

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-SMP-12-009 ; CERN-PH-EP-2012-283 | ||
| Observation of Z decays to four leptons with the CMS detector at the LHC | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 15 October 2012 | ||
| J. High Energy Phys. 12 (2012) 034 | ||
| Abstract: The first observation of the Z boson decaying to four leptons in proton-proton collisions is presented. The analyzed data set corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 5.02 fb$^{-1}$ at $\sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV collected by the CMS detector at the Large Hadron Collider. A pronounced resonance peak, with a statistical significance of 9.7$\sigma$, is observed in the distribution of the invariant mass of four leptons (electrons and/or muons) with mass and width consistent with expectations for Z boson decays. The branching fraction and cross section reported here are defined by phase space restrictions on the leptons, namely, 80 $ < m_{4\ell} < $ 100 GeV, where $m_{4\ell}$ is the invariant mass of the four leptons, and $m_{\ell\ell} > $ 4 GeV for all pairs of leptons, where $m_{\ell\ell}$ is the two-lepton invariant mass. The measured branching fraction is $\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell) =$ ( 4.2 $^{+0.9}_{-0.8}$ (stat.) $\pm$ 0.2 (syst.) ) $\times 10^{-6}$ and agrees with the standard model prediction of 4.45 $\times 10^{-6}$. The measured cross section times branching fraction is $\sigma(Z) \, \mathcal{B}(\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell) =$ 112 $^{+23}_{-20}$ (stat.) $^{+7}_{-5}$ (syst.) $^{+3}_{-2}$ (lumi.) fb, also consistent with the standard model prediction of 120 fb. The four-lepton mass peak arising from $\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell$ decays provides a calibration channel for the Higgs boson search in the $\mathrm{H} \to \mathrm{ZZ} \to 4\ell$ decay mode. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:1210.3844 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; Public twiki page ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png |
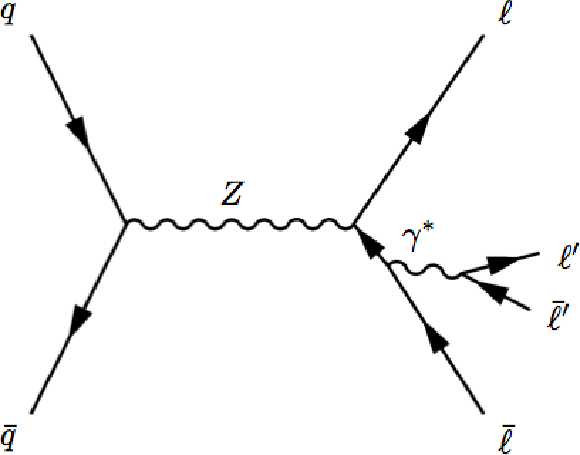
Figure 1-a:
(a) Diagram of the $\mathrm {Z}\rightarrow 4\ell $ process. (b) Diagram of the $\mathrm {Z}\gamma ^* \rightarrow 4\ell $ process for the irreducible background of $Z \to 2\ell $ production with the initial-state radiation undergoing an internal conversion $\gamma ^* \to 2\ell $. Both Z and $\gamma ^*$ are present in all propagators. The choice of propagators shown in the figures corresponds to the dominant contributions in the phase space 80 $ < m_{4\ell } < $ 100 GeV. |
png |
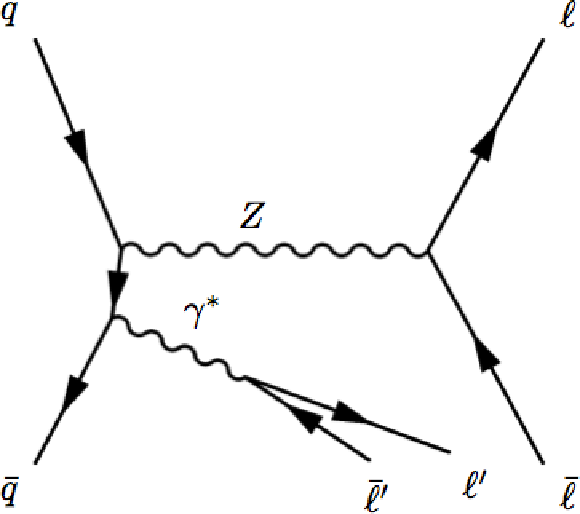
Figure 1-b:
(a) Diagram of the $\mathrm {Z}\rightarrow 4\ell $ process. (b) Diagram of the $\mathrm {Z}\gamma ^* \rightarrow 4\ell $ process for the irreducible background of $Z \to 2\ell $ production with the initial-state radiation undergoing an internal conversion $\gamma ^* \to 2\ell $. Both Z and $\gamma ^*$ are present in all propagators. The choice of propagators shown in the figures corresponds to the dominant contributions in the phase space 80 $ < m_{4\ell } < $ 100 GeV. |

png pdf |
Figure 2:
Four-lepton invariant mass distribution for events passing all selection requirements except that on $m_{4\ell }$. The data are shown by points. The filled histograms represent standard model expectations for $\mathrm {pp} \to \mathrm {Z}/\mathrm {Z}\gamma ^{*} \to 4\ell $ and for reducible backgrounds. The three final states, $4\mathrm {e}$, $4\mu $, and $2\mathrm {e}2\mu $, are combined. |
png pdf |
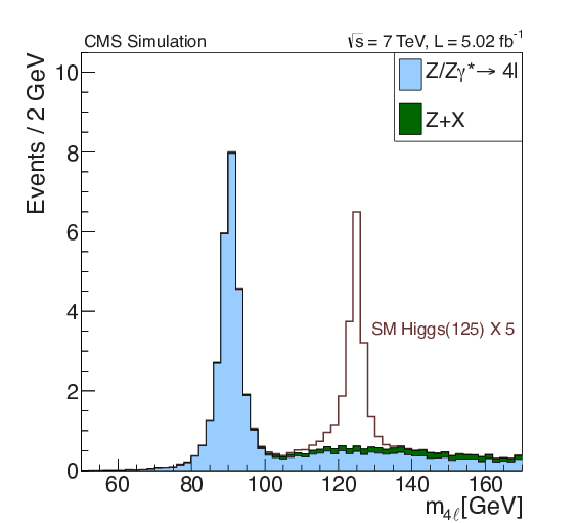
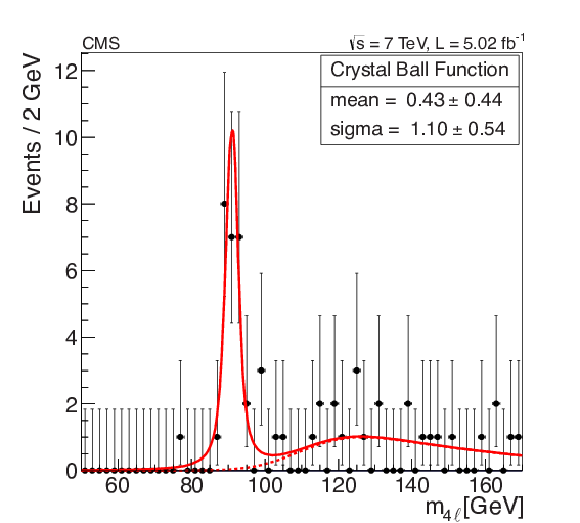
Figure 3-a:
(a) Four-lepton mass distribution in simulation for $\mathrm {pp} \to 4\ell $, without the Higgs boson (light shaded histogram), $\mathrm {Z}+\mathrm {X}$ background (dark shaded histogram), and $\mathrm {pp} \to \mathrm {H} \to \mathrm {ZZ} \to 4\ell $ for a Higgs boson mass $m_{\mathrm {H}}= $ 125 GeV. The three contributions are stacked. The standard model cross section for the Higgs boson is scaled up by a factor of 5. (b) Four-lepton mass distribution with data represented by the points with error bars. The three final states, $4\mathrm {e}$, $4\mu $, and $2\mathrm {e}2\mu $, are combined. The solid line represents a simultaneous fit to the background and Z boson peak. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
(a) Four-lepton mass distribution in simulation for $\mathrm {pp} \to 4\ell $, without the Higgs boson (light shaded histogram), $\mathrm {Z}+\mathrm {X}$ background (dark shaded histogram), and $\mathrm {pp} \to \mathrm {H} \to \mathrm {ZZ} \to 4\ell $ for a Higgs boson mass $m_{\mathrm {H}}= $ 125 GeV. The three contributions are stacked. The standard model cross section for the Higgs boson is scaled up by a factor of 5. (b) Four-lepton mass distribution with data represented by the points with error bars. The three final states, $4\mathrm {e}$, $4\mu $, and $2\mathrm {e}2\mu $, are combined. The solid line represents a simultaneous fit to the background and Z boson peak. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
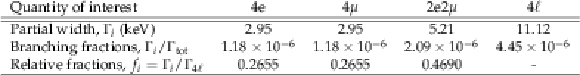
Table 1:
Partial widths and branching fractions for Z boson decays to $4\mathrm {e}$, $4\mu $, $2\mathrm {e}2\mu $ final states with $m_{\ell \ell }> $ 4 GeV for all lepton pairs. The branching fractions are calculated with CalcHEP 3.2 [7] at LO using the total Z boson width $\Gamma _{\mathrm {tot}}= $ 2.4952 GeV [9]. Theoretical uncertainties are smaller than experimental uncertainties and are not shown in the table. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Numbers of expected and observed events with 80 $ < m_{4\ell } < $ 100 GeV. The yields are determined by means of fits described in the text; the fit results in the $4\mathrm {e}$ channel are not meaningful because only two events are selected. |
| Summary |
| The first observation of the Z boson decaying to four leptons (electrons and/or muons) in proton-proton collisions has been presented. The data set analyzed corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 5.02 fb$^{-1}$ at $\sqrt{s}= $ 7 TeV. A pronounced resonance peak, with a statistical significance of 9.7$\sigma$, is observed in the distribution of the invariant mass of four leptons with mass and width consistent with expectations for Z boson decays. The event yields, branching fraction, and cross section reported here are defined by phase space restrictions on the leptons, namely, 80 $ < m_{4\ell} < $ 100 GeV, where $m_{4\ell}$ is the invariant mass of the four leptons, and $m_{\ell\ell} > $ 4 GeV for all pairs of leptons, where $m_{\ell\ell}$ is the two-lepton invariant mass. We observe 28 events, in agreement with the expectation of 30.0 $\pm$ 2.6 events, comprised of 29.4 $\pm$ 2.6 $\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell$ events and 0.6 $\pm$ 0.2 events from backgrounds. The measured branching fraction is $\mathcal{B}(\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell) =$ ( 4.2 $^{+0.9}_{-0.8}$ (stat.) $\pm$ 0.2 (syst.) ) $ \times 10^{-6}$, in agreement with the standard model prediction of 4.45 $\times 10^{-6}$. The measured cross section times branching fraction is $\sigma(Z) \, \mathcal{B}(\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell) =$ 112 $^{+23}_{-20}$ (stat.) $^{+7}_{-5}$ (syst.) $^{+3}_{-2}$ (lumi.) fb, also consistent with the standard model prediction of 120 fb. The four-lepton mass peak arising from $\mathrm{Z} \to 4\ell$ decays provides a calibration channel for the Higgs boson search in the $\mathrm{H} \to \mathrm{ZZ} \to 4\ell$ decay mode. |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|