

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-EXO-13-002 ; CERN-EP-2016-068 | ||
| Search for lepton flavour violating decays of heavy resonances and quantum black holes to an $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ pair in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 16 April 2016 | ||
| Eur. Phys. J. C 76 (2016) 317 | ||
| Abstract: A search for narrow resonances decaying to an electron and a muon is presented. The $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ mass spectrum is also investigated for non-resonant contributions from the production of quantum black holes (QBHs). The analysis is performed using data corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ collected in proton-proton collisions at a centre-of-mass energy of 8 TeV with the CMS detector at the LHC. With no evidence for physics beyond the standard model in the invariant mass spectrum of selected $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ pairs, upper limits are set at 95% confidence level on the product of cross section and branching fraction for signals arising in theories with charged lepton flavour violation. In the search for narrow resonances, the resonant production of a $\tau$ sneutrino in R-parity violating supersymmetry is considered. The $\tau$ sneutrino is excluded for masses below 1.28 TeV for couplings $\lambda_{132}=\lambda_{231}=\lambda'_{311}= $ 0.01 , and below 2.30 TeV for $\lambda_{132}=\lambda_{231}= $ 0.07 and $\lambda'_{311}= $ 0.11. These are the most stringent limits to date from direct searches at high-energy colliders. In addition, the resonance searches are interpreted in terms of a model with heavy partners of the Z boson and the photon. In a framework of TeV-scale quantum gravity based on a renormalization of Newton's constant, the search for non-resonant contributions to the $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ mass spectrum excludes QBH production below a threshold mass $M_{\mathrm{th}}$ of 1.99 TeV. In models that invoke extra dimensions, the bounds range from 2.36 TeV for one extra dimension to 3.63 TeV for six extra dimensions. This is the first search for QBHs decaying into the $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ final state. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:1604.05239 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
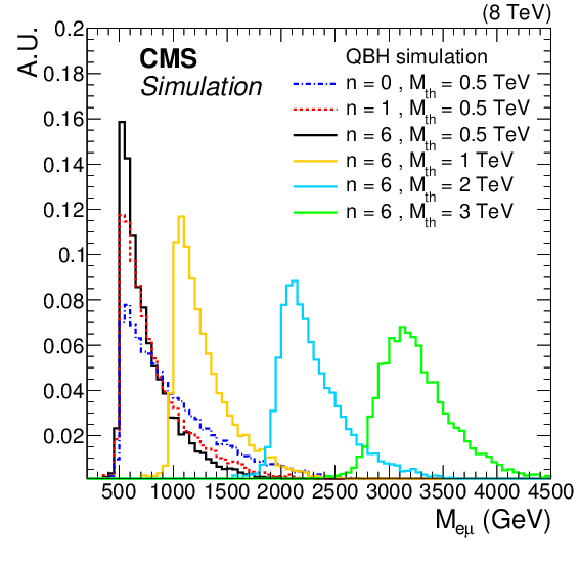
Figure 1:
Invariant mass distributions of reconstructed $\mathrm{ e } \mu$ pairs from simulated QBH signal events that pass the event selection, normalized to unit area. The steps at the threshold masses ${M_{\mathrm {th}}}$ are smeared out by the detector resolution. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
The invariant mass distribution of selected $\mathrm{ e } \mu$ pairs (a), and the corresponding cumulative distribution, where all events above the mass value on the $x$-axis are summed (b). The points with error bars represent the data and the stacked histograms represent the expectations from SM processes. The label 'Jets' refers to the estimate of the W+jet and QCD multijet backgrounds from data. The ratio of the data to the background for each bin is shown at the bottom. The horizontal lines on the data points indicate the bin width. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
The invariant mass distribution of selected $\mathrm{ e } \mu$ pairs (a), and the corresponding cumulative distribution, where all events above the mass value on the $x$-axis are summed (b). The points with error bars represent the data and the stacked histograms represent the expectations from SM processes. The label 'Jets' refers to the estimate of the W+jet and QCD multijet backgrounds from data. The ratio of the data to the background for each bin is shown at the bottom. The horizontal lines on the data points indicate the bin width. |

png pdf |
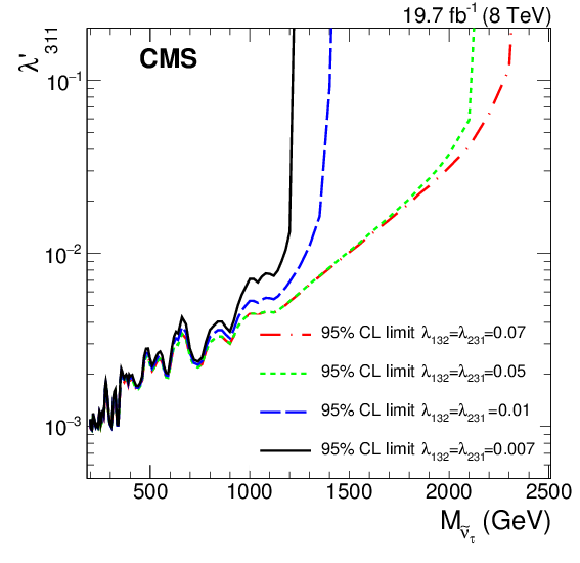
Figure 3-a:
a: The 95% CL upper limit on the product of signal cross section and branching fraction for the RPV ${\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ signal as a function of the mass of the resonance ${M_{\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}}$. b: The 95% CL limit contours for the RPV ${\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ signal in the (${M_{\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}}$ , ${\lambda '_{311}}$) parameter plane. The values of the parameter $ {\lambda _{132}} = {\lambda _{231}} $ are fixed to 0.07 (red dashed and dotted), 0.05 (green small-dashed), 0.01 (blue dashed), and 0.007 (black solid). The regions above the curves are excluded. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
a: The 95% CL upper limit on the product of signal cross section and branching fraction for the RPV ${\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ signal as a function of the mass of the resonance ${M_{\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}}$. b: The 95% CL limit contours for the RPV ${\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ signal in the (${M_{\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}}$ , ${\lambda '_{311}}$) parameter plane. The values of the parameter $ {\lambda _{132}} = {\lambda _{231}} $ are fixed to 0.07 (red dashed and dotted), 0.05 (green small-dashed), 0.01 (blue dashed), and 0.007 (black solid). The regions above the curves are excluded. |
png pdf |
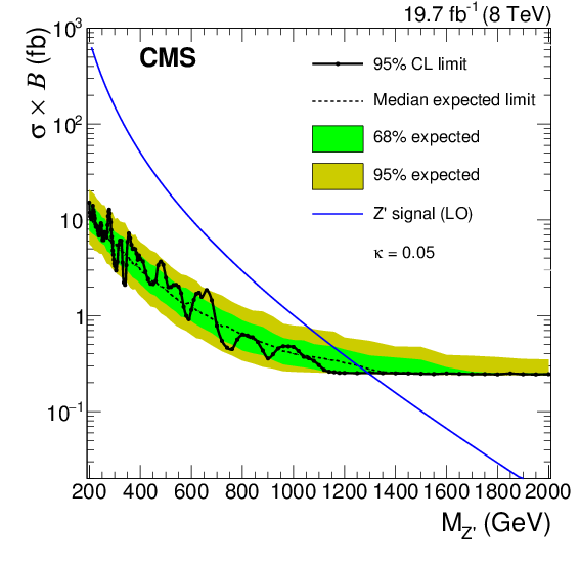
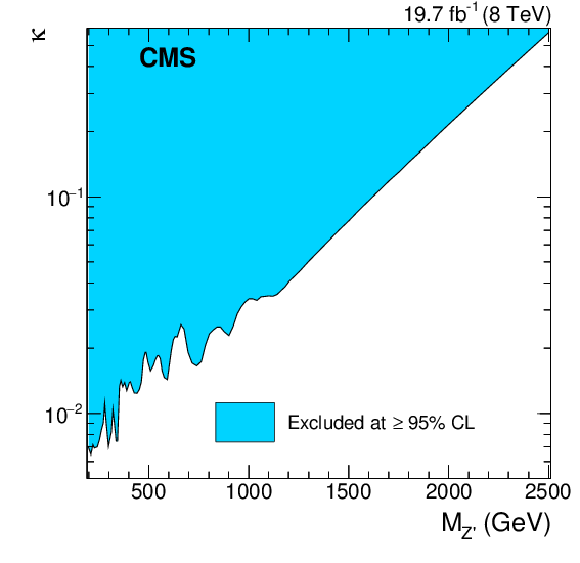
Figure 4-a:
a: The 95% CL exclusion limit on the product of signal cross section and branching fraction for the Z' signal as a function of the mass $M_{\mathrm{Z}' }$. b: The 95% CL limit contour for the Z' signal in the ($M_{\mathrm{Z}' }$, ${\kappa}$) parameter plane. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
a: The 95% CL exclusion limit on the product of signal cross section and branching fraction for the Z' signal as a function of the mass $M_{\mathrm{Z}' }$. b: The 95% CL limit contour for the Z' signal in the ($M_{\mathrm{Z}' }$, ${\kappa}$) parameter plane. |

png pdf |
Figure 5:
The 95% CL exclusion limit on the product of signal cross section and branching fraction for the QBH signal as a function of the threshold mass $M_{\mathrm {th}}$. The limits have been calculated using the signal shape of the QBH model without extra dimensions ($n= $ 0 ). For signal masses $M_{\mathrm {th}} \geq $ 1 TeV, the change in the QBH signal shape for different numbers of extra dimensions has a negligible impact on the limit. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Signal acceptance ($A$) and the product of acceptance and efficiency($A \epsilon $) for different signal masses, for the RPV ${\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ and LFV Z' models. The acceptance is defined as the fraction of signal events in the simulation passing the selection on lepton $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} $ and $\eta $ applied to the generated leptons. |
png pdf |
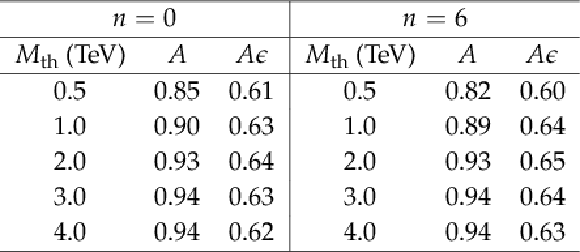
Table 2:
Signal acceptance ($A$) and the product of acceptance and efficiency($A \epsilon $) for different threshold masses $M_{\mathrm {th}}$, for the QBH models with $n= $ 0 and $n= $ 6 extra dimensions. The acceptance is defined as the fraction of signal events in the simulation passing the selection on lepton $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} $ and $\eta $ applied to the generated leptons. |

png pdf |
Table 3:
Parametrization of the product of signal acceptance and efficiency($A \epsilon $) as a function of signal mass $M$, for the RPV $ {\tilde{\nu }_{\tau }}$ and LFV Z' models. The value of $M$ is expressed in units of GeV . |
png pdf |
Table 4:
The number of observed events compared to the background expectation in five invariant mass ranges and in the full invariant mass range. The yields obtained from simulations are normalized according to their expected cross sections. The background label 'Jets' refers to the estimate of the W+jet and QCD multijet backgrounds from data. |
png pdf |
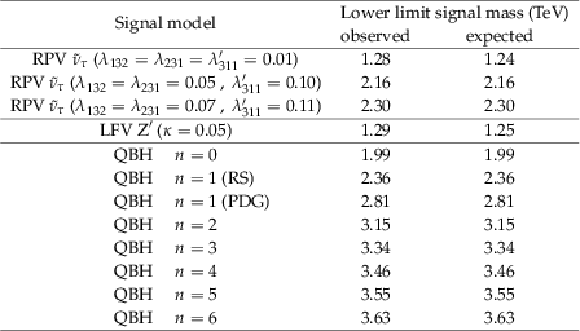
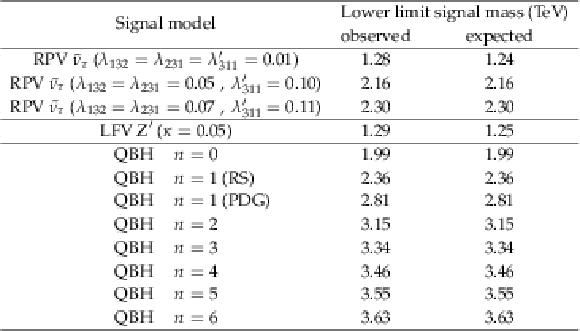
Table 5:
The 95% CL observed and expected lower bounds on the signal masses of $\tau$ sneutrinos in RPV SUSY, resonances in the LFV Z' model, and QBHs, each with subsequent decay into an $\mathrm{ e } \mu$ pair. For the QBH signal with $n =$ 1 , two signal cross sections are considered with the Schwarzschild radius evaluated in either the Randall-Sundrum(RS) or the Particle Data Group(PDG) convention. |
| Summary |
| A search has been reported for heavy states decaying promptly into an electron and a muon using 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ of proton-proton collision data recorded with the CMS detector at the LHC at a centre-of-mass energy of $8 TeV$. Agreement is observed between the data and the standard model expectation with new limits set on resonant production of $\tau$ sneutrinos in R-parity violating supersymmetry with subsequent decay into $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ pairs. For couplings ${\lambda_{132}} ={\lambda_{231}} =$ 0.01 and ${\lambda'_{311}} =$ 0.01, $\tau$ sneutrino lightest supersymmetric particles for masses ${M_{\tilde{\nu}_{\tau}}} $ below 1.28 TeV are excluded at 95% CL. For couplings ${\lambda_{132}} ={\lambda_{231}} =$ 0.07 and ${\lambda'_{311}} =$ 0.11, masses ${M_{\tilde{\nu}_{\tau}}} $ below 2.30 TeV are excluded. These are the most stringent limits from direct searches at high-energy colliders. For the Z' signal model, a lower mass limit of $M_{\mathrm{Z}'}=M_{\gamma^\prime}=$ 1.29 TeV is set at 95% CL for the coupling modifier ${\kappa} = $ 0.05. This direct search for resonant production of an $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ pair at the TeV scale does not reach the sensitivity of dedicated low-energy experiments, but complements such indirect searches and can readily be interpreted in terms of different signals of new physics involving a heavy state that decays promptly into an electron and a muon. Lower bounds are set on the mass threshold for the production of quantum black holes with subsequent decay into an $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ pair in models with zero to six extra dimensions, assuming the threshold mass to be at the Planck scale, ranging from $M_{\mathrm{th}}=$ 1.99 TeV ($n$=0) to 3.63 TeV ($n$=6). These are the first limits on quantum black holes decaying into $\mathrm{ e }\mu$ final states. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | L. Evans and P. Bryant | LHC Machine | JINST 3 (2008) S08001 | |
| 2 | R. Barbier et al. | R-parity violating supersymmetry | PR 420 (2005) 1 | hep-ph/0406039 |
| 3 | J. M. Frere, M. V. Libanov, E. Y. Nugaev, and S. V. Troitsky | Searching for family number conserving neutral gauge bosons from extra dimensions | JEPTL 79 (2004) 598 | hep-ph/0404139 |
| 4 | P. Meade and L. Randall | Black holes and quantum gravity at the LHC | JHEP 05 (2008) 003 | 0708.3017 |
| 5 | X. Calmet, W. Gong, and S. D. H. Hsu | Colorful quantum black holes at the LHC | PLB 668 (2008) 20 | 0806.4605 |
| 6 | D. M. Gingrich | Quantum black holes with charge, colour, and spin at the LHC | JPG 37 (2010) 105008 | 0912.0826 |
| 7 | M. A. Bernhardt, S. P. Das, H. K. Dreiner, and S. Grab | Sneutrino as lightest supersymmetric particle in $ B_{3} $ mSUGRA models and signals at the LHC | PRD 79 (2009) 035003 | 0810.3423 |
| 8 | J. M. Frere, M. V. Libanov, E. Y. Nugaev, and S. V. Troitsky | Fermions in the vortex background on a sphere | JHEP 06 (2003) 009 | hep-ph/0304117 |
| 9 | L. Randall and R. Sundrum | Large mass hierarchy from a small extra dimension | PRL 83 (1999) 3370 | hep-ph/9905221 |
| 10 | L. Randall and R. Sundrum | An alternative to compactification | PRL 83 (1999) 4690 | hep-th/9906064 |
| 11 | N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, and G. R. Dvali | The hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter | PLB 429 (1998) 263 | hep-ph/9803315 |
| 12 | N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, and G. R. Dvali | Phenomenology, astrophysics, and cosmology of theories with submillimeter dimensions and TeV scale quantum gravity | PRD 59 (1999) 086004 | hep-ph/9807344 |
| 13 | X. Calmet, S. D. H. Hsu, and D. Reeb | Quantum gravity at a TeV and the renormalization of Newton's constant | PRD 77 (2008) 125015 | 0803.1836 |
| 14 | T. Banks and W. Fischler | A model for high-energy scattering in quantum gravity | hep-th/9906038 | |
| 15 | S. Dimopoulos and G. L. Landsberg | Black holes at the LHC | PRL 87 (2001) 161602 | hep-ph/0106295 |
| 16 | S. B. Giddings and S. D. Thomas | High-energy colliders as black hole factories: the end of short distance physics | PRD 65 (2002) 056010 | hep-ph/0106219 |
| 17 | X. Calmet | A review of quantum gravity at the Large Hadron Collider | MPLA 25 (2010) 1553 | 1005.1805 |
| 18 | X. Calmet | The lightest of black holes | MPLA 29 (2014) 1450204 | 1410.2807 |
| 19 | Particle Data Group, K. A. Olive et al. | Review of Particle Physics | CPC 38 (2014) 090001 | |
| 20 | CDF Collaboration | Search for R-parity violating decays of $ \tau $ sneutrinos to $ \mathrm{ e }\mu $, $ \mu\tau $, and $ \mathrm{ e }\tau $ pairs in $ \mathrm{ p } \mathrm{ \bar{p} } $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 1.96 TeV | PRL 105 (2010) 191801 | 1004.3042 |
| 21 | D0 Collaboration | Search for sneutrino production in $ \mathrm{ e }\mu $ final states in 5.3$ fb$^{-1}$ $ of $ \mathrm{ p }\mathrm{ \bar{p} } $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 1.96 TeV | PRL 105 (2010) 191802 | 1007.4835 |
| 22 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for a heavy neutral particle decaying to $ \mathrm{ e }\mu $, $ \mathrm{ e }\tau $, or $ \mu\tau $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRL 115 (2015) 031801 | 1503.04430 |
| 23 | SINDRUM II Collaboration | A search for muon to electron conversion in muonic gold | EPJC 47 (2006) 337 | |
| 24 | J. Sato and M. Yamanaka | Way to crosscheck $ \mu-\mathrm{ e } $ conversion in the case of no signals of $ \mu\rightarrow\mathrm{ e }\gamma $ and $ \mu\rightarrow 3\mathrm{ e } $ | PRD 91 (2015) 055018 | 1409.1697 |
| 25 | J. M. Frere, M. V. Libanov, E. Y. Nugaev, and S. V. Troitsky | Flavour violation with a single generation | JHEP 03 (2004) 001 | hep-ph/0309014 |
| 26 | CMS Collaboration | Search for microscopic black holes in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JHEP 07 (2013) 178 | CMS-EXO-12-009 1303.5338 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Search for resonances and quantum black holes using dijet mass spectra in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | PRD 91 (2015) 052009 | CMS-EXO-12-059 1501.04198 |
| 28 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances decaying to dijets in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 116 (2016) 071801 | CMS-EXO-15-001 1512.01224 |
| 29 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in the dijet mass distribution using pp collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 91 (2015) 052007 | 1407.1376 |
| 30 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in dijet mass and angular distributions from pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 754 (2016) 302 | 1512.01530 |
| 31 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in photon+jet events collected in proton--proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PLB 728 (2014) 562 | 1309.3230 |
| 32 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena with photon+jet events in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 03 (2016) 041 | 1512.05910 |
| 33 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for quantum black hole production in high-invariant-mass lepton+jet final states using pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV and the ATLAS detector | PRL 112 (2014) 091804 | 1311.2006 |
| 34 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for high-mass dilepton resonances in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | PRD 90 (2014) 052005 | 1405.4123 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 36 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of CMS muon reconstruction in pp collision events at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JINST 7 (2012) P10002 | CMS-MUO-10-004 1206.4071 |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of electron reconstruction and selection with the CMS detector in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P06005 | CMS-EGM-13-001 1502.02701 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of inclusive $ \mathrm{ W } $ and $ \mathrm{ Z } $ cross sections in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | JHEP 01 (2011) 080 | CMS-EWK-10-002 1012.2466 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Search for narrow resonances in dilepton mass spectra in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | PLB 714 (2012) 158 | CMS-EXO-11-019 1206.1849 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Search for physics beyond the standard model in dilepton mass spectra in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JHEP 04 (2015) 025 | CMS-EXO-12-061 1412.6302 |
| 41 | M. Cacciari and G. P. Salam | Pileup subtraction using jet areas | PLB 659 (2008) 119 | 0707.1378 |
| 42 | A. Belyaev, N. D. Christensen, and A. Pukhov | CalcHEP 3.4 for collider physics within and beyond the Standard Model | CPC 184 (2013) 1729 | 1207.6082 |
| 43 | H. K. Dreiner, S. Grab, M. Kr\"amer, and M. K. Trenkel | Supersymmetric NLO QCD corrections to resonant slepton production and signals at the Fermilab Tevatron and the CERN LHC | PRD 75 (2007) 035003 | hep-ph/0611195 |
| 44 | J. Pumplin et al. | New generation of parton distributions with uncertainties from global QCD analysis | JHEP 07 (2002) 012 | hep-ph/0201195 |
| 45 | A. Belyaev and X. Calmet | Quantum black holes and their lepton signatures at the LHC with CalCHEP | JHEP 08 (2015) 139 | 1412.2661 |
| 46 | J. Alwall et al. | MadGraph 5: going beyond | JHEP 06 (2011) 128 | 1106.0522 |
| 47 | T. Sj\"ostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Skands | PYTHIA 6.4 physics and manual | JHEP 05 (2006) 026 | hep-ph/0603175 |
| 48 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4---a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 49 | R. Field | Early LHC underlying event data - findings and surprises | 1010.3558 | |
| 50 | P. Nason | A new method for combining NLO QCD with shower Monte Carlo algorithms | JHEP 11 (2004) 040 | hep-ph/0409146 |
| 51 | S. Frixione, P. Nason, and C. Oleari | Matching NLO QCD computations with Parton Shower simulations: the POWHEG method | JHEP 11 (2007) 070 | 0709.2092 |
| 52 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower Monte Carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 53 | H.-L. Lai et al. | New parton distributions for collider physics | PRD 82 (2010) 074024 | 1007.2241 |
| 54 | M. Czakon, P. Fiedler, and A. Mitov | Total top-quark pair-production cross section at hadron colliders through $ \mathcal{O}(\alpha^{4}_{S}) $ | PRL 110 (2013) 252004 | 1303.6254 |
| 55 | Y. Li and F. Petriello | Combining QCD and electroweak corrections to dilepton production in the framework of the FEWZ simulation code | PRD 86 (2012) 094034 | 1208.5967 |
| 56 | N. Kidonakis | Differential and total cross sections for top pair and single top production | 1205.3453 | |
| 57 | J. M. Campbell and R. K. Ellis | MCFM for the Tevatron and the LHC | NPPS 205-206 (2010) 10 | 1007.3492 |
| 58 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity based on pixel cluster counting --- Summer 2013 update | CMS-PAS-LUM-13-001 | CMS-PAS-LUM-13-001 |
| 59 | S. Alekhin et al. | The PDF4LHC Working Group interim report | 1101.0536 | |
| 60 | M. Botje et al. | The PDF4LHC Working Group interim recommendations | 1101.0538 | |
| 61 | N. Kidonakis | NNNLO soft-gluon corrections for the top-quark $ p_{\mathrm{T}} $ and rapidity distributions | PRD 91 (2015) 031501 | 1411.2633 |
| 62 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Procedure for the LHC Higgs boson search combination in Summer 2011 | CMS-NOTE-2011-005 | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|