

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-BPH-18-005 | ||
| Study of the $\mathrm{B}^{+}\rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p}$ decay in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| March 2019 | ||
| Abstract: A study of the $\mathrm{B}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p}$ decay is reported, using proton-proton collision data collected at $\sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV by the CMS experiment at the LHC, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 19.6 fb$^{-1}$. The ratio of branching fractions ${{\cal B}(\mathrm{B}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p})}/{{\cal B}(\mathrm{B}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi \mathrm{K}^{*+})}$ is measured to be 1.054 $\pm$ 0.057 (stat) $\pm$ 0.028 (syst) $\pm$ 0.011 (${\cal B}$)%, where the first uncertainty is statistical, the second is systematic, and the third reflects the uncertainties in the world-average branching fractions. The invariant mass distributions of $\mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda}$, $\mathrm{J}/\psi \mathrm{p}$, and $\bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p}$ systems produced in the $\mathrm{B}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p}$ decay are investigated and found to be inconsistent with the pure phase space hypothesis. The analysis is extended by using a model-independent angular amplitude analysis, which shows that the inclusion of contributions from excited kaons in the $\bar{\Lambda} \mathrm{p}$ system does improve the description of the observed invariant mass distributions. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, JHEP 12 (2019) 100. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
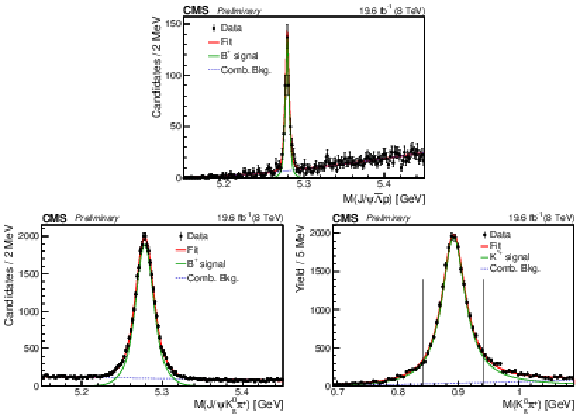
Figure 1:
Invariant mass distribution of the selected $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ candidates (upper). The $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {\mathrm {K^0_S}} {\pi ^+}$ (lower left) and $ {\mathrm {K^0_S}} {\pi ^+}$ (lower right) invariant mass distributions in the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}} $ decay. The points are data and the curves are results of the fits described in the text. The vertical lines in the last plot indicate the $ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}} $ invariant mass window used for the normalization, as described in the text. |
png pdf |
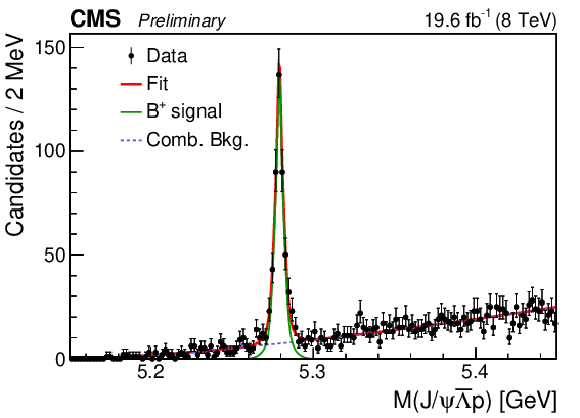
Figure 1-a:
Invariant mass distribution of the selected $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ candidates. The points are data and the curves are results of the fits described in the text. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
The $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {\mathrm {K^0_S}} {\pi ^+}$ invariant mass distribution in the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}} $ decay. The points are data and the curves are results of the fits described in the text. |
png pdf |
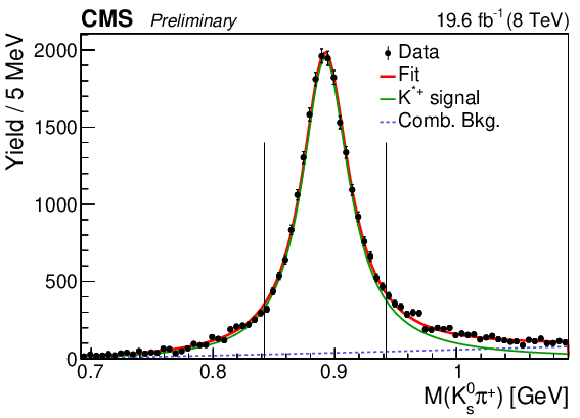
Figure 1-c:
The $ {\mathrm {K^0_S}} {\pi ^+}$ invariant mass distribution in the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}} $ decay. The points are data and the curves are results of the fits described in the text. The vertical lines indicate the $ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}} $ invariant mass window used for the normalization, as described in the text. |
png pdf |
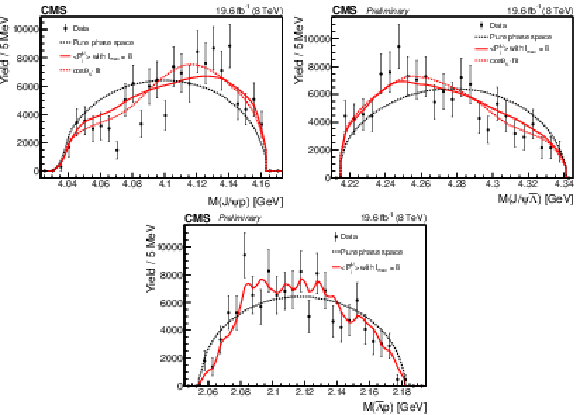
Figure 2:
The invariant mass distributions of the $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} \, {\mathrm {p}}$ (upper left), $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}}$ (upper right), and $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ (lower) systems from the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ decay. The points are efficiency-corrected and background-subtracted data. Superimposed curves are obtained from simulation: the red curve represents the phase space distribution corrected by the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ angular structure with the inclusion of the first eight moments corresponding to the resonances in the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ system with the maximum spin $S=4$; the dashed red curve is the fit to the phase space distribution reweighted according to the 1D $\cos\theta _{{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}}$ distribution, which is defined as the $H_1$ hypothesis and explained in Section 8.3; the black dashed line corresponds to the pure phase space fit. |
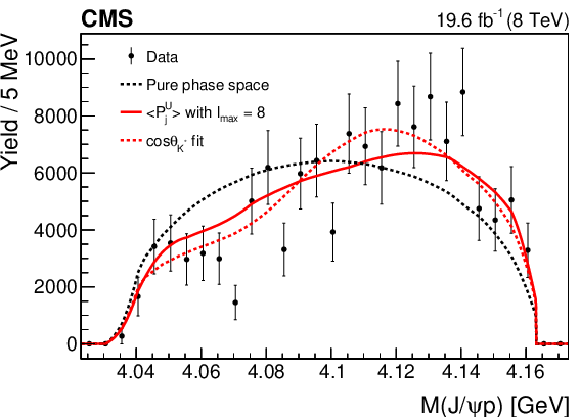
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
The invariant mass distribution of the $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} \, {\mathrm {p}}$ system from the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ decay. The points are efficiency-corrected and background-subtracted data. Superimposed curves are obtained from simulation: the red curve represents the phase space distribution corrected by the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ angular structure with the inclusion of the first eight moments corresponding to the resonances in the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ system with the maximum spin $S=4$; the dashed red curve is the fit to the phase space distribution reweighted according to the 1D $\cos\theta _{{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}}$ distribution, which is defined as the $H_1$ hypothesis and explained in Section 8.3; the black dashed line corresponds to the pure phase space fit. |
png pdf |
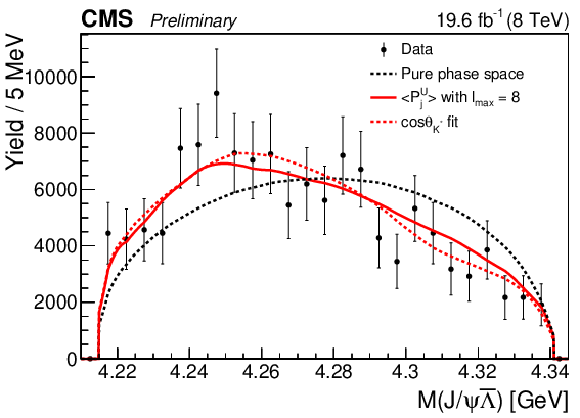
Figure 2-b:
The invariant mass distribution of the $ {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}}$ system from the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ decay. The points are efficiency-corrected and background-subtracted data. Superimposed curves are obtained from simulation: the red curve represents the phase space distribution corrected by the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ angular structure with the inclusion of the first eight moments corresponding to the resonances in the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ system with the maximum spin $S=4$; the dashed red curve is the fit to the phase space distribution reweighted according to the 1D $\cos\theta _{{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}}$ distribution, which is defined as the $H_1$ hypothesis and explained in Section 8.3; the black dashed line corresponds to the pure phase space fit. |
png pdf |
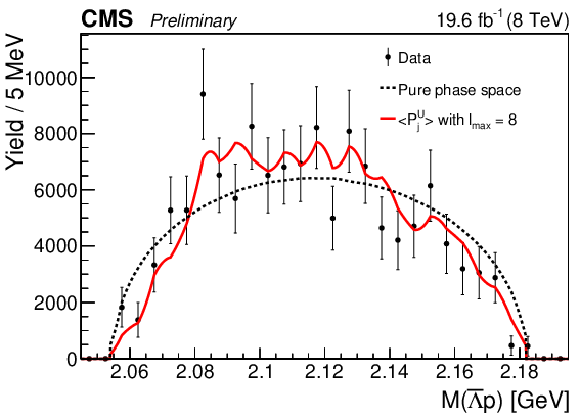
Figure 2-c:
The invariant mass distribution of the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ system from the $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ decay. The points are efficiency-corrected and background-subtracted data. Superimposed curves are obtained from simulation: the red curve represents the phase space distribution corrected by the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ angular structure with the inclusion of the first eight moments corresponding to the resonances in the $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ system with the maximum spin $S=4$; the dashed red curve is the fit to the phase space distribution reweighted according to the 1D $\cos\theta _{{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}}$ distribution, which is defined as the $H_1$ hypothesis and explained in Section 8.3; the black dashed line corresponds to the pure phase space fit. |

png pdf |
Figure 3:
The illustration of decay angles in $ {{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$ decay. |

png pdf |
Figure 4:
The background-subtracted and efficiency-corrected $\cos(\theta _{{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}})$ distribution on data and simulation. |

png pdf |
Figure 5:
The dependence of first unnormalized Legendre moments on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |

png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
The dependence of the first unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
png pdf |
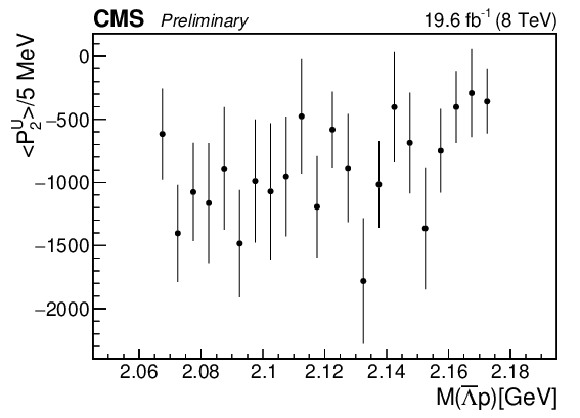
Figure 5-b:
The dependence of the second unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
png pdf |
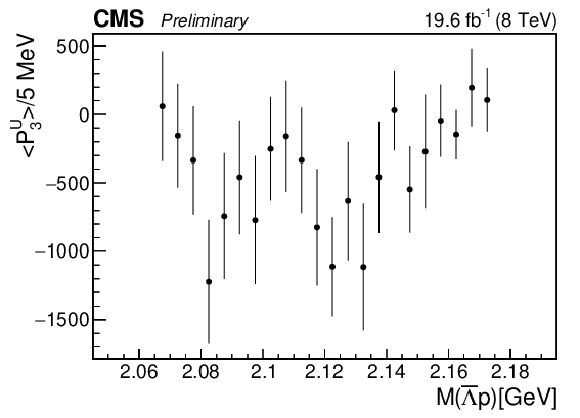
Figure 5-c:
The dependence of the third unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |

png pdf |
Figure 5-d:
The dependence of the fourth unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
png pdf |
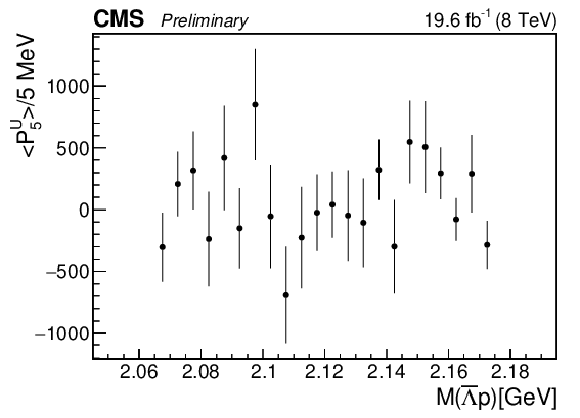
Figure 5-e:
The dependence of the fifth unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
png pdf |
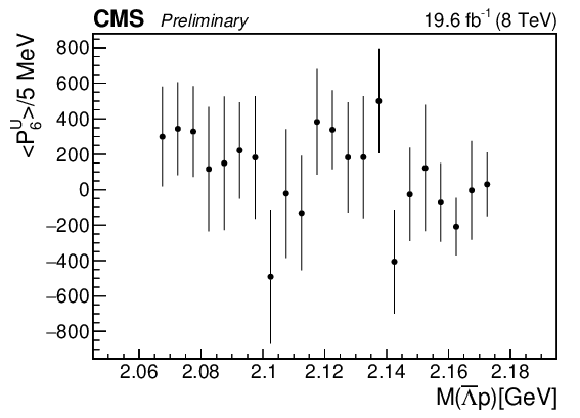
Figure 5-f:
The dependence of the sixth unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
png pdf |
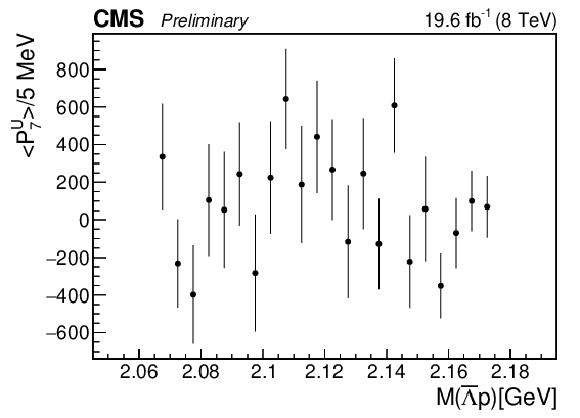
Figure 5-g:
The dependence of the seventh unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
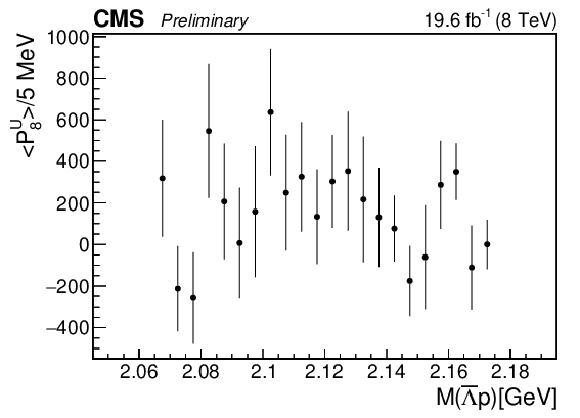
png pdf |
Figure 5-h:
The dependence of the eighth unnormalized Legendre moment on $M( {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})$. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Summary of the relative systematic uncertainties in the $ {{\cal B}({{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}})} / {{\cal B}({{\mathrm {B}^{+}}}\to {\mathrm {J}/\psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*+}})}$ ratio. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Known excited $ {{\mathrm {K}}} ^{*}$ states [3] that can decay to $ {{\overline {\Lambda}}} {\mathrm {p}}$. |
| Summary |
| Using the data set of proton-proton collisions, collected by the CMS experiment at $\sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV and corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 19.6 fb$^{-1}$, we measured the branching fraction ratio ${{\cal B}(\mathrm{B^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\bar{\Lambda} {\mathrm{p}})}/{{\cal B}(\mathrm{B^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi \mathrm{K}^{*+})} = $ (1.054 $\pm$ 0.057 (stat) $\pm$ 0.028 (syst) $\pm$ 0.011 (${\cal B}$) )$\times 10^{-2}$. Using the world-average branching fraction of the $\mathrm{B^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi \mathrm{K}^{*+}$ decay, we obtained ${\cal B}(\mathrm{B^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\bar{\Lambda} {\mathrm{p}}) = $ (15.07 $\pm$ 0.81 (stat) $\pm$ 0.40 (syst) $\pm$ 0.86 (${\cal B}$) )$\times 10^{-6}$. The study of two-body invariant mass distributions of the $\mathrm{B^{+}} \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\bar{\Lambda} {\mathrm{p}}$ decay products was performed, showing that the spectra can not be satisfactory modeled with a phase space distribution. The incompatibility with the phase space hypothesis is more than 5.5, 6, and 3.4 standard deviations for the $\mathrm{J}/\psi \bar{\Lambda}$, $\mathrm{J}/\psi\,{\mathrm{p}}$, and $\bar{\Lambda} {\mathrm{p}}$ mass spectra, respectively. A model-independent approach was used to conclude that the agreement is improved significantly, and is within three standard deviations, once the contribution from K$^{*}$ resonances with spins up to 4 in the $\bar{\Lambda} {\mathrm{p}}$ system is accounted for. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | BaBar Collaboration | Evidence for $ B^+ \to J/\psi p \overline{\Lambda} $ and search for $ B^0 \to J/\psi p \bar{p} $ | PRL 90 (2003) 231801 | hep-ex/0303036 |
| 2 | Belle Collaboration | Observation of $ \mathrm{B}^- \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\Lambda\bar{\mathrm{p}} $ and searches for $ \mathrm{B}^- \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\Sigma^0 \bar{\mathrm{p}} $ and $ \mathrm{B}^0 \to \mathrm{J}/\psi {\mathrm{p}}\bar{\mathrm{p}} $ decays | PRD 72 (2005) 051105 | hep-ex/0508011 |
| 3 | Particle Data Group Collaboration | Review of Particle Physics | PRD 98 (2018) 030001 | |
| 4 | S. J. Brodsky and F. S. Navarra | Looking for exotic multi - quark states in nonleptonic B decays | PLB 411 (1997) 152 | hep-ph/9704348 |
| 5 | CLEO Collaboration | Inclusive decays of $ B $ mesons to charmonium | PRD 52 (1995) 2661 | |
| 6 | BaBar Collaboration | Study of inclusive production of charmonium mesons in $ B $ decay | PRD 67 (2003) 032002 | hep-ex/0207097 |
| 7 | M. Beneke, G. A. Schuler, and S. Wolf | Quarkonium momentum distributions in photoproduction and B decay | PRD 62 (2000) 034004 | hep-ph/0001062 |
| 8 | Belle Collaboration | Search for $ \mathrm{B}^- \to \mathrm{J}/\psi\Lambda\bar{\mathrm{p}} $ decay | PRD 69 (2004) 017101 | hep-ex/0309060 |
| 9 | LHCb Collaboration | First observation of a baryonic $ B_c^+ $ decay | PRL 113 (2014) 152003 | 1408.0971 |
| 10 | LHCb Collaboration | Searches for $ B^0_{(s)} \to J/\psi p\bar{p} $ and $ B^+ \to J/\psi p\bar{p}\pi^+ $ decays | JHEP 09 (2013) 006 | 1306.4489 |
| 11 | LHCb Collaboration | Observation of $ B^0_{(s)} \to J/\psi p \overline{p} $ decays and precision measurements of the $ B^0_{(s)} $ masses | 1902.05588 | |
| 12 | LHCb Collaboration | Observation of $ J/\psi p $ resonances consistent with pentaquark states in $ \Lambda_b^0 \to J/\psi K^- p $ decays | PRL 115 (2015) 072001 | 1507.03414 |
| 13 | LHCb Collaboration | Observation of the $ \Xi^{-}_{b}\to J/\psi\varLambda K^{-} $ decay | PLB 772 (2017) 265 | 1701.05274 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of cms muon reconstruction in $ pp $ collision events at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV | JINST 7 (2012) P10002 | CMS-MUO-10-004 1206.4071 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | CMS tracking performance results from early LHC operation | EPJC 70 (2010) 1165 | CMS-TRK-10-001 1007.1988 |
| 20 | T. Sjostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Skands | PYTHIA 6.4 physics and manual | JHEP 05 (2006) 026 | hep-ph/0603175 |
| 21 | D. J. Lange | The EVTGEN particle decay simulation package | NIMA 462 (2001) 152 | |
| 22 | S. Agostinelli et al. | GEANT4 -- a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 23 | M. Pivk and F. R. Le Diberder | SPlot: A statistical tool to unfold data distributions | NIMA 555 (2005) 356 | physics/0402083 |
| 24 | M. J. Oreglia | A study of the reactions $\psi' \to \gamma\gamma \psi$ | PhD thesis, Stanford University, 1980 SLAC Report SLAC-R-236, see Appendix D | |
| 25 | J. Gaiser | Charmonium Spectroscopy From Radiative Decays of the $\mathrm{J}/\psi$ and $\psi'$ | PhD thesis, SLAC | |
| 26 | BaBar Collaboration | Search for the Z(4430)$ ^- $ at BaBar | PRD 79 (2009) 112001 | 0811.0564 |
| 27 | LHCb Collaboration | Model-independent confirmation of the $ Z(4430)^- $ state | PRD 92 (2015) 112009 | 1510.01951 |
| 28 | LHCb Collaboration | Model-independent evidence for $ J/\psi p $ contributions to $ \Lambda_b^0\to J/\psi p K^- $ decays | PRL 117 (2016) 082002 | 1604.05708 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|