

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-FTR-18-030 | ||
| Sensitivity study for a heavy gauge boson W' in the decay channel with a tau lepton and a neutrino at the High-Luminosity LHC | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| February 2019 | ||
| Abstract: A sensitivity study for the discovery or exclusion of a heavy vector boson W' in the final state with a tau lepton and a neutrino is presented. Event samples are simulated for the Phase-2 CMS detector at the High-Luminosity LHC (corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 3 ab$^{-1}$), using the parameterized detector simulation program DELPHES. A signal would appear as an excess of events with high transverse mass of the hadronic tau and missing transverse momentum, compared to the standard model background. With the high integrated luminosity during Phase-2, a W' boson with SM-like couplings could be observed with a significance exceeding five standard deviations with a mass up to 6.0 TeV. In case of no observation, the results are interpreted as lower limits on the mass of the W' boson in the context of the sequential standard model. In addition, variations in the coupling strength are studied, and a model-independent cross section limit is provided. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
Figure 1:
Illustration of the production and decay of the W' boson with the subsequent hadronic decay of tau ($\tau _h$). |
png pdf |
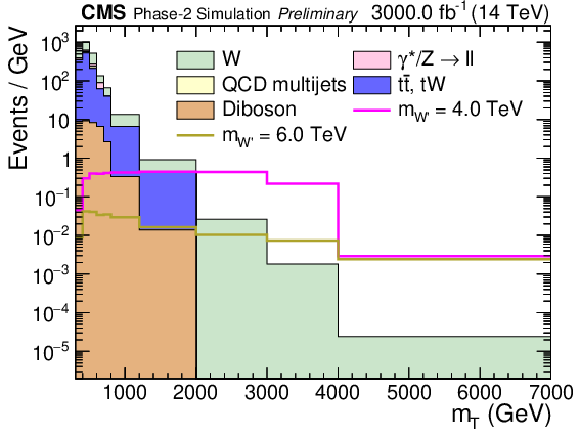
Figure 2:
Distribution of ${m_\mathrm {T}}$, after all selections for HL-LHC conditions of 3000 fb$^{-1}$ and 200 PU. The relevant SM backgrounds are shown according to the labels in the legend. Signal examples for values of the W' boson mass of $m_{{\mathrm {W}'}}=$ 4 TeV and 6 TeV are scaled to their SSM LO cross section and 3000 fb$^{-1}$ integrated luminosity. |
png pdf |
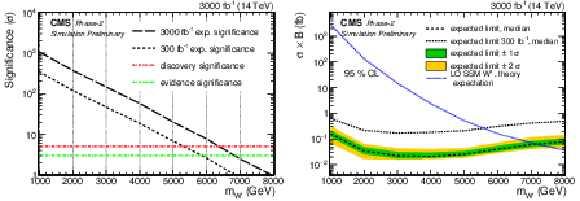
Figure 3:
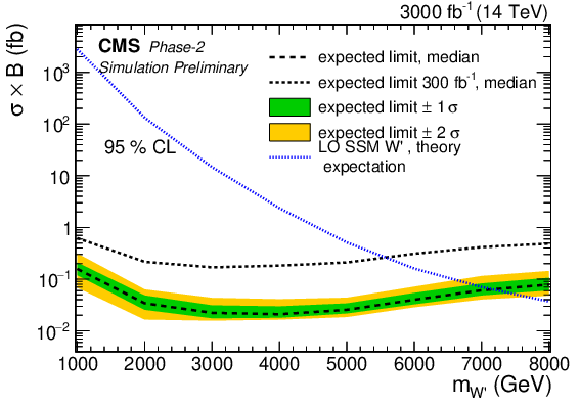
Sensitivity for a SSM W' boson for 300 fb$^{-1}$ and 3000 fb$^{-1}$. Discovery significance (left) and expected exclusion limit on the SSM W' boson mass at 95% CL (right). |
png pdf |
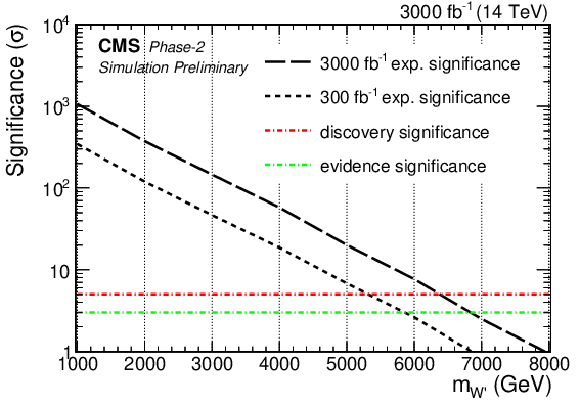
Figure 3-a:
Discovery significance for a SSM W' boson for 300 fb$^{-1}$ and 3000 fb$^{-1}$. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Expected exclusion limit on the SSM W' boson mass at 95% CL for 300 fb$^{-1}$ and 3000 fb$^{-1}$. |
png pdf |
Figure 4:
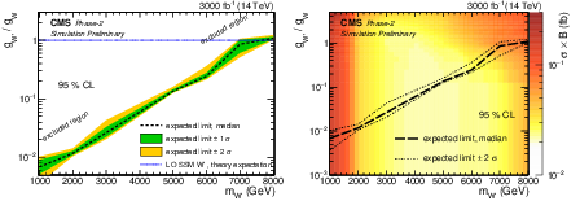
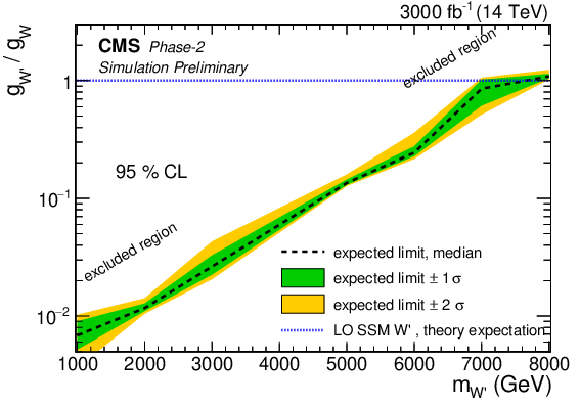
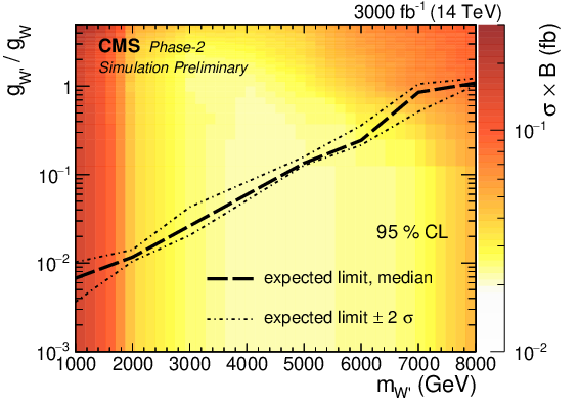
Sensitivity to the coupling ratio $g_{{\mathrm {W}'}}/g_{{\mathrm {W}}}$ of a W' boson using 3000 fb$^{-1}$ of integrated luminosity at the HL-LHC. On the left, the coupling ratio $g_{{\mathrm {W}'}}/g_{{\mathrm {W}}}$ is shown as a function of the W' boson mass. The theory line of the SSM W' boson is shown in blue. The 2D graph on the right includes additionally the limit on the cross section represented by the color code. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Expected limit on the coupling ratio $g_{{\mathrm {W}'}}/g_{{\mathrm {W}}}$ as a function of the W' boson mass, using 3000 fb$^{-1}$ of integrated luminosity at the HL-LHC. The theory line of the SSM W' boson is shown in blue. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Expected limit on the coupling ratio $g_{{\mathrm {W}'}}/g_{{\mathrm {W}}}$ as a function of the W' boson mass, using 3000 fb$^{-1}$ of integrated luminosity at the HL-LHC. The 2D limit on the cross section is represented by the color code. |
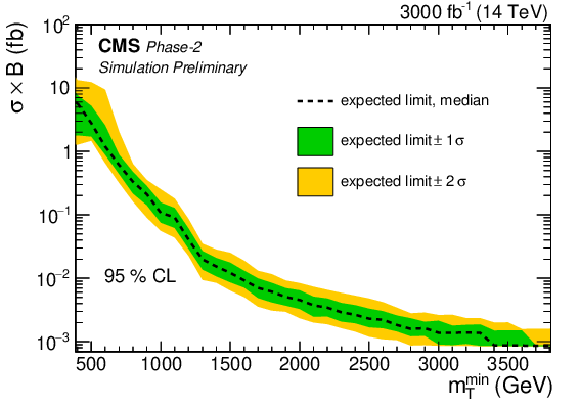
png pdf |
Figure 5:
Model-independent cross section limit scaled to 3000 fb$^{-1}$. For this, a single-bin limit is calculated considering events above a lower threshold ${m_\mathrm {T}^\mathrm {min}}$ while keeping the signal yield constant in order to avoid including any signal shape information on this limit calculation. |
| Summary |
|
Taking guidance from the published Run 2 analysis based on proton-proton collisions corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 35.9 fb$^{-1}$ at $\sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV [4], the physics reach at the High-Luminosity LHC with 3000 fb$^{-1}$ at $\sqrt{s} = $ 14 TeV with the upgraded CMS detector was studied. The final state consists of a hadronically decaying tau lepton and ${p_{\mathrm{T}}}^{\text{miss}}$ caused by neutrinos. The interpretation was performed in the benchmark sequential standard model (SSM) with an additional charged gauge boson W'. With the high luminosity, the sensitivity can be substantially improved. The discovery at a significance level of 3(5) standard deviations is possible for W' boson masses of 6.9(6.4) TeV, respectively. In case of no observation, SSM W' boson masses up to 7.0 TeV can be excluded. While the SSM assumes standard-model-like couplings, weaker couplings are possible. Depending on the value of the W' boson mass, the high-luminosity data will allow to study couplings down to nearly 10$^{-2}$. To allow interpretations in other models, a model-independent limit on the cross section was provided. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | G. Apollinari et al. | High-luminosity large hadron collider (HL-LHC) : Preliminary design report | ||
| 2 | DELPHES 3 Collaboration | Delphes 3, a modular framework for fast simulation of a generic collider experiment | JHEP 02 (2014) 057 | 1307.6346 |
| 3 | CMS Collaboration | Expected performance of the physics objects with the upgraded CMS detector at the HL-LHC | CDS | |
| 4 | CMS Collaboration | Search for a W' boson decaying to a $ \tau $ lepton and a neutrino in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | Submitted to: PL(2018) | CMS-EXO-17-008 1807.11421 |
| 5 | G. Altarelli, B. Mele, and M. Ruiz-Altaba | Searching for new heavy vector bosons in $ p \bar{p} $ colliders | Z. Phys. C45 (1989) 109, .[Erratum: Z. Phys. C47, 676(1990)] | |
| 6 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 7 | D. Contardo et al. | Technical proposal for the Phase-II upgrade of the CMS detector | CERN-LHCC-2015-010, LHCC-P-008, CMS-TDR-15-02 | |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | The phase-2 upgrade of the CMS tracker | CDS | |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | The phase-2 upgrade of the CMS barrel calorimeters | CDS | |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | The phase-2 upgrade of the CMS muon detectors | CDS | |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | The phase-2 upgrade of the CMS endcap calorimeter | CDS | |
| 12 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 13 | T. Sjostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Z. Skands | A brief introduction to PYTHIA 8.1 | CPC 178 (2008) 852 | 0710.3820 |
| 14 | P. Skands, S. Carrazza, and J. Rojo | Tuning PYTHIA 8.1: the Monash 2013 Tune | EPJC 74 (2014) 3024 | 1404.5630 |
| 15 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with parton shower simulations: the $ POWHEG $ method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 16 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 17 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the $ POWHEG $ box | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 18 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | NLO single-top production matched with shower in $ POWHEG: s $- and $ t $-channel contributions | JHEP 09 (2009) 111 | 0907.4076 |
| 19 | E. Re | Single-top Wt-channel production matched with parton showers using the $ POWHEG $ method | EPJC 71 (2011) 1547 | 1009.2450 |
| 20 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and G. Ridolfi | A positive-weight next-to-leading-order Monte Carlo for heavy flavour hadroproduction | JHEP 09 (2007) 126 | 0707.3088 |
| 21 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ {k_{\mathrm{T}}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 22 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 23 | D. Bertolini, P. Harris, M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup Per Particle Identification | JHEP 10 (2014) 059 | 1407.6013 |
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of reconstruction and identification of $ \tau $ leptons decaying to hadrons and $ \nu_\tau $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV | JINST 13 (2018), no. 10, P10005 | CMS-TAU-16-003 1809.02816 |
| 25 | G. Cowan, ``Statistics'', Ch. 39 in Particle Data Group, C. Patrignani et al. | Statistics'', Ch. 39 in Particle Data Group, C.~Patrignani et~al., ``Review of particle physics | CPC 40 (2016) 100001 | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|