

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIN-16-017 | ||
| Charge asymmetry dependence of elliptic and triangular flow in pPb and PbPb collisions at $\sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| February 2017 | ||
| Abstract: Charge dependent elliptic azimuthal anisotropy ($v_{\rm 2}$) in pPb and both $v_{\rm 2}$ and triangular azimuthal anisotropy ($v_{\rm 3}$) in PbPb collisions are measured at $\sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV with the CMS detector at the LHC. The normalized difference of $v_{\rm 2}$ between positively and negatively charged particles, ($v_{\rm 2}^{-}-v_{\rm 2}^{+}$)/($v_{\rm 2}^{-}+v_{\rm 2}^{+}$), shows a linear dependence with respect to the event-charged asymmetry $A_{\rm ch}$, with comparable slopes observed for pPb and PbPb collisions at similar multiplicities. In PbPb collisions, the slopes are found to be the same for the $v_{\rm 2}$ and $v_{\rm 3}$ coefficients within uncertainties. These observations pose a challenge to the hypothesis that the charge asymmetry dependence of $v_{\rm 2}$ arises from a chiral magnetic wave. However, the results are in qualitative agreement with expectations based on local charge conservation. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
inSPIRE record ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, PRC 100 (2019) 064908. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
Figure 1:
Elliptic flow $v_2$ for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $v_{2}$ difference, $(v^{-}_{2} - v^{+}_{2})/(v^{-}_{2} + v^{+}_{2})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are indicated by the error bars. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Elliptic flow $v_2$ for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $v_{2}$ difference, $(v^{-}_{2} - v^{+}_{2})/(v^{-}_{2} + v^{+}_{2})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in pPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are indicated by the error bars. |

png pdf |
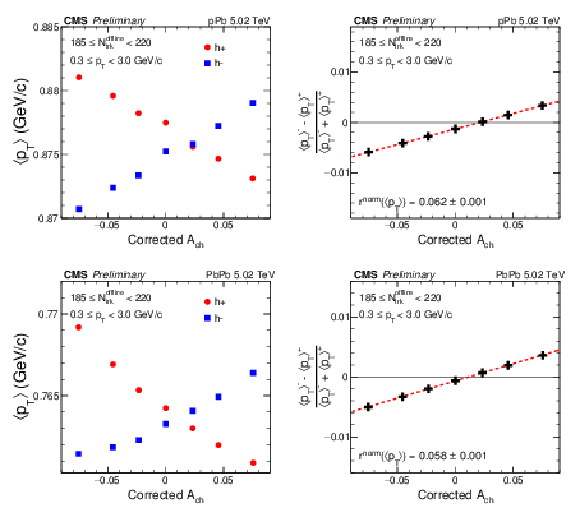
Figure 1-b:
Elliptic flow $v_2$ for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $v_{2}$ difference, $(v^{-}_{2} - v^{+}_{2})/(v^{-}_{2} + v^{+}_{2})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are indicated by the error bars. |
png pdf |
Figure 2:
The event-averaged $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} $ value ($ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$) for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$ difference, $( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} - < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})/( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} + < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in pPb and PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are covered by the data points. |
png pdf |
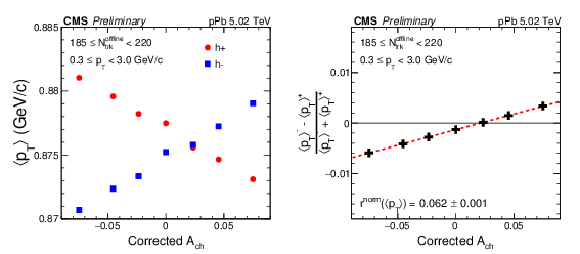
Figure 2-a:
The event-averaged $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} $ value ($ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$) for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$ difference, $( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} - < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})/( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} + < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in pPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are covered by the data points. |
png pdf |
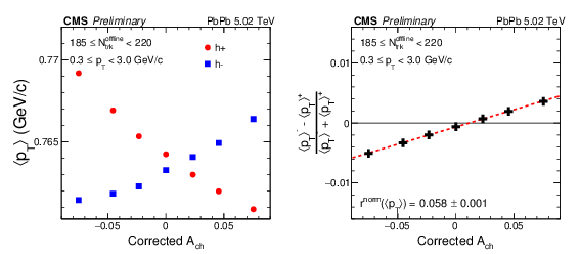
Figure 2-b:
The event-averaged $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} $ value ($ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$) for positive- and negative-charged particles as a function of charge asymmetry (left) and the normalized $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$ difference, $( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} - < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})/( < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{-} + < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >^{+})$, as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry (right) for multiplicity range 185 $ \leq {N_\mathrm {trk}^\mathrm {offline}} < $ 220 in PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are covered by the data points. |

png pdf |
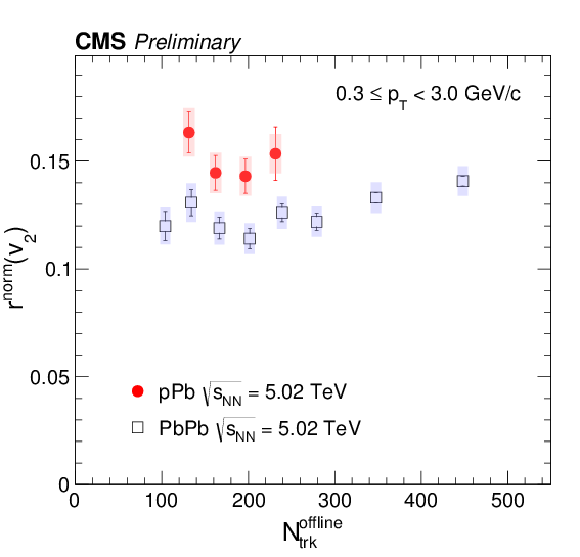
Figure 3:
The linear slope for $v_2$ (left) and $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$ (right) parameters $r^{\rm norm}_{2}$ and $r^{\rm norm}_{ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >}$ as a function of event multiplicity in pPb and PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. Statistical and systematic uncertainties are indicated by the error bars and shaded regions, respectively. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
The linear slope for $v_2$ parameter $r^{\rm norm}_{2}$ as a function of event multiplicity in pPb and PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. Statistical and systematic uncertainties are indicated by the error bars and shaded regions, respectively. |
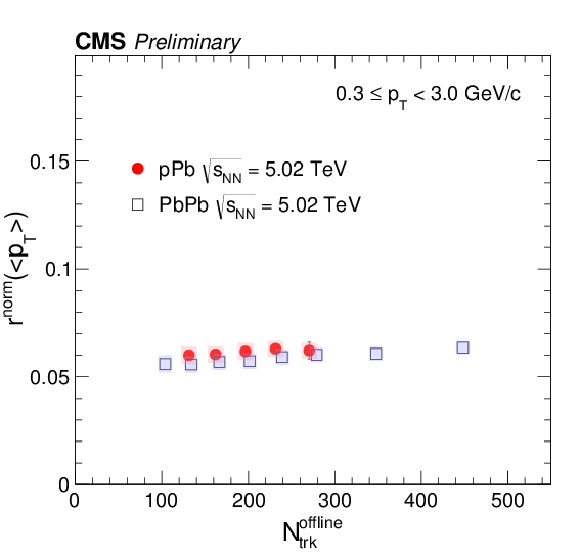
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
The linear slope for $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >$ parameter $r^{\rm norm}_{ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} >}$ as a function of event multiplicity in pPb and PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. Statistical and systematic uncertainties are indicated by the error bars and shaded regions, respectively. |
png pdf |
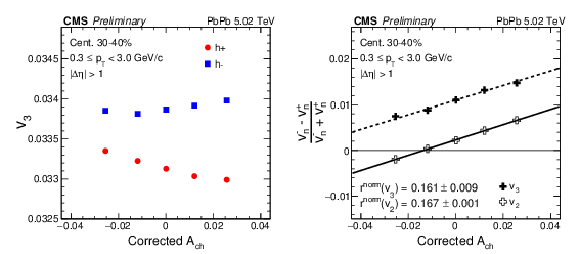
Figure 4:
The triangular flow $v_3$ for positive- and negative-charged particles (left) and the normalized difference in $v_{n}$, $(v^{-}_{n} - v^{+}_{n})/(v^{-}_{n} + v^{+}_{n})$, for $n=$ 2 and $n=$ 3 (right) as a function of corrected event charge asymmetry for 30-40% centrality of PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. Statistical uncertainties are covered by the data points. |
png pdf |
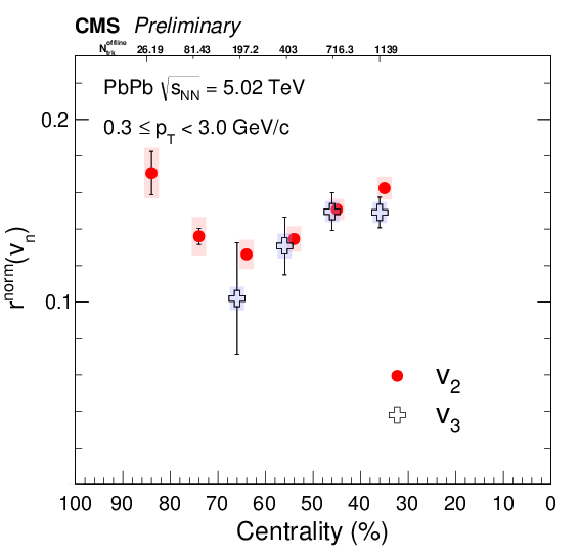
Figure 5:
The linear slope ($r^{\rm norm}_{n}$) parameter for elliptic ($n=$ 2) and triangular ($n=$ 3) flow as a function of centrality for PbPb collisions at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. Statistical and systematic uncertainties are indicated by the error bars and shaded regions, respectively. |
| Summary |
| The charged-dependent elliptic flow coefficients ($v_{2}$) in pPb and both $v_{2}$ and triangular flow coefficients ($v_{3}$) in PbPb have been measured as a function of event-charged asymmetry at $ \sqrt{ s_{\text{NN}} } = $ 5.02 TeV. The normalized slope parameters of $v_{2}$ in pPb and PbPb collisions are found to be similar at the same event-charged particle multiplicities. Moreover, the normalized slope parameters of the $v_{2}$ and $v_{3}$ coefficients show similar magnitudes in various centralities. These observations would not be expected if the charge dependence resulted from a Chiral Magnetic Wave mechanism. The data are qualitatively consistent with predictions from the local charge conservation mechanism. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | T. D. Lee | A Theory of Spontaneous T Violation | PRD8 (1973) 1226--1239, .[,516(1973)] | |
| 2 | T. D. Lee and G. C. Wick | Vacuum Stability and Vacuum Excitation in a Spin 0 Field Theory | PRD9 (1974) 2291--2316 | |
| 3 | P. D. Morley and I. A. Schmidt | Strong P, CP, T violations in heavy-ion collisions | Zeitschrift f\"ur Physik C Particles and Fields 26 (1985) 627 | |
| 4 | D. Kharzeev, R. D. Pisarski, and M. H. G. Tytgat | Possibility of Spontaneous Parity Violation in Hot QCD | PRL 81 (1998) 512 | hep-ph/9804221 |
| 5 | D. Kharzeev | Parity violation in hot QCD: Why it can happen, and how to look for it | PLB 633 (2006) 260 | hep-ph/0406125 |
| 6 | D. E. Kharzeev, L. D. McLerran, and H. J. Warringa | The Effects of topological charge change in heavy ion collisions: 'Event by event P and CP violation' | Nucl. Phys. A 803 (2008) 227--253 | 0711.0950 |
| 7 | D. E. Kharzeev, J. Liao, S. A. Voloshin, and G. Wang | Chiral magnetic and vortical effects in high-energy nuclear collisions—A status report | Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 88 (2016) 1--28 | 1511.04050 |
| 8 | Y. Burnier, D. E. Kharzeev, J. Liao, and H.-U. Yee | Chiral magnetic wave at finite baryon density and the electric quadrupole moment of quark-gluon plasma in heavy ion collisions | PRL 107 (2011) 052303 | 1103.1307 |
| 9 | G. M. Newman | Anomalous hydrodynamics | JHEP 01 (2006) 158 | hep-ph/0511236 |
| 10 | E. V. Gorbar, V. A. Miransky, and I. A. Shovkovy | Normal ground state of dense relativistic matter in a magnetic field | PRD 83 (2011) 085003 | 1101.4954 |
| 11 | ALICE Collaboration | Charge separation relative to the reaction plane in Pb-Pb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}}= $ 2.76 TeV | PRL 110 (2013) 012301 | 1207.0900 |
| 12 | STAR Collaboration | Observation of charge asymmetry dependence of pion elliptic flow and the possible chiral magnetic wave in heavy-ion collisions | PRL 114 (2015) 252302 | 1504.02175 |
| 13 | ALICE Collaboration | Charge-dependent flow and the search for the chiral magnetic wave in Pb-Pb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PRC 93 (2016) 044903 | 1512.05739 |
| 14 | A. Bzdak and P. Bozek | Contributions to the event-by-event charge asymmetry dependence for the elliptic flow of $ pi^{+} $ and $ pi^{-} $ in heavy-ion collisions | PLB 726 (2013) 239 | 1303.1138 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of Long-Range Near-Side Angular Correlations in Proton-Proton Collisions at the LHC | JHEP 09 (2010) 091 | CMS-QCD-10-002 1009.4122 |
| 16 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of Long-Range Elliptic Azimuthal Anisotropies in $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 and 2.76 TeV pp Collisions with the ATLAS Detector | PRL 116 (2016) 172301 | 1509.04776 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of Long-Range Near-Side Two-Particle Angular Correlations in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 116 (2016) 172302 | CMS-FSQ-15-002 1510.03068 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for collectivity in pp collisions at the LHC | Submitted to PLB | CMS-HIN-16-010 1606.06198 |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of long-range near-side angular correlations in proton-lead collisions at the LHC | PLB 718 (2013) 795 | CMS-HIN-12-015 1210.5482 |
| 20 | ALICE Collaboration | Long-range angular correlations on the near and away side in pPb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 719 (2013) 29 | 1212.2001 |
| 21 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of associated near-side and away-side long-range correlations in $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = $ 5.02 TeV proton-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRL 110 (2013) 182302 | 1212.5198 |
| 22 | LHCb Collaboration | Measurements of long-range near-side angular correlations in $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}}= $ 5 TeV proton-lead collisions in the forward region | 1512.00439 | |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | Long-range two-particle correlations of strange hadrons with charged particles in pPb and PbPb collisions at LHC energies | PLB 742 (2015) 200 | CMS-HIN-14-002 1409.3392 |
| 24 | ALICE Collaboration | Long-range angular correlations of $ \pi $, K and p in p--Pb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 726 (2013) 164 | 1307.3237 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration | Multiplicity and transverse momentum dependence of two- and four-particle correlations in pPb and $PbPb collisions | PLB 724 (2013) 213 | CMS-HIN-13-002 1305.0609 |
| 26 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of long-range pseudorapidity correlations and azimuthal harmonics in $ \sqrt{s_{\rm NN}} = $ 5.02 TeV proton-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRC 90 (2014) 044906 | 1409.1792 |
| 27 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for Collective Multiparticle Correlations in p-Pb Collisions | PRL 115 (2015) 012301 | CMS-HIN-14-006 1502.05382 |
| 28 | K. Dusling, W. Li, and B. Schenke | Novel collective phenomena in high-energy proton-proton and proton-nucleus collisions | Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 25 (2016) 1630002 | 1509.07939 |
| 29 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of charge-dependent azimuthal correlations in pPb collisions and its implication for the search for the chiral magnetic effect | CMS-HIN-16-009 1610.00263 |
|
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 32 | T. Pierog et al. | EPOS LHC : test of collective hadronization with LHC data | 1306.0121 | |
| 33 | M. Gyulassy and X.-N. Wang | HIJING 1.0: A Monte Carlo program for parton and particle production in high-energy hadronic and nuclear collisions | CPC 83 (1994) 307 | nucl-th/9502021 |
| 34 | I. P. Lokhtin et al. | Heavy ion event generator HYDJET++ (HYDrodynamics plus JETs) | CPC 180 (2009) 779 | 0809.2708 |
| 35 | A. Bilandzic, R. Snellings, and S. Voloshin | Flow analysis with cumulants: Direct calculations | Phys.Rev. C83 (2011) 044913 | 1010.0233 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|