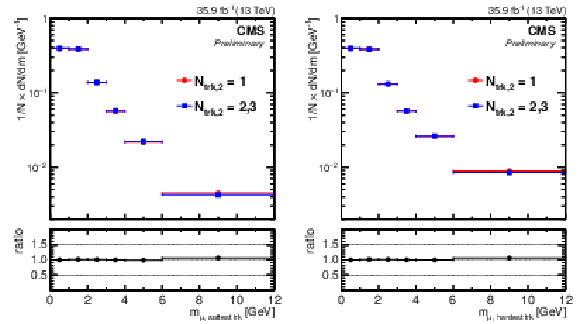
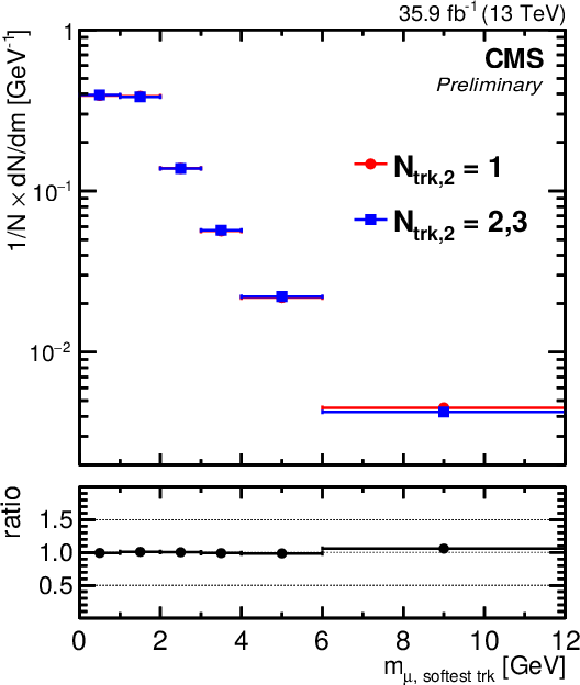
Figure 3:
The observed invariant mass distribution, normalized to unity, of the first muon and the softest (left plot) or hardest (right plot) accompanying track for different isolation requirements imposed on the second muon: when the second muon has only one accompanying track ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 1; circles); or when it has two or three accompanying tracks ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 2, 3; squares). |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
The observed invariant mass distribution, normalized to unity, of the first muon and the softest accompanying track for different isolation requirements imposed on the second muon: when the second muon has only one accompanying track ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 1; circles); or when it has two or three accompanying tracks ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 2, 3; squares). |
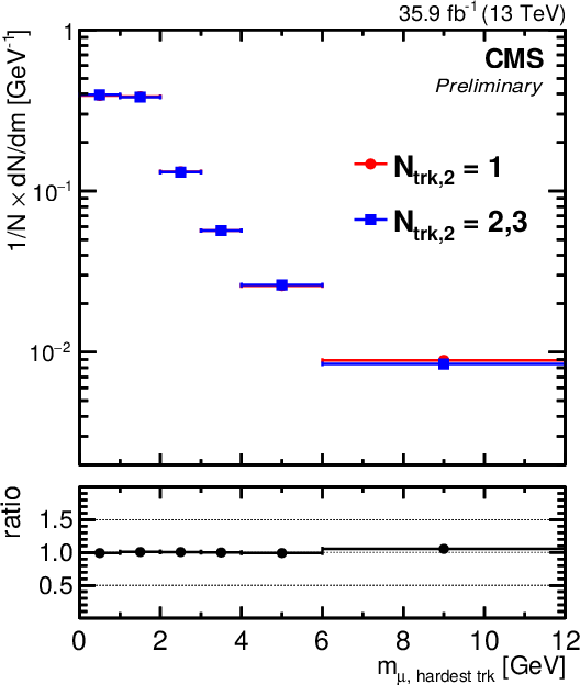
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
The observed invariant mass distribution, normalized to unity, of the first muon and the hardest accompanying track for different isolation requirements imposed on the second muon: when the second muon has only one accompanying track ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 1; circles); or when it has two or three accompanying tracks ($N_\mathrm {trk,2}=$ 2, 3; squares). |
png pdf |
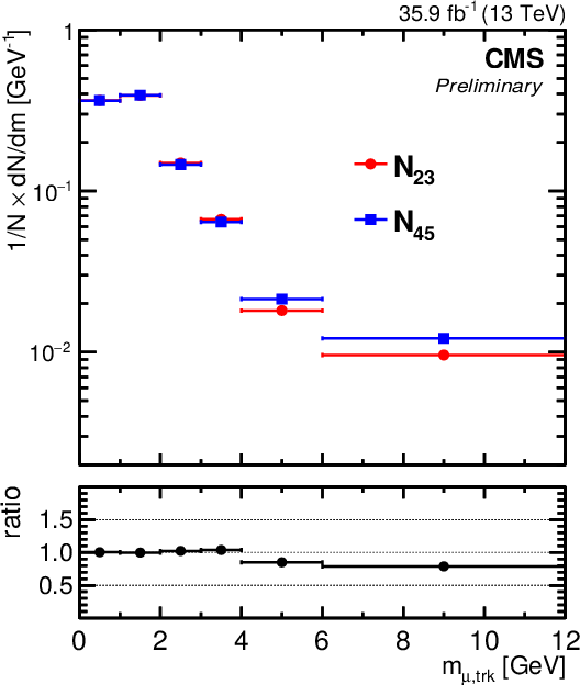
Figure 4:
The observed invariant mass distribution, normalized to unity, of the muon-track invariant mass in control regions $N_{23}$ (circles) and $N_{45}$ (squares). |
png pdf |
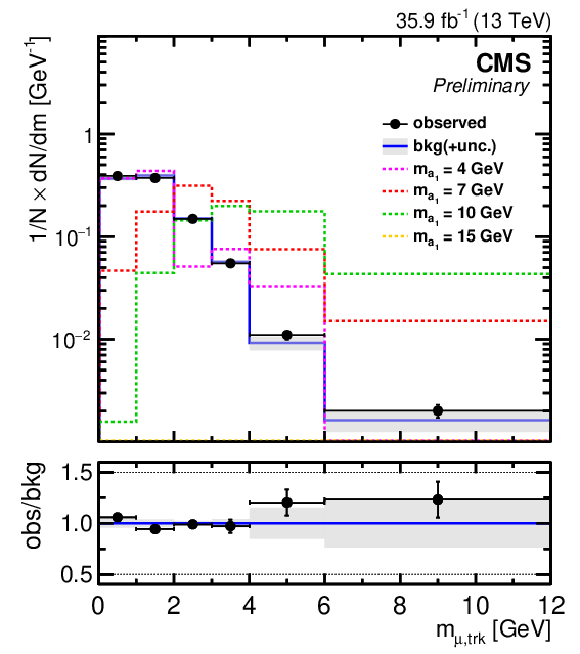
Figure 5:
Normalized invariant mass distribution of the muon-track system for events passing the signal selection. Observed numbers of events are represented by data points with error bars. The QCD multijet background model is derived from the control region $N_{23}$. Also shown are the normalized distributions from signal simulations for four mass hypotheses, $m_{{\mathrm {a}_1}}=$ 4, 7, 10, and 15 GeV (dashed histograms). Each event in the observed and expected signal distributions contributes two entries, corresponding to the two muon-track systems in each event passing the requirements. The lower panel shows the ratio of the observed to expected number of background events in each bin of the distribution. The grey shaded area represents the statistical uncertainties. |
png pdf |
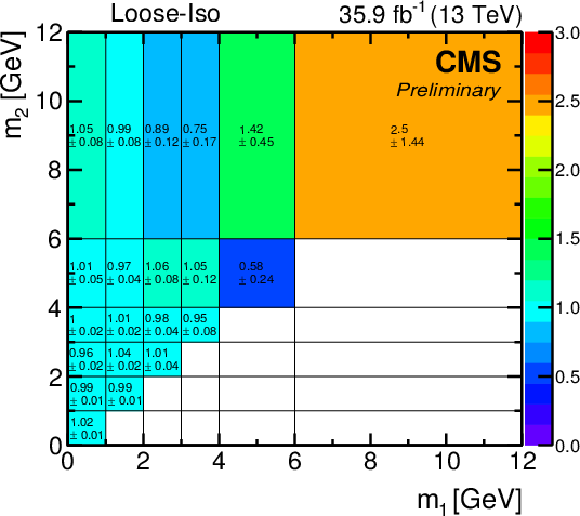
Figure 6:
The ($m_1$, $m_2$) correlation factors $C(i,j)$ with their statistical uncertainties, derived from data in the CR {{Loose-Iso}}. |
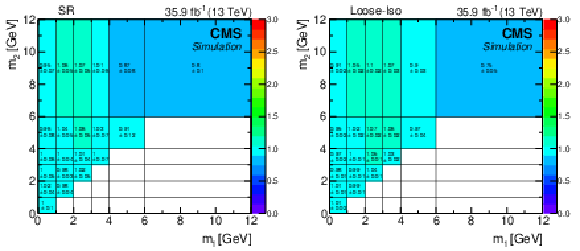
png pdf |
Figure 7:
Left (Right) : The ($m_1$, $m_2$) correlation factors $C(i,j)$ along with their MC statistical uncertainties, derived from simulated samples in the signal region (Loose-Iso CR). |
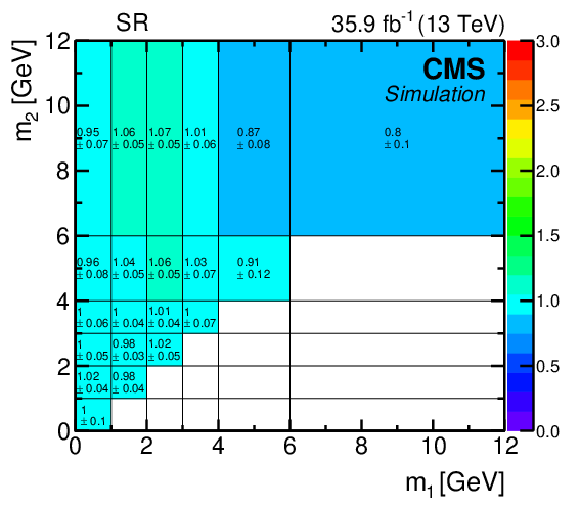
png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
The ($m_1$, $m_2$) correlation factors $C(i,j)$ along with their MC statistical uncertainties, derived from simulated samples in the signal region. |
png pdf |
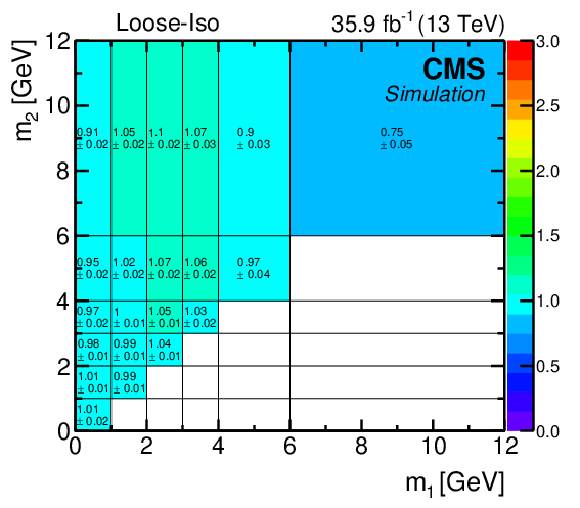
Figure 7-b:
The ($m_1$, $m_2$) correlation factors $C(i,j)$ along with their MC statistical uncertainties, derived from simulated samples in the Loose-Iso CR. |
png pdf |
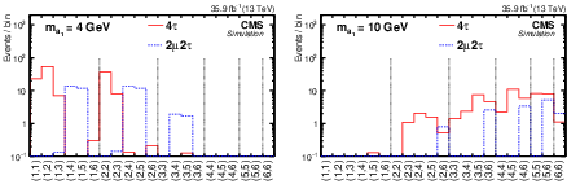
Figure 8:
The distribution of the signal templates $f_\text {2D}(i,j)$ in one row for mass hypotheses $m_{{\mathrm {a}_1}}=$ 4 GeV (left plot) and 10 GeV (right plot). The $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 2\mu 2\tau $ (blue histogram) and $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 4\tau $ (red histogram) contributions are shown. |
png pdf |
Figure 8-a:
The distribution of the signal templates $f_\text {2D}(i,j)$ in one row for mass hypotheses $m_{{\mathrm {a}_1}}=$ 10 GeV. The $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 2\mu 2\tau $ (blue histogram) and $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 4\tau $ (red histogram) contributions are shown. |
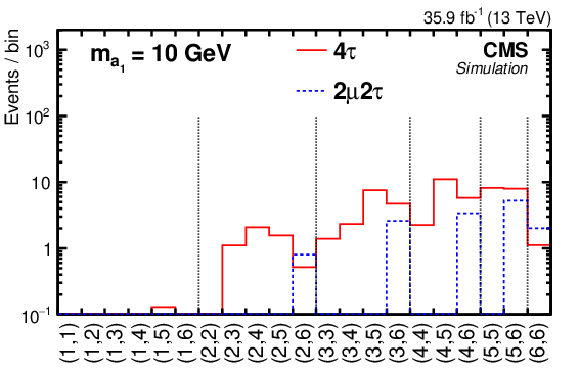
png pdf |
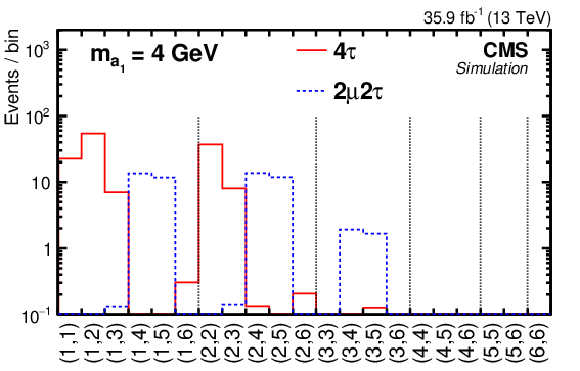
Figure 8-b:
The distribution of the signal templates $f_\text {2D}(i,j)$ in one row for mass hypotheses $m_{{\mathrm {a}_1}}=$ 4 GeV. The $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 2\mu 2\tau $ (blue histogram) and $ {\mathrm {H}} (125)\to {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 4\tau $ (red histogram) contributions are shown. |
png pdf |
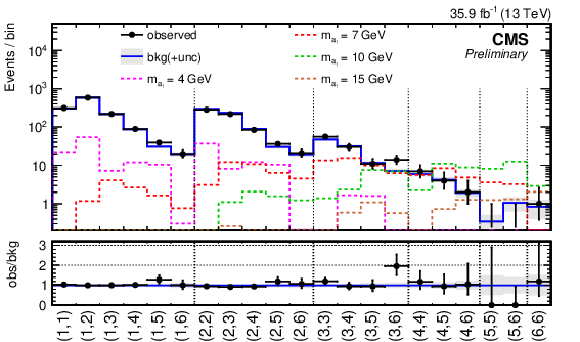
Figure 9:
The ($m_1$, $m_2$) in one row distribution used to extract the signal. Observed numbers of events are represented by data points with error bars. The background with its uncertainty is shown as blue histogram with the shaded error band. The distribution for the background is obtained after performing a maximum likelihood fit to the observed data under the background-only hypothesis. Signal expectations are shown as dotted histograms for the mass hypotheses of $m_{{\mathrm {a}_1}}=$ 4, 7, 10, and 15 GeV. The signal normalization is computed assuming that the H(125) boson is produced in pp collisions with a rate predicted by the SM, and decays into $ {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}\to 4\tau $ final state with the branching fraction of 20%. The lower plot shows the ratio of the observed data events to the expected background yield in each bin of the ($m_1$, $m_2$) distribution. |
png pdf |
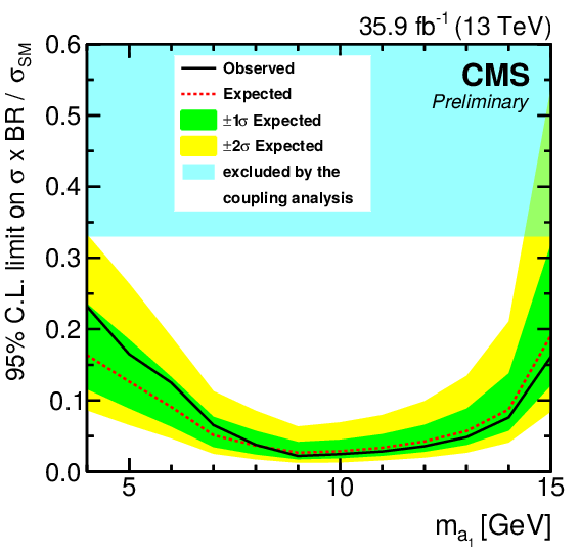
Figure 10:
The observed and expected upper 95% confidence level limits on the signal cross section times the branching fraction $\sigma (pp \rightarrow {\mathrm {H}} (125)+X) \cdot {\cal {B}} ({\mathrm {H}} (125) \rightarrow {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}) \cdot {\cal {B}}^{2} ({\mathrm {a}_1}\rightarrow \tau \tau)$, relative to the inclusive Higgs boson production cross section $\sigma _\text {SM}$ predicted in the SM. The green and yellow bands indicate the regions that contain 68% and 95% of the distribution of upper limits expected assuming no signal is present. The shaded area indicates the excluded value of the branching fraction of the H(125) decay into non-SM particles at 95% CL from Ref. [24]. |
| Tables | |
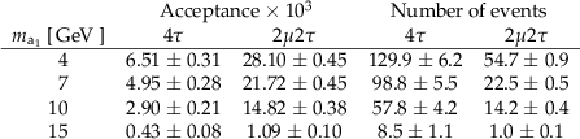
png pdf |
Table 1:
The signal acceptance and the number of expected signal events after final selection. The former is presented for the final state with two same-sign muons, while the signal yields are shown for the benchmark value of branching fraction, ${\cal {B}}({\mathrm {H}} (125) \rightarrow {\mathrm {a}_1} {\mathrm {a}_1}) \cdot {\cal {B}}^{2} ({\mathrm {a}_1}\rightarrow \tau \tau)=$ 0.2. The quoted uncertainties for predictions from simulation include only statistical ones. The number of observed events selected in the signal region amounts to 2035. |
png pdf |
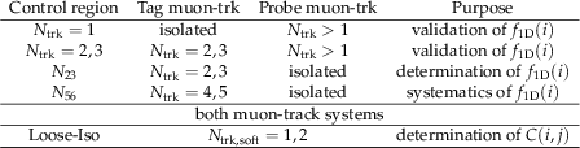
Table 2:
The list of control regions used to model background shape. $N_\mathrm {trk}$ denotes the number of close-by tracks within a cone of $\Delta \rm {R}=$ 0.5 around the muon momentum direction. $N_\mathrm {trk,soft}$ is the number of soft tracks with 1.0 GeV $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} < $ 2.5 GeV in the cone of $\Delta \rm {R}=$ 0.5 around the muon momentum direction. |
png pdf |
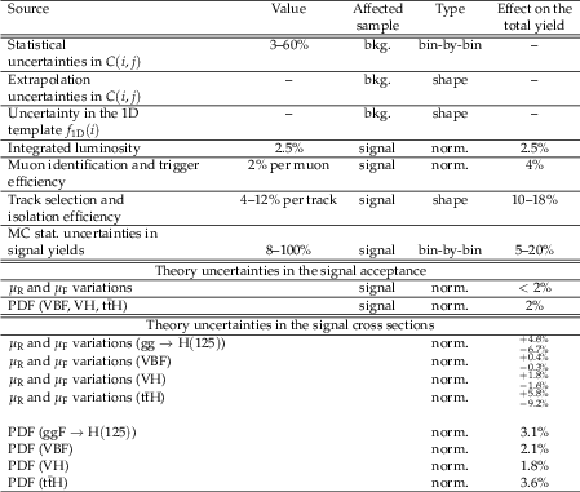
Table 3:
Systematic uncertainties and their effect on the estimates of the QCD multijet background and signal. The effect of the uncertainties in $C(i,j)$ on the total background yield is absorbed by the overall background normalization, which is allowed to vary freely in the fit. |
| Summary |
| A search for a light pseudoscalar boson ${\mathrm{a}_1}$, produced in decays of the H(125) boson is presented, using a data set corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 35.9 fb$^{-1}$ of proton-proton collisions at a centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV. The analysis targets the inclusive production of the H(125) boson and exploits the $\mathrm{H}(125)\to {\mathrm{a}_1} {\mathrm{a}_1} \to 4\tau$ decay mode. The contribution of the $\mathrm{H}(125)\to {\mathrm{a}_1} {\mathrm{a}_1} \to 2\mu 2\tau$ decay channel is also taken into account in the search. No evidence of signal is found in data. The observed 95% confidence level upper limit on the signal cross section times branching fraction, relative to the cross section of the H(125) boson production predicted in the SM ranges from 0.023 at $m_{{\mathrm{a}_1}}=$ 9 GeV to 0.26 at $m_{{\mathrm{a}_1}}=$ 4 GeV. The expected upper limit ranges from 0.028 at $m_{{\mathrm{a}_1}}=$ 9 GeV to 0.19 at $m_{{\mathrm{a}_1}}=$ 15 GeV. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | P. Fayet | Supergauge invariant extension of the Higgs mechanism and a model for the electron and its neutrino | NPB 90 (1975) 104 | |
| 2 | R. K. Kaul and P. Majumdar | Cancellation of quadratically divergent mass corrections in globally supersymmetric spontaneously broken gauge theories | NPB 199 (1982) 36 | |
| 3 | R. Barbieri, S. Ferrara, and C. A. Savoy | Gauge models with spontaneously broken local supersymmetry | PLB 119 (1982) 343 | |
| 4 | H. P. Nilles, M. Srednicki, and D. Wyler | Weak interaction breakdown induced by supergravity | PLB 120 (1983) 346 | |
| 5 | J.-M. Frere, D. R. T. Jones, and S. Raby | Fermion masses and induction of the weak scale by supergravity | NPB 222 (1983) 11 | |
| 6 | J.-P. Derendinger and C. A. Savoy | Quantum effects and SU(2)$ \times $U(1) breaking in supergravity gauge theories | NPB 237 (1984) 307 | |
| 7 | U. Ellwanger, C. Hugonie, and A. M. Teixeira | The Next-to-Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model | PR 496 (2010) 1 | 0910.1785 |
| 8 | M. Maniatis | The Next-to-Minimal Supersymmetric extension of the Standard Model reviewed | Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 25 (2010) 3505 | 0906.0777 |
| 9 | J. E. Kim and H. P. Nilles | The $ \mu $-problem and the strong CP-problem | PLB 138 (1984) 150 | |
| 10 | G. Belanger et al. | Higgs Bosons at 98 and 125 GeV at LEP and the LHC | JHEP 01 (2013) 069 | 1210.1976 |
| 11 | G. Belanger et al. | Two Higgs Bosons at the Tevatron and the LHC? | 1208.4952 | |
| 12 | J. F. Gunion, Y. Jiang, and S. Kraml | Diagnosing Degenerate Higgs Bosons at 125 GeV | PRL 110 (2013) 051801 | 1208.1817 |
| 13 | J. F. Gunion, Y. Jiang, and S. Kraml | Could two NMSSM Higgs bosons be present near 125 GeV? | PRD 86 (2012) 071702 | 1207.1545 |
| 14 | S. F. King, M. Muhlleitner, and R. Nevzorov | NMSSM Higgs benchmarks near 125 GeV | NPB 860 (2012) 207 | 1201.2671 |
| 15 | S. F. King, M. Muhlleitner, R. Nevzorov, and K. Walz | Natural NMSSM Higgs bosons | NPB 870 (2013) 323 | 1211.5074 |
| 16 | U. Ellwanger, J. F. Gunion, and C. Hugonie | Difficult scenarios for NMSSM Higgs discovery at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2005) 041 | hep-ph/0503203 |
| 17 | U. Ellwanger, J. F. Gunion, C. Hugonie, and S. Moretti | Towards a No-Lose Theorem for NMSSM Higgs Discovery at the LHC | in Physics at TeV colliders, Les Houches workshop 2003 | hep-ph/0305109 |
| 18 | U. Ellwanger, J. F. Gunion, C. Hugonie, and S. Moretti | NMSSM Higgs Discovery at the LHC | in Physics at TeV colliders, Les Houches workshop 2003 | hep-ph/0401228 |
| 19 | A. Belyaev et al. | The Scope of the 4 tau Channel in Higgs-strahlung and Vector Boson Fusion for the NMSSM No-Lose Theorem at the LHC | 0805.3505 | |
| 20 | A. Belyaev et al. | LHC discovery potential of the lightest NMSSM Higgs boson in the $ h_1 \to a_1 a_1 \rightarrow 4 \mu $ channel | PRD 81 (2010) 075021 | 1002.1956 |
| 21 | M. Lisanti and J. G. Wacker | Discovering the Higgs boson with low mass muon pairs | PRD 79 (2009) 115006 | 0903.1377 |
| 22 | M. M. Almarashi and S. Moretti | Scope of Higgs production in association with a bottom quark pair in probing the Higgs sector of the NMSSM at the LHC | 1205.1683 | |
| 23 | M. M. Almarashi and S. Moretti | LHC signals of a heavy CP-even Higgs boson in the NMSSM via decays into a $ Z $ and a light CP-odd Higgs state | PRD 85 (2012) 017701 | 1109.1735 |
| 24 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Measurements of the Higgs boson production and decay rates and constraints on its couplings from a combined ATLAS and CMS analysis of the LHC pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 08 (2016) 045 | 1606.02266 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | Search for light bosons in decays of the 125 GeV Higgs boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV | JHEP 10 (2017) 076 | CMS-HIG-16-015 1701.02032 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a very light NMSSM Higgs boson produced in decays of the 125 GeV scalar boson and decaying into $ \tau $ leptons in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV | JHEP 01 (2016) 079 | CMS-HIG-14-019 1510.06534 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | A search for pair production of new light bosons decaying into muons | PLB 752 (2016) 146 | CMS-HIG-13-010 1506.00424 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Search for an exotic decay of the Higgs boson to a pair of light pseudoscalars in the final state of two muons and two $ \tau $ leptons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JHEP 11 (2018) 018 | CMS-HIG-17-029 1805.04865 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Search for an exotic decay of the Higgs boson to a pair of light pseudoscalars in the final state with two b quarks and two $ \tau $ leptons in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | PLB785 (2018) 462 | CMS-HIG-17-024 1805.10191 |
| 30 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for the Higgs boson produced in association with a W boson and decaying to four $ b $-quarks via two spin-zero particles in pp collisions at 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 76 (2016) 605 | 1606.08391 |
| 31 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new light gauge bosons in Higgs boson decays to four-lepton final states in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PRD 92 (2015) 092001 | 1505.07645 |
| 32 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in events with at least three photons collected in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 76 (2016) 210 | 1509.05051 |
| 33 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for Higgs bosons decaying to $ aa $ in the $ {\mu} {\mu} {\tau} {\tau} $ final state in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}=8\text{}\text{}\mathrm{TeV} $ with the ATLAS experiment | PRD 92 (2015) 052002 | 1505.01609 |
| 34 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for Higgs boson decays into pairs of light (pseudo)scalar particles in the $ \gamma\gamma jj $ final state in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB782 (2018) 750--767 | 1803.11145 |
| 35 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for higgs decays to beyond the standard model light gauge bosons in four-lepton events with the atlas detector at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 tev | Submitted to JHEP | 1802.03388 |
| 36 | CMS Collaboration | A search for pair production of new light bosons decaying into muons in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV | Submitted to: PL(2018) | CMS-HIG-18-003 1812.00380 |
| 37 | D. Curtin et al. | Exotic decays of the 125 GeV Higgs boson | PRD 90 (2014) 075004 | 1312.4992 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 40 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | CPC 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 41 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 42 | G. Bozzi, S. Catani, D. de Florian, and M. Grazzini | Transverse-momentum resummation and the spectrum of the Higgs boson at the LHC | NPB737 (2006) 73--120 | hep-ph/0508068 |
| 43 | D. de Florian, G. Ferrera, M. Grazzini, and D. Tommasini | Transverse-momentum resummation: Higgs boson production at the Tevatron and the LHC | JHEP 11 (2011) 064 | 1109.2109 |
| 44 | NNPDF Collaboration | Parton distributions for the LHC Run II | JHEP 04 (2015) 040 | 1410.8849 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | Event generator tunes obtained from underlying event and multiparton scattering measurements | EPJC76 (2016) 155 | CMS-GEN-14-001 1512.00815 |
| 46 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4 --- a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017), no. 10, P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 48 | W. Adam, B. Mangano, T. Speer, and T. Todorov | Track reconstruction in the CMS tracker | CMS-NOTE-2006-041 | |
| 49 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014), no. 10, P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 50 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ k_t $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 51 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet User Manual | EPJC72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 52 | M. Lisanti and J. G. Wacker | Discovering the higgs boson with low mass muon pairs | PRD 79 (2010) 115006 | 0903.1377 |
| 53 | CMS Collaboration | CMS Luminosity Measurements for the 2016 Data Taking Period | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 |
| 54 | J. Pumplin et al. | New generation of parton distributions with uncertainties from global QCD analysis | JHEP 07 (2002) 012 | hep-ph/0201195 |
| 55 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: the $ \rm CL_s $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 56 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIMA 434 (1999) 435 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 57 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 58 | L. Moneta et al. | The RooStats Project | in 13th International Workshop on Advanced Computing and Analysis Techniques in Physics Research (ACAT2010) SISSA | 1009.1003 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|