

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-BPH-19-001 ; CERN-EP-2020-146 | ||
| Measurement of $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ and $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ cross section ratios in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 19 August 2020 | ||
| Phys. Rev. D 102 (2020) 092007 | ||
| Abstract: The ratios of the $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, and $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ production cross sections are measured in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV, using a data sample collected by the CMS experiment at the LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 143 fb$^{-1}$. The three measurements are made in the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ meson phase space region defined by the transverse momentum ${p_{\mathrm{T}}} > $ 15 GeV and absolute rapidity $|y| < $ 2.4, with the excited $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ states reconstructed through the ${ \mathrm{B_c^{+}} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}} $, followed by the ${ \mathrm{B_c^{+}} \! \to \! \mathrm{J/\psi} \, \pi^{+}}$ and ${ \mathrm{J/\psi} \! \to \! \mu^{+}\mu^{-}}$ decays. The $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, and $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ cross section ratios, including the unknown $ \mathrm{B^{(*)}_c(2S)^{+}} \!\to\! \mathrm{B_{c}^{(*)+}} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}$ branching fractions, are (3.47 $\pm$ 0.63 (stat) $\pm$ 0.33 (syst))%, (4.69 $\pm$ 0.71 (stat) $\pm$ 0.56 (syst))%, and 1.35 $\pm$ 0.32 (stat) $\pm$ 0.09 (syst), respectively. None of these ratios shows a significant dependence on the ${p_{\mathrm{T}}}$ or $|y|$ of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ meson. The normalized dipion invariant mass distributions from the decays ${ \mathrm{B^{(*)}_c(2S)^{+}} \!\to\! \mathrm{B_{c}^{(*)+}} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}} $ are also reported. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2008.08629 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
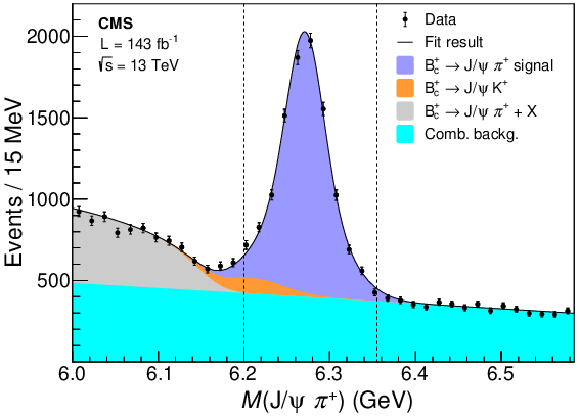
Figure 1:
Invariant mass distribution of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}} \, \to \, \mathrm{J}/\psi \, \pi^{+}$ candidates, after applying all event selection criteria [1]. The fitted contributions are shown by the stacked distributions, the solid line representing their sum. The vertical dashed lines indicate the mass window used to select the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ candidates for the $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ reconstruction. |
png pdf |
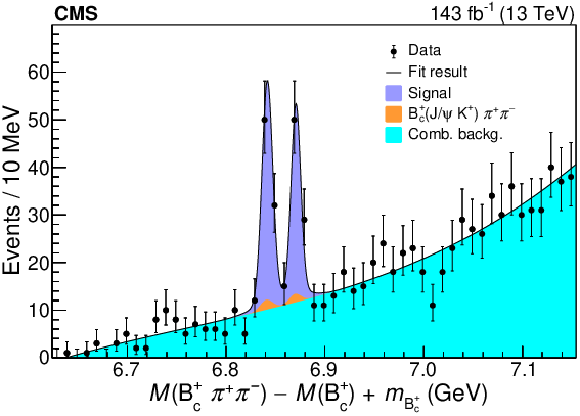
Figure 2:
Invariant mass distribution of the ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ candidates [1]. The ${\mathrm{B_c} ^{*}\mathrm {(2S)}^{\,+}}$ corresponds to the lower-mass peak, the ${\mathrm{B_c} \mathrm {(2S)}^{\,+}}$ to the higher. The fitted contributions are shown by the stacked distributions, the solid line representing their sum. |

png pdf |
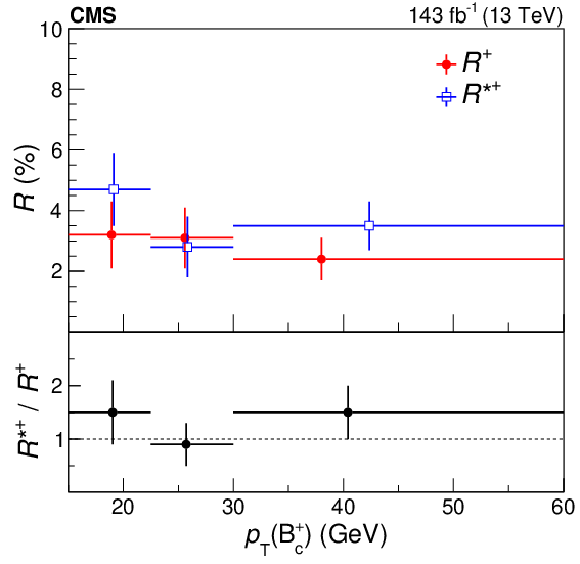
Figure 3:
The $R^{+}$ and $R^{*+}$ (upper), and $R^{*+}/R^{+}$ (lower) cross section ratios, including the ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ branching fractions, as functions of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ ${p_{\mathrm {T}}}$ (left) and $ {| y |}$ (right). The horizontal bars show the bin widths. The markers are shown at the average $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ ${p_{\mathrm {T}}}$ or $ {| y |}$ values of the events contributing to each bin, in the background-subtracted distributions, and the vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainties only. The systematic uncertainties are essentially independent of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ kinematics. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
The $R^{+}$ and $R^{*+}$ (upper), and $R^{*+}/R^{+}$ (lower) cross section ratios, including the ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ branching fractions, as functions of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ ${p_{\mathrm {T}}}$. The horizontal bars show the bin widths. The markers are shown at the average $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ ${p_{\mathrm {T}}}$ values of the events contributing to each bin, in the background-subtracted distributions, and the vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainties only. The systematic uncertainties are essentially independent of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ kinematics. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
The $R^{+}$ and $R^{*+}$ (upper), and $R^{*+}/R^{+}$ (lower) cross section ratios, including the ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ branching fractions, as functions of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ $ {| y |}$. The horizontal bars show the bin widths. The markers are shown at the average $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ $ {| y |}$ values of the events contributing to each bin, in the background-subtracted distributions, and the vertical bars represent the statistical uncertainties only. The systematic uncertainties are essentially independent of the $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ kinematics. |
png pdf |
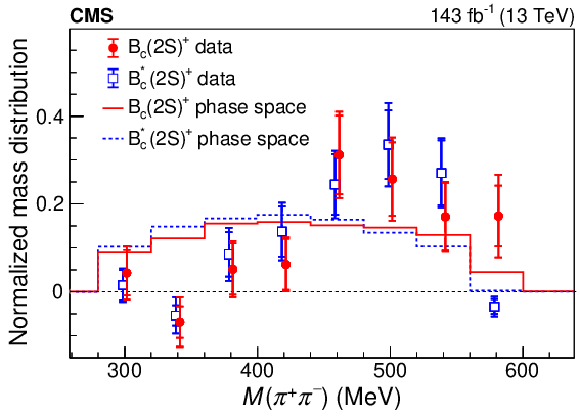
Figure 4:
The dipion invariant mass distributions from ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ decays in data, normalized to unity. The inner and outer tick marks designate the statistical and total uncertainties, respectively. The lines show the corresponding predictions from phase space simulations. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Ratios of the reconstruction efficiencies relevant for the determination of the $R^{+}$, $R^{*+}$, and $R^{*+}/R^{+}$ cross section ratios. The central values are followed by the several uncertainties presented in the text. |
png pdf |
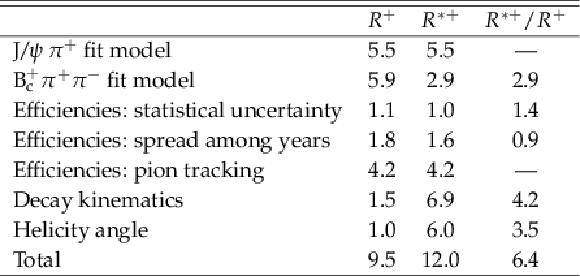
Table 2:
Relative systematic uncertainties (in %) in the cross section ratios, including the ${\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}} \,\to \, \mathrm{B_c} ^{(*)+} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ branching fractions, corresponding to the sources described in the text. The total uncertainty is the sum in quadrature of the individual terms. |
| Summary |
|
The ratios of the $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$, and $\mathrm{B^{*}_c(2S)^{+}}$ to $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ production cross sections, $R^{+}$, $R^{*+}$, and $R^{*+}/R^{+}$, respectively, have been measured in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV. Data set used in the analysis corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 143 fb$^{-1}$ collected by the CMS experiment at the LHC between 2015 and 2018. The $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ mesons were reconstructed through the decays ${ \mathrm{B^{(*)}_c(2S)^{+}} \!\to\! \mathrm{B_{c}^{(*)+}} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}} $, followed by the ${ \mathrm{B_c^{+}} \! \to \! \mathrm{J/\psi} \, \pi^{+}}$ and ${ \mathrm{J/\psi} \! \to \! \mu^{+}\mu^{-}}$. The measured cross section ratios, including the (unknown) ${ \mathrm{B^{(*)}_c(2S)^{+}} \!\to\! \mathrm{B_{c}^{(*)+}} \pi^{+}\pi^{-}}$ branching fractions, are |
| References | ||||
| 1 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of two excited $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ states and measurement of the $\mathrm{B_c(2S)^{+}}$ mass in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 122 (2019) 132001 | CMS-BPH-18-007 1902.00571 |
| 2 | LHCb Collaboration | Observation of an excited $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ state | PRL 122 (2019) 232001 | 1904.00081 |
| 3 | E. B. Gregory et al. | A prediction of the $\mathrm{B_c^{*}}$ mass in full lattice QCD | PRL 104 (2010) 022001 | 0909.4462 |
| 4 | R. J. Dowdall, C. T. H. Davies, T. C. Hammant, and R. R. Horgan | Precise heavy-light meson masses and hyperfine splittings from lattice QCD including charm quarks in the sea | PRD 86 (2012) 094510 | 1207.5149 |
| 5 | N. Mathur, M. Padmanath, and S. Mondal | Precise predictions of charmed-bottom hadrons from lattice QCD | PRL 121 (2018) 202002 | 1806.04151 |
| 6 | E. J. Eichten and C. Quigg | Mesons with beauty and charm: New horizons in spectroscopy | PRD 99 (2019) 054025 | 1902.09735 |
| 7 | A. V. Berezhnoy, I. N. Belov, A. K. Likhoded, and A. V. Luchinsky | $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ excitations at LHC experiments | MPLA. 34 (2019) 1950331 | 1904.06732 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS muon detector and muon reconstruction with proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018) P06015 | CMS-MUO-16-001 1804.04528 |
| 13 | Particle Data Group, M. Tanabashi et al. | Review of particle physics | PRD 98 (2018) 030001 | |
| 14 | R. Fruhwirth, W. Waltenberger, and P. Vanlaer | Adaptive vertex fitting | JPG 34 (2007) N343 | |
| 15 | ARGUS Collaboration | Search for hadronic b$ \to $u decays | PLB 241 (1990) 278 | |
| 16 | LHCb Collaboration | Measurement of the ratio of branching fractions $ \mathcal{B}(\mathrm{B_c^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi K^{+})/\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{B_c^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\pi^{+}) $ | JHEP 09 (2016) 153 | 1607.06823 |
| 17 | C.-H. Chang, X.-Y. Wang, and X.-G. Wu | BCVEGPY2.2: a newly upgraded version for hadronic production of the meson $\mathrm{B_c^{+}}$ and its excited states | CPC 197 (2015) 335 | 1507.05176 |
| 18 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | CPC 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 19 | D. Lange | The EvtGen particle decay simulation package | NIMA 462 (2001) 152 | |
| 20 | N. Davidson, T. Przedzinski, and Z. Was | PHOTOS interface in C++: technical and physics documentation | CPC 199 (2016) 86 | 1011.0937 |
| 21 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4--a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2015 data-taking period | CMS-PAS-LUM-15-001 | CMS-PAS-LUM-15-001 |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurements for the 2016 data-taking period | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-001 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2017 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-004 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement for the 2018 data-taking period at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 | CMS-PAS-LUM-18-002 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Tracking POG results for pion efficiency with the D* meson using data from 2016 and 2017 | CDS | |
| 27 | S. Jackman | Bayesian analysis for the social sciences | John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, USA | |
| 28 | M. Pivk and F. R. Le Diberder | SPlot: a statistical tool to unfold data distributions | NIMA 555 (2005) 356 | physics/0402083 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|