

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-BPH-16-003 | ||
| Observation of the $\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}(5840)^0\rightarrow\mathrm{B}^0\mathrm{K}^0_{\mathrm{S}}$ decay and studies of excited $\mathrm{B}^0_\mathrm{s}$ mesons in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s}=$ 8 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| June 2018 | ||
| Abstract: The observation of the $\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}(5840)^0\rightarrow\mathrm{B}^0\mathrm{K}^0_{\mathrm{S}}$ decay is presented and a measurement of its relative branching fraction to the $\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}(5840)^0\rightarrow\mathrm{B}^+\mathrm{K}^{-}$ decay using a data sample of 19.6 fb$^{-1}$ collected with the CMS detector in proton-proton collision at the centre-of-mass energy 8 TeV. The analysis is performed by studying P-wave $\mathrm{B}^{0}_\mathrm{s}$ meson decays into $\mathrm{B}^+\mathrm{K}^-$ and $\mathrm{B}^0 \mathrm{K}^0_{\mathrm{S}}$ states, where the ground-state $\mathrm{B}$ mesons are identified using the decays $\mathrm{B}^+ \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi\mathrm{K}^+$ and $\mathrm{B}^0 \rightarrow \mathrm{J}/\psi\mathrm{K}^+ \pi^-$. The masses of P-wave $\mathrm{B}^0_\mathrm{s}$ meson states are measured and the natural width of the $\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}(5840)^0$ state is determined to be $\Gamma(\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}(5840)^0)= $ (1.52 $\pm$ 0.34 (stat) $\pm$ 0.30 (syst) MeV. The first measurement of the mass difference between the charged and neutral $\mathrm{B}^*$ mesons is also presented. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
inSPIRE record ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, EPJC 78 (2018) 939. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
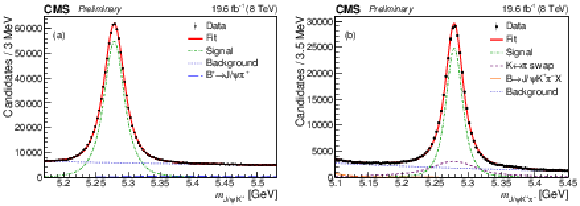
Figure 1:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} $ (a) and $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $ (b) candidates in the data with the fit results superimposed. |
png pdf |
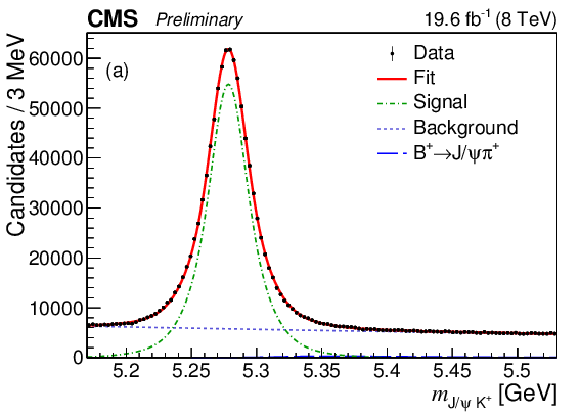
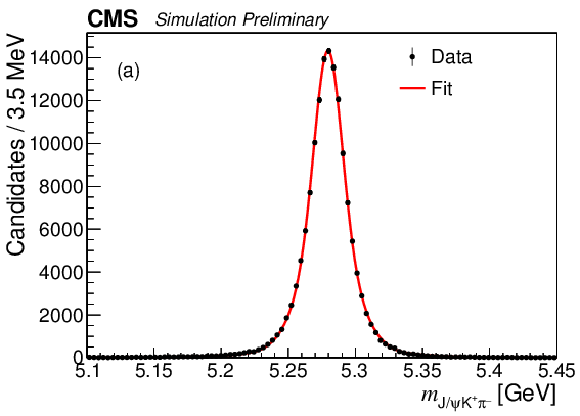
Figure 1-a:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} $ (a) and $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $ (b) candidates in the data with the fit results superimposed. |
png pdf |
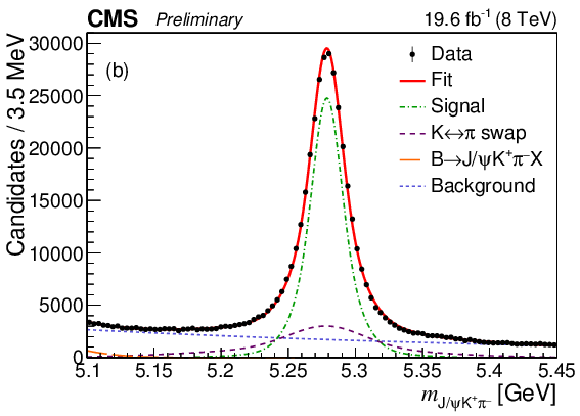
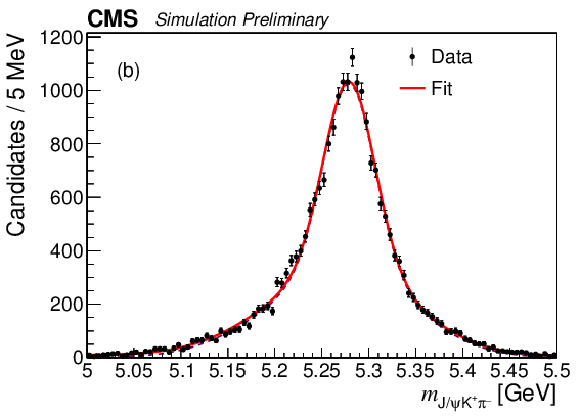
Figure 1-b:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} $ (a) and $ {\mathrm {J} / \psi} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $ (b) candidates in the data with the fit results superimposed. |
png pdf |
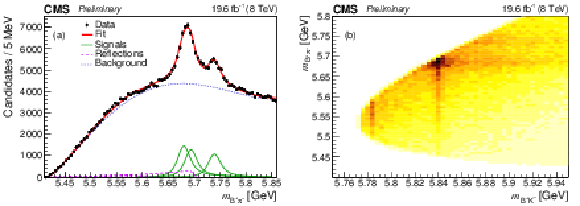
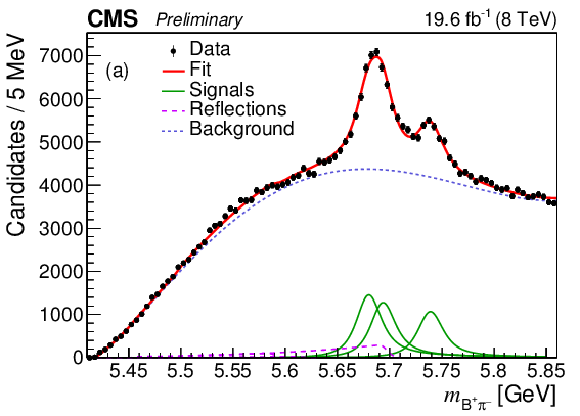
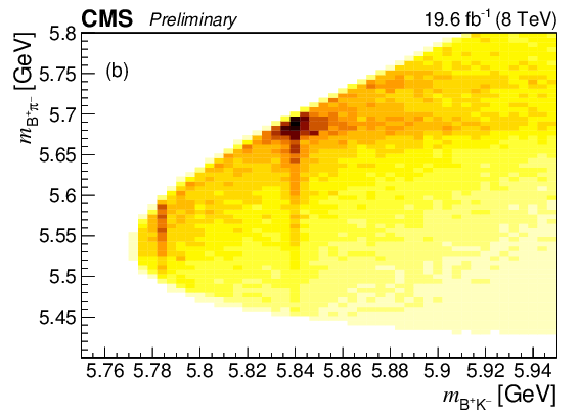
Figure 2:
(a) The fitted $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distribution. The points represent the data, the thick solid curve is the fit projection, the thin lines indicate the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ signal contributions, the dashed curve is the background, and the long-dashed lines show the contributions from the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0_ {\mathrm {s}}} $ decays. (b) Two-dimensional distribution of ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}}}$ versus ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{\pi} ^-}}}$ in data. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
(a) The fitted $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distribution. The points represent the data, the thick solid curve is the fit projection, the thin lines indicate the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ signal contributions, the dashed curve is the background, and the long-dashed lines show the contributions from the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0_ {\mathrm {s}}} $ decays. (b) Two-dimensional distribution of ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}}}$ versus ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{\pi} ^-}}}$ in data. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
(a) The fitted $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distribution. The points represent the data, the thick solid curve is the fit projection, the thin lines indicate the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ signal contributions, the dashed curve is the background, and the long-dashed lines show the contributions from the excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0_ {\mathrm {s}}} $ decays. (b) Two-dimensional distribution of ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}}}$ versus ${m_{{{{\mathrm {B}} ^+}} {{\pi} ^-}}}$ in data. |
png pdf |
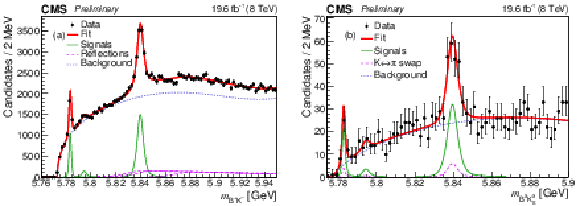
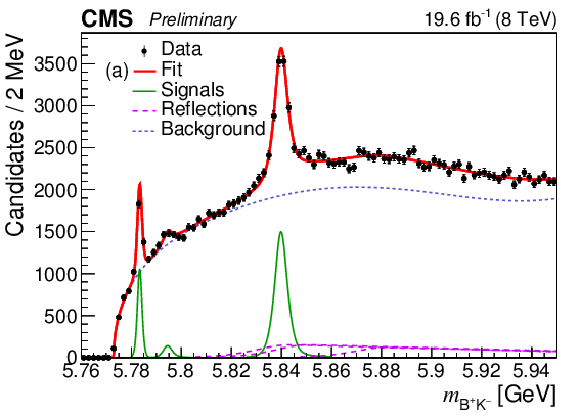
Figure 3:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ (a) and $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^0} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^0_{\rm {S}}}} $ (b) candidates with the results of the fit overlaid. The points represent the data, the thick curves are the fit projections, the thin lines display the signal contributions, and the long-dashed lines show: in (a) the contributions from excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ meson decays; in (b) the contributions from $ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap in $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ reconstruction. The dashed lines show the background contribution. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ (a) and $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^0} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^0_{\rm {S}}}} $ (b) candidates with the results of the fit overlaid. The points represent the data, the thick curves are the fit projections, the thin lines display the signal contributions, and the long-dashed lines show: in (a) the contributions from excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ meson decays; in (b) the contributions from $ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap in $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ reconstruction. The dashed lines show the background contribution. |
png pdf |
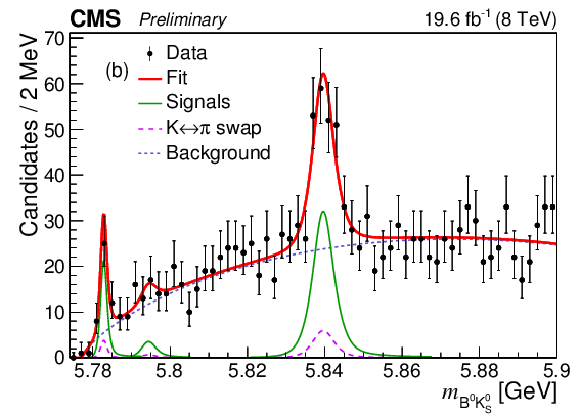
Figure 3-b:
Invariant mass distributions of $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ (a) and $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^0} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^0_{\rm {S}}}} $ (b) candidates with the results of the fit overlaid. The points represent the data, the thick curves are the fit projections, the thin lines display the signal contributions, and the long-dashed lines show: in (a) the contributions from excited $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ meson decays; in (b) the contributions from $ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap in $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^0} $ reconstruction. The dashed lines show the background contribution. |
png pdf |
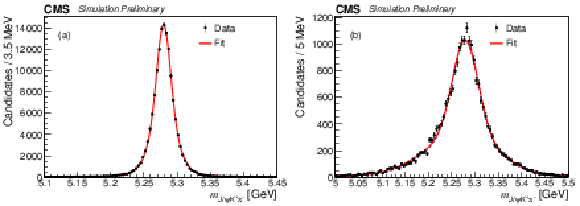
Figure 4:
$ {m_{{{\mathrm {B}} ^0}}} $ distribution in simulation with the fit result superimposed. (a) signal with matching; (b) reflection from '$ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap' obtained by requiring the reconstructed kaon candidate to be matched to the generated pion and vice versa. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
$ {m_{{{\mathrm {B}} ^0}}} $ distribution in simulation with the fit result superimposed. (a) signal with matching; (b) reflection from '$ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap' obtained by requiring the reconstructed kaon candidate to be matched to the generated pion and vice versa. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
$ {m_{{{\mathrm {B}} ^0}}} $ distribution in simulation with the fit result superimposed. (a) signal with matching; (b) reflection from '$ {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^\pm} \leftrightarrow {{\pi} ^\pm} $ swap' obtained by requiring the reconstructed kaon candidate to be matched to the generated pion and vice versa. |
png pdf |
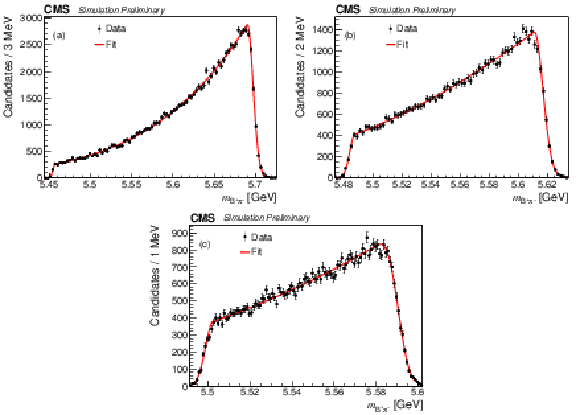
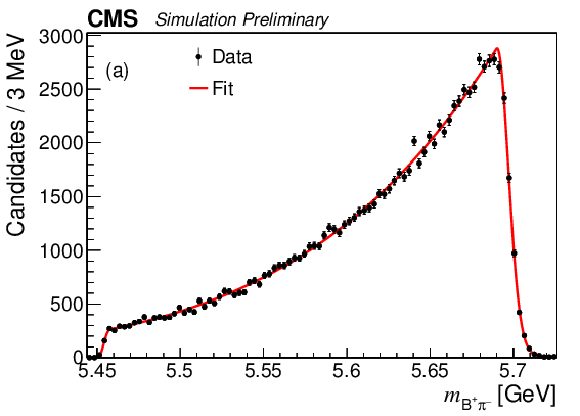
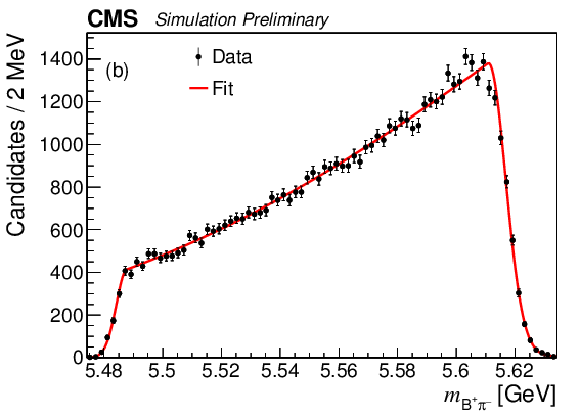
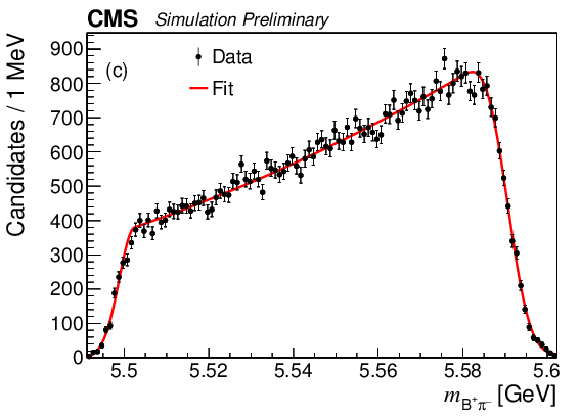
Figure 5:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (b) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (b) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (b) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
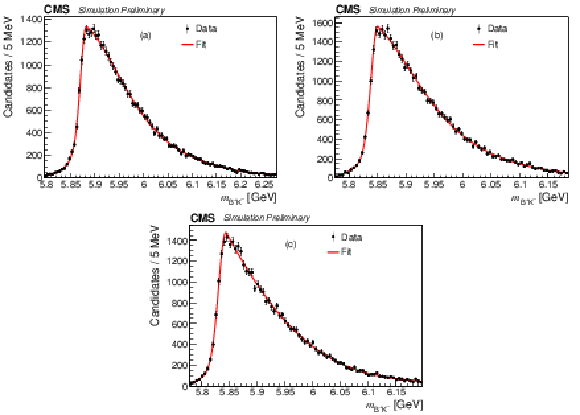
Figure 5-c:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (b) $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $; (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
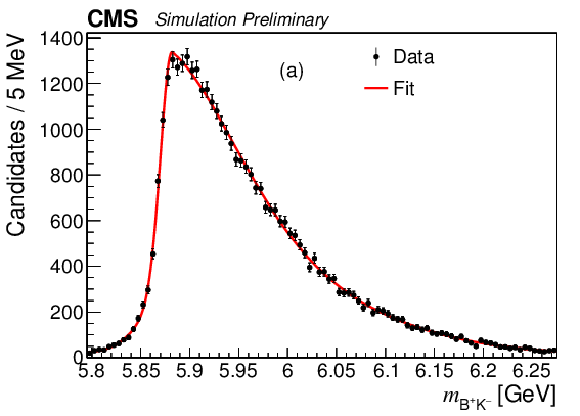
Figure 6:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $, (b) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $ and (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
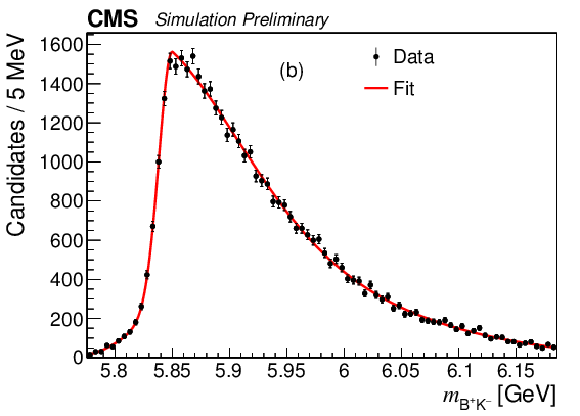
Figure 6-a:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $, (b) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $ and (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $, (b) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $ and (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $. |
png pdf |
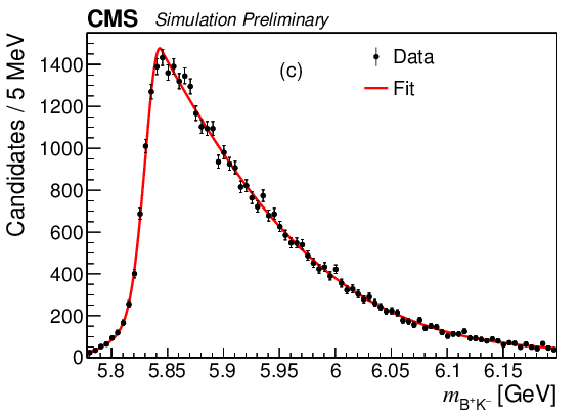
Figure 6-c:
The $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ invariant mass distributions from the simulated decay: (a) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{\pi} ^-} $, (b) $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{2}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $ and (c) $ {{\mathrm {B}} _{1}} \to {{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}} {{\pi} ^-} $. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
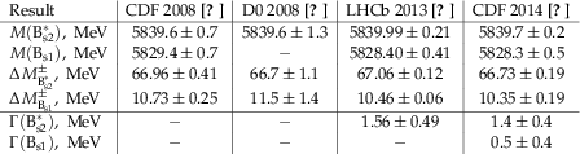
Table 1:
Results on $ {{\mathrm {B}} ^{(*)}_{{\mathrm {s}} 1,2}} $ from previous measurements. Mass differences are designated as $ {\Delta M_{{{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}}}^{\pm}} \equiv {M({{\mathrm {B}} _{{\mathrm {s}} 1}})-M({{\mathrm {B}} ^{*+}})-M({{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-})} $, $ {\Delta M_{{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}}}^{\pm}} \equiv {M({{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}})-M({{\mathrm {B}} ^+})-M({{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-})} $. |
png pdf |
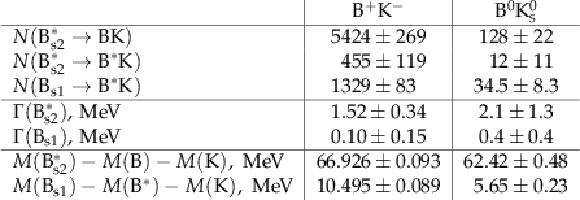
Table 2:
Results from the fits to the $ {m_{{{\mathrm {B}} {{\mathrm {K}}}}}} $ distributions in data. |
png pdf |
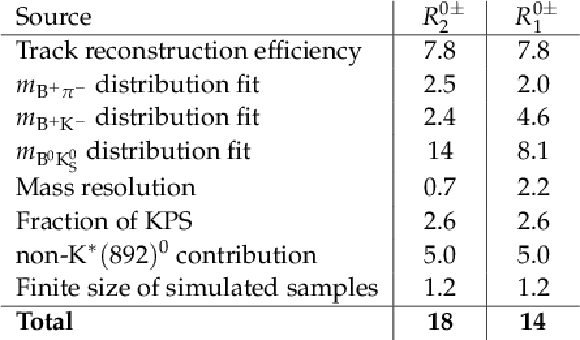
Table 3:
Systematic uncertainties in percent in the ratios $ {R^{0\pm}_{2}} $ and $ {R^{0\pm}_{1}} $. |
png pdf |
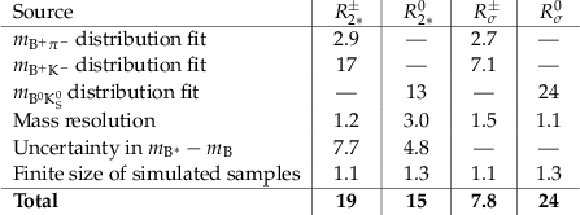
Table 4:
Systematic uncertainties (in%) in the ratios $ {R^{\pm}_{2*}} $, $ {R^{0}_{2*}} $, $ {R^{\pm}_{\sigma}} $, and $ {R^{0}_{\sigma}} $. |
png pdf |
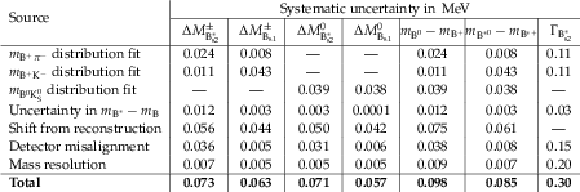
Table 5:
Systematic uncertainties (in MeV) in the measured mass differences and natural width ($ {\Gamma _{{{\mathrm {B}} ^{*}_{{\mathrm {s}} 2}}}} $, measured only in $ {{{\mathrm {B}} ^+} {{{\mathrm {K}}} ^-}} $ channel). |
| Summary |
| In summary, the P-wave $\mathrm{B}^{0}_\mathrm{s}$ meson states are studied using a data sample corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 19.6 fb$^{-1}$ of pp collisions collected by the CMS experiment at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV in 2012. The observation and the first evidence are reported for the decays $\mathrm{B}^{*}_{\mathrm{s}2}\rightarrow\mathrm{B}^0\mathrm{K}^0_{\mathrm{S}}$ and $\mathrm{B}_{\mathrm{s}1}\rightarrow\mathrm{B}^{*0}\mathrm{K}^0_{\mathrm{S}}$, respectively. Four ratios of branching fractions and two ratios of cross section multiplied by the branching fractions of the P-wave $\mathrm{B}^{0}_\mathrm{s}$ mesons into B meson and kaon are measured. In addition, the differences between the ${\mathrm{B}^{(*)}_{\mathrm{s}1,2}} $ mass and the sum of B meson and kaon mass are determined, as well as the ${\mathrm{B}^{(*)}_{\mathrm{s}2}}$ natural width. Finally, using a new approach, the mass differences $m_{\mathrm{B}^0}-m_{\mathrm{B}^+}$ and $m_{\mathrm{B}^{*0}}-m_{\mathrm{B}^{*+}}$ are measured, where the latter mass difference is measured for the first time. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | F. E. Close and Z.-p. Li | Effective heavy quark theory | PLB 289 (1992) 143 | hep-ph/9206217 |
| 2 | A. G. Grozin | Heavy quark effective theory | Springer Tracts Mod. Phys. 201 (2004) 1 | |
| 3 | CDF Collaboration | Observation of orbitally excited $ \mathrm{B}_\mathrm{s} $ mesons | PRL 100 (2008) 082001 | 0710.4199 |
| 4 | D0 Collaboration | Observation and properties of the orbitally excited B*(s2) meson | PRL 100 (2008) 082002 | 0711.0319 |
| 5 | LHCb Collaboration | First observation of the decay $ \mathrm{B}_{\rm{s2}}^*(5840)^0 \to {\rm B}^{*+} {\rm K}^- $ and studies of excited $ {\rm B}^0_{\rm s} $ mesons | PRL 110 (2013) 151803 | 1211.5994 |
| 6 | CDF Collaboration | Study of orbitally excited B mesons and evidence for a new $ \mathrm{B}\pi $ resonance | PRD 90 (2014) 012013 | 1309.5961 |
| 7 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of CMS muon reconstruction in $ \rm{pp} $ collision events at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JINST 7 (2012) P10002 | CMS-MUO-10-004 1206.4071 |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) P01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the CP-violating weak phase $ \phi_s $ and the decay width difference $ \Delta \Gamma_s $ using the B$ _s^0 \to {\rm J}/\psi\phi $(1020) decay channel in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 ~TeV | PLB 757 (2016) 97 | CMS-BPH-13-012 1507.07527 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Search for the X(5568) state decaying into $ \mathrm{B}^{0}_{\mathrm{s}}\pi^{\pm} $ in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | PRL 120 (2018) 202005 | CMS-BPH-16-002 1712.06144 |
| 13 | Particle Data Group, C. Patrignani et al. | Review of particle physics | CPC 40 (2016) 100001 | |
| 14 | T. Sjostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Skands | PYTHIA 6.4 physics and manual | JHEP 05 (2006) 026 | hep-ph/0603175 |
| 15 | D. J. Lange | The EvtGen particle decay simulation package | NIMA 462 (2001) 152 | |
| 16 | E. Barberio, B. van Eijk, and Z. W\cas | PHOTOS --- a universal Monte Carlo for QED radiative corrections in decays | CPC 66 (1991) 115 | |
| 17 | E. Barberio and Z. W\cas | PHOTOS -- a universal Monte Carlo for QED radiative corrections: version 2.0 | CPC 79 (1994) 291 | |
| 18 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4---a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 19 | M. Pivk and F. R. Le Diberder | $ {}_\mathrm{s} $Plot: a statistical tool to unfold data distributions | NIMA 555 (2005) 356--369 | physics/0402083 |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | Alignment of the CMS tracker with LHC and cosmic ray data | JINST 9 (2014) P06009 | CMS-TRK-11-002 1403.2286 |
| 21 | Z.-H. Wang, G.-L. Wang, H.-F. Fu, and Y. Jiang | The strong decays of orbitally excited $ \mathrm{B}^{*}_{\rm sJ} $ mesons by improved Bethe-Salpeter method | PLB 706 (2012) 389 | 1202.1224 |
| 22 | Q.-F. Lu et al. | Excited bottom and bottom-strange mesons in the quark model | PRD 94 (2016) 074012 | 1607.02812 |
| 23 | X.-h. Zhong and Q. Zhao | Strong decays of heavy-light mesons in a chiral quark model | PRD 78 (2008) 014029 | 0803.2102 |
| 24 | P. Colangelo, F. De Fazio, F. Giannuzzi, and S. Nicotri | New meson spectroscopy with open charm and beauty | PRD 86 (2012) 054024 | 1207.6940 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|