

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-FTR-18-036 | ||
| Anomalous couplings in the ttZ final state at the HL-LHC | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| December 2018 | ||
| Abstract: The electroweak couplings of the top quark provide a crucial window to physics beyond the standard model and can be put to stringent tests with the CERN High-Luminosity LHC (HL-LHC). The expected sensitivity of the CMS detector for anomalous electroweak top quark interactions based on differential cross section measurements of the ttZ process in the three lepton final state is provided for a HL-LHC scenario with 3000 fb$^{-1}$ of proton-proton collision data at a centre-of-mass energy of 14 TeV. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures & Tables | Summary | Additional Figures & Tables | References | CMS Publications |
|---|
| Figures | |
png pdf |
Figure 1:
Representative Feynman diagram for the ttZ process. |
png pdf |
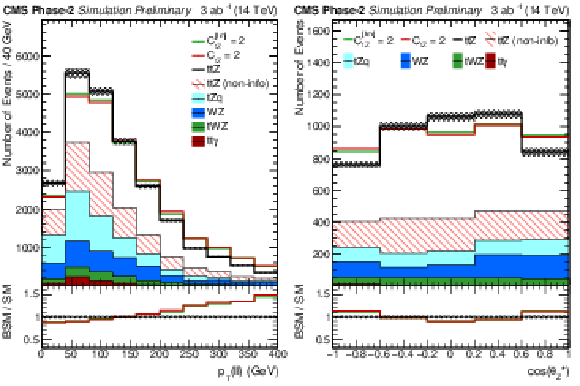
Figure 2:
Differential cross sections with respect to $ { {p_\textrm {T}} ({\mathrm {Z}})} $ (left) and $\cos\theta ^\ast _{{\mathrm {Z}}}$ (right) in the ttZ (${N_{\textrm {lep}}}= $ 3) channel as specified in Table 2 and for the Phase-2 scenario. For $\cos\theta ^\ast _{{\mathrm {Z}}}$, an additional requirement of $ { {p_\textrm {T}} ({\mathrm {Z}})} > $ 200 GeV is applied. The SM distributions are shown in black with systematic uncertainties, while colored lines show hypotheses for ${C_\text {tZ}} $=2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$ and ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}} = $ 2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$, with yields that are area-normalized to the SM distribution. The non-informative contribution to ttZ is described in Sec. 4 and shown hatched. Backgrounds are shown in solid colors. |
png pdf |
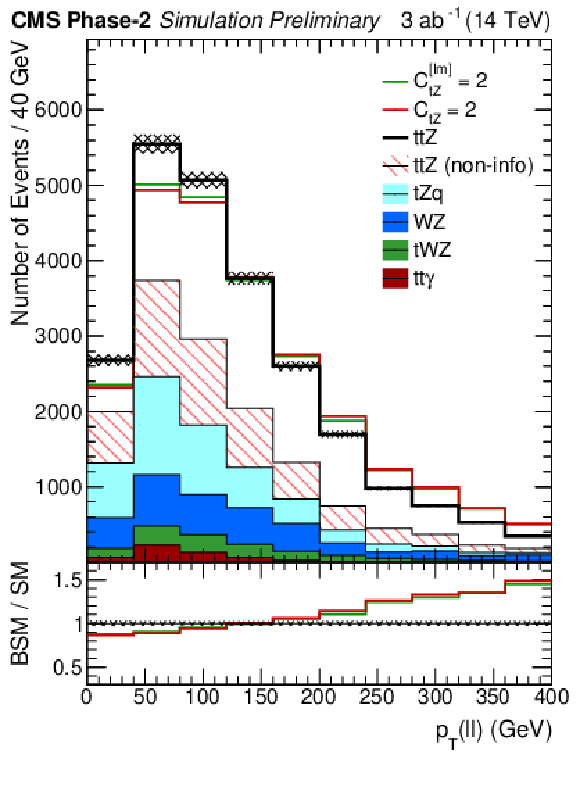
Figure 2-a:
Differential cross sections with respect to $ { {p_\textrm {T}} ({\mathrm {Z}})} $ in the ttZ (${N_{\textrm {lep}}}= $ 3) channel as specified in Table 2 and for the Phase-2 scenario. For $\cos\theta ^\ast _{{\mathrm {Z}}}$, an additional requirement of $ { {p_\textrm {T}} ({\mathrm {Z}})} > $ 200 GeV is applied. The SM distributions are shown in black with systematic uncertainties, while colored lines show hypotheses for ${C_\text {tZ}} $=2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$ and ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}} = $ 2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$, with yields that are area-normalized to the SM distribution. The non-informative contribution to ttZ is described in Sec. 4 and shown hatched. Backgrounds are shown in solid colors. |
png pdf |
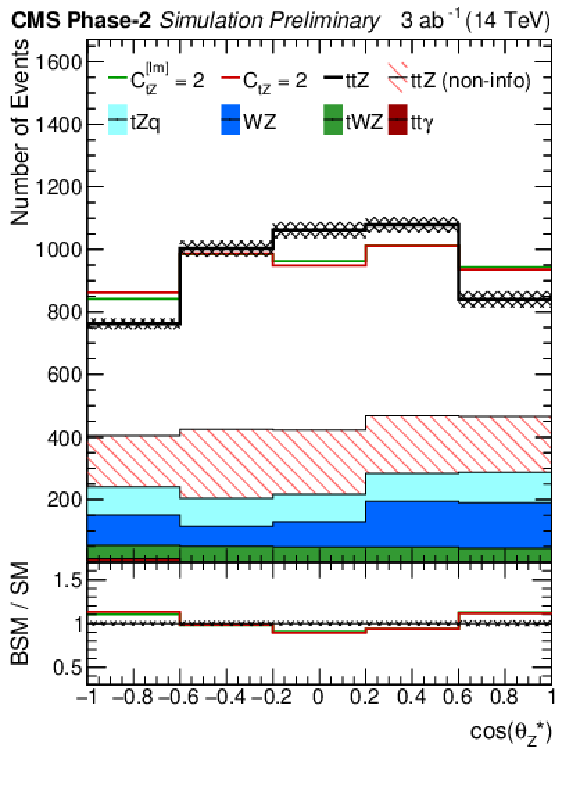
Figure 2-b:
Differential cross sections with respect to $\cos\theta ^\ast _{{\mathrm {Z}}}$ in the ttZ (${N_{\textrm {lep}}}= $ 3) channel as specified in Table 2 and for the Phase-2 scenario. For $\cos\theta ^\ast _{{\mathrm {Z}}}$, an additional requirement of $ { {p_\textrm {T}} ({\mathrm {Z}})} > $ 200 GeV is applied. The SM distributions are shown in black with systematic uncertainties, while colored lines show hypotheses for ${C_\text {tZ}} $=2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$ and ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}} = $ 2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$, with yields that are area-normalized to the SM distribution. The non-informative contribution to ttZ is described in Sec. 4 and shown hatched. Backgrounds are shown in solid colors. |
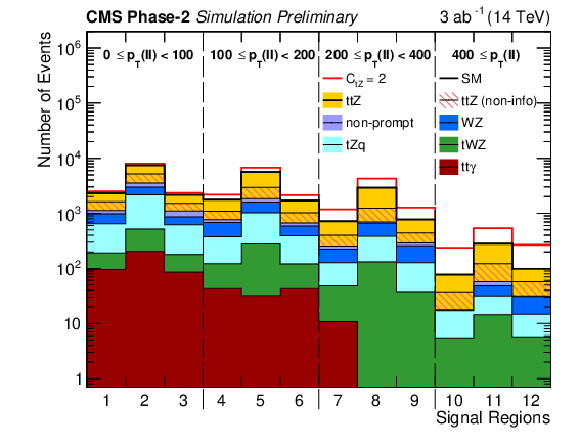
png pdf |
Figure 3:
Signal region yields from simulation for SM processes (colored histograms). The yields are estimated for an integrated luminosity of 3/ab, the cross section is scaled to 14 TeV. The total SM yield is shown with the black line, the dashed red line reflects the total expected yield assuming modified couplings, with the chosen value ${C_\text {tZ}} = $ 2 ($\Lambda $/TeV)$^2$. The hatched area represents the non-informative contribution to ttZ as described in Sec. 4. |
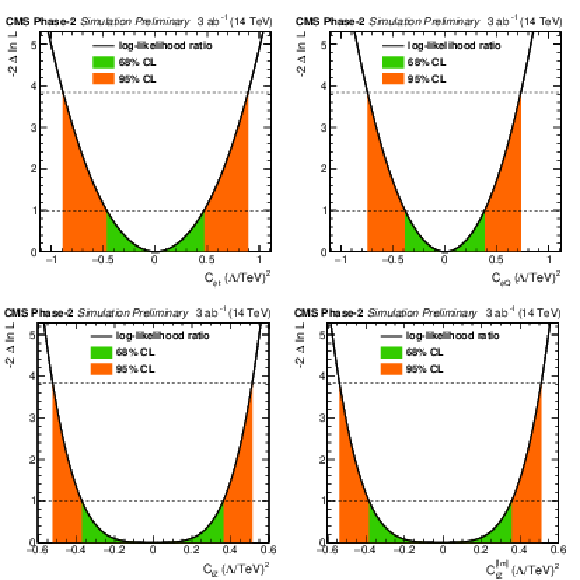
png pdf |
Figure 4:
Individual likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients $ {C_{\phi t}} $ and ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}}$ (top) and ${C_\text {tZ}}$ and ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ (bottom) for the ttZ process. Here, only one Wilson coefficient at a time is considered non-zero. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
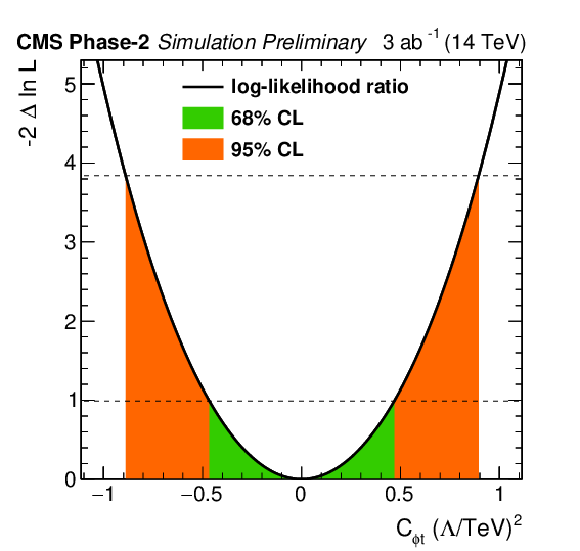
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Individual likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients $ {C_{\phi t}} $ for the ttZ process. Other Wilson coefficients are set to zero. The 68% (95%) CL interval is given in green (red). |
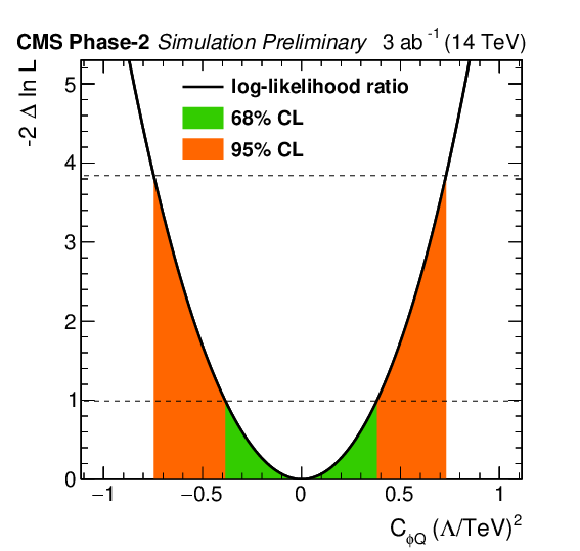
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Individual likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}}$ for the ttZ process. Other Wilson coefficients are set to zero. The 68% (95%) CL interval is given in green (red). |
png pdf |
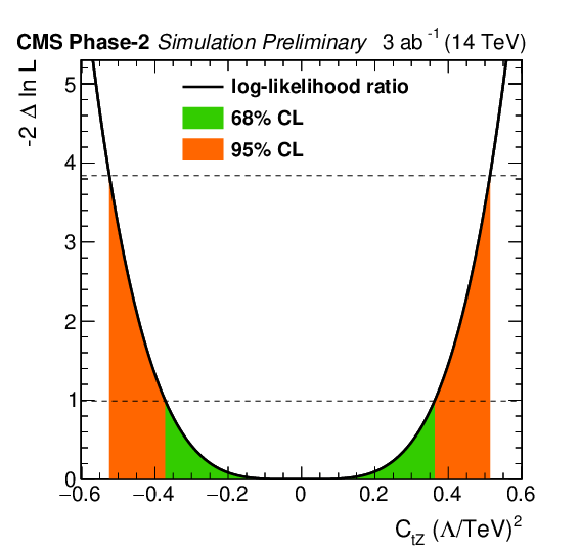
Figure 4-c:
Individual likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_\text {tZ}}$ for the ttZ process. Other Wilson coefficients are set to zero. The 68% (95%) CL interval is given in green (red). |
png pdf |
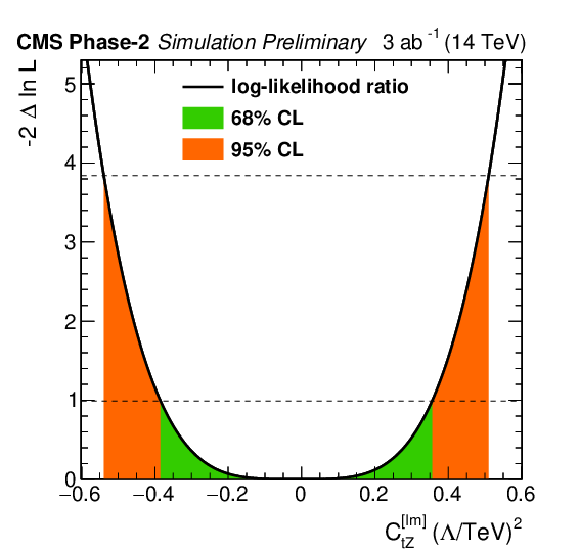
Figure 4-d:
Individual likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ for the ttZ process. Other Wilson coefficients are set to zero. The 68% (95%) CL interval is given in green (red). |
png pdf |
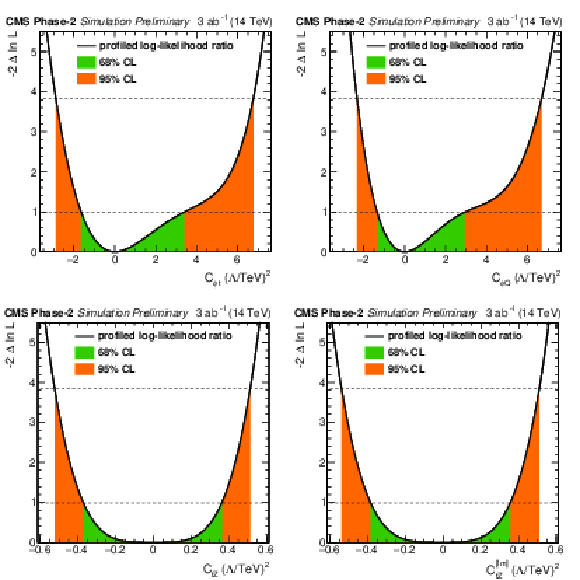
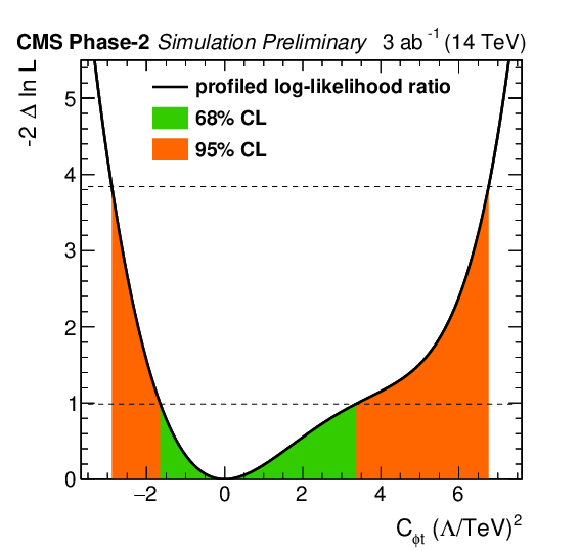
Figure 5:
Individual profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients $ {C_{\phi t}} $ and ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}}$ (top) and ${C_\text {tZ}}$ and ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ (bottom) for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
Individual profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients $ {C_{\phi t}} $ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
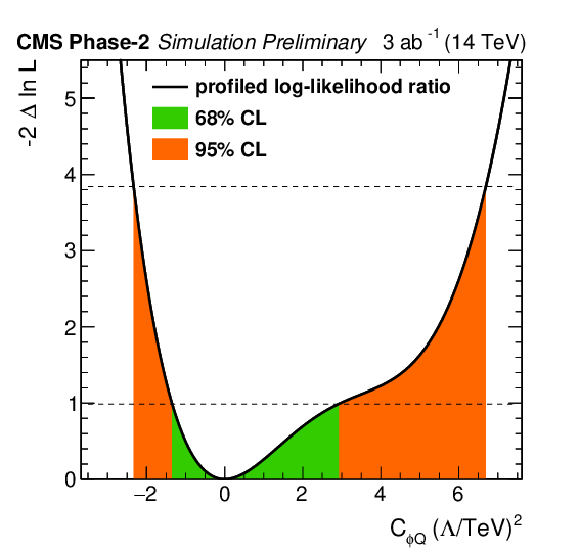
Figure 5-b:
Individual profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
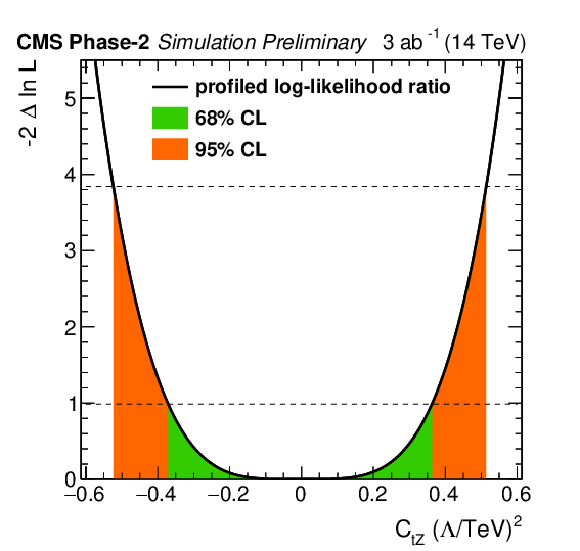
Figure 5-c:
Individual profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_\text {tZ}}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
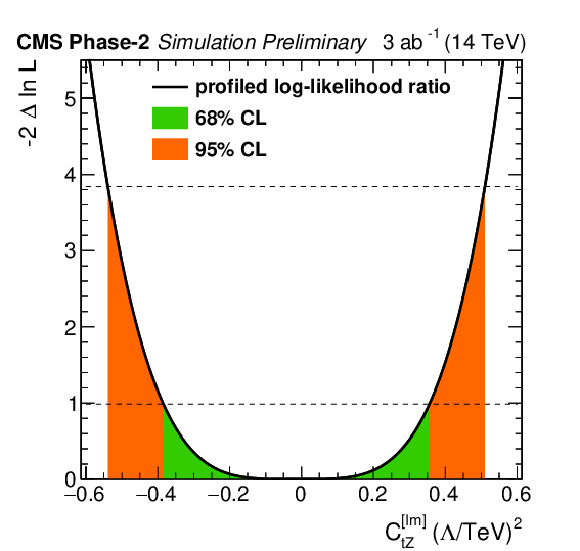
Figure 5-d:
Individual profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficients ${C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
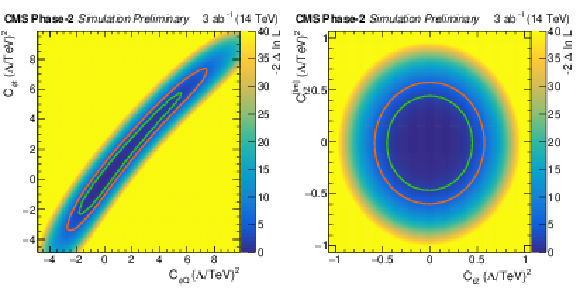
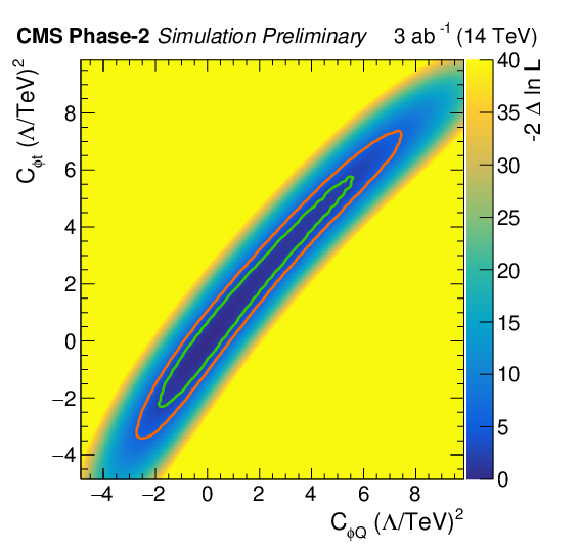
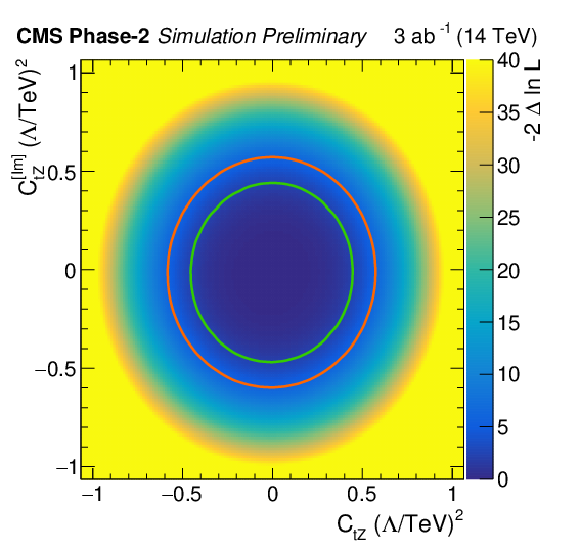
Figure 6:
Scan of the negative likelihood in the ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}} / {C_{\phi t}}$ (left) and ${C_\text {tZ}} / {C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ parameter planes (right) for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL contour lines are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
Figure 6-a:
Scan of the negative likelihood in the ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}} / {C_{\phi t}}$ parameter plane for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL contour lines are given in green (red). |
png pdf |
Figure 6-b:
Scan of the negative likelihood in the ${C_\text {tZ}} / {C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$ parameter plane for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL contour lines are given in green (red). |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
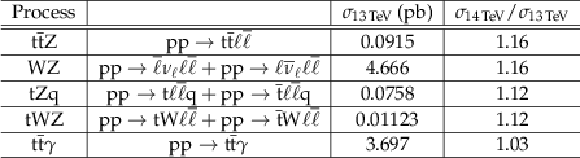
Table 1:
Simulated processes with a Monte-Carlo sample size of one million events, the cross section for $\sqrt {s}=13 TeV $ and the scale factor for $\sqrt {s}=$ 14 TeV . Here, $\ell =$ e, $\mu$, $\tau $ and $\nu _\ell =\nu _e$, $\nu _\mu$, $\nu _\tau $. |
png pdf |
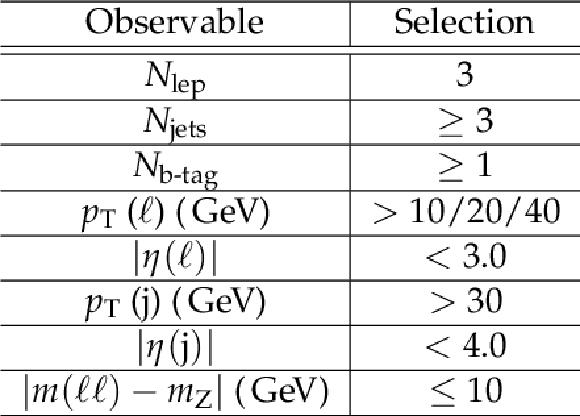
Table 2:
Event selection and object level thresholds for the ttZ selection. |
png pdf |
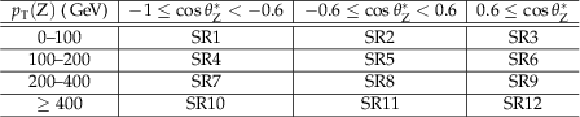
Table 3:
Definition of the ttZ signal regions. |
png pdf |
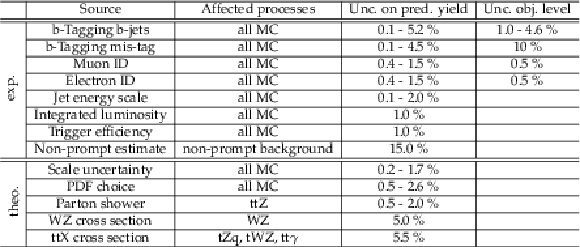
Table 4:
The sources of systematic uncertainty grouped in experimental systematic uncertainties (exp.) and theoretical uncertainties (theo.) as well as their impacts on reconstructed objects and event yields. |
png pdf |
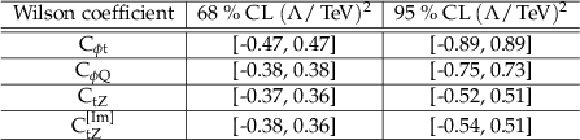
Table 5:
Expected 68% and 95% CL intervals, where one Wilson coefficient at a time is considered non-zero. |
png pdf |
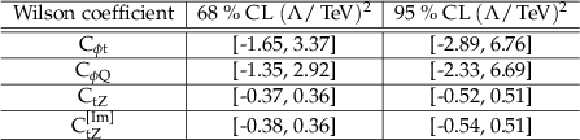
Table 6:
Expected 68% and 95% CL intervals for the selected Wilson coefficients in a profiled scan over the 2D parameter planes ${C_{\phi Q}^{-}} / {C_{\phi t}}$ and ${C_\text {tZ}} / {C_\text {tZ}^\text {[Im]}}$. The respective second parameter of the scan is left free. |
| Summary |
| The CMS sensitivity to anomalous interactions using ttZ measurements in the HL-LHC era corresponding to a simulated data set of 3 ab$^{-1}$ of integrated luminosity has been been estimated in the context of SM-EFT. The considered scenario assumed advances in both experimental methods and theoretical descriptions of the relevant physics effects. With the reduced theoretical and experimental uncertainties, tight constraints are expected in two planes spanned by a total of four Wilson coefficients and in one dimensional log-likelihood scans. |
| Additional Figures | |
png pdf |
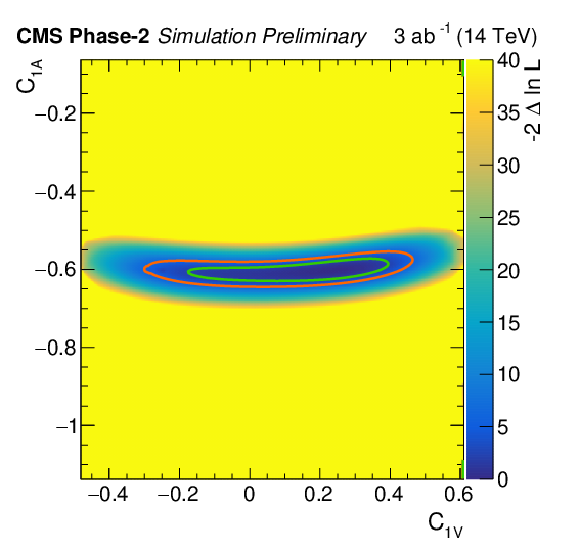
Additional Figure 1:
Scan of the negative likelihood in the $C_\text {1V}$/$C_\text {1A}$ parameter plane for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL contour lines are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. The Standard Model values for $C_\text {1V}$ and $C_\text {1A}$ correspond to 0.244 and -0.601 respectively. |
png pdf |
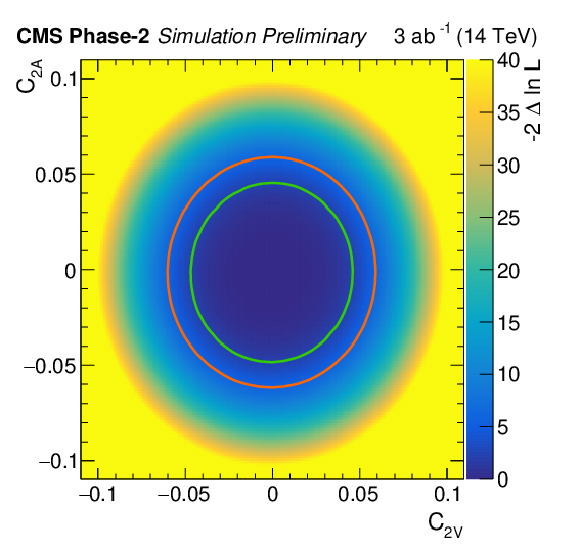
Additional Figure 2:
Scan of the negative likelihood in the $C_\text {2V}$/$C_\text {2A}$ parameter plane for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL contour lines are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. |
png pdf |
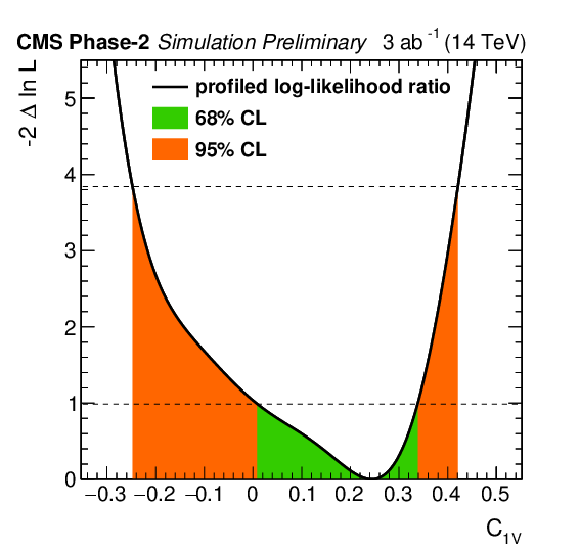
Additional Figure 3:
Profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficient $C_\text {1V}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. The Standard Model value for $C_\text {1V}$ corresponds to 0.244. |
png pdf |
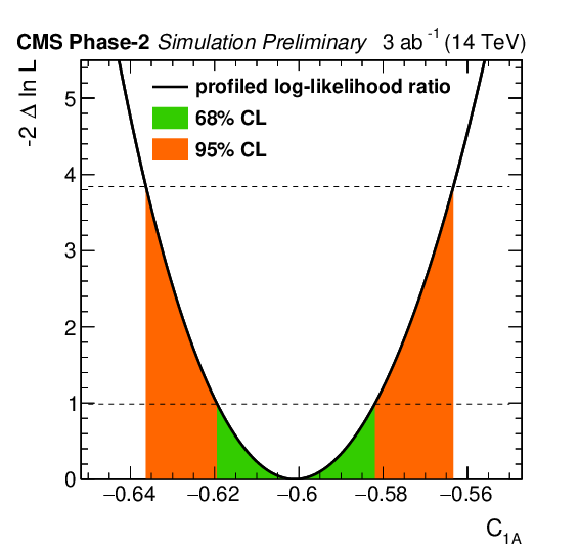
Additional Figure 4:
Profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficient $C_\text {1A}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. The Standard Model value for $C_\text {1A}$ corresponds to -0.601. |
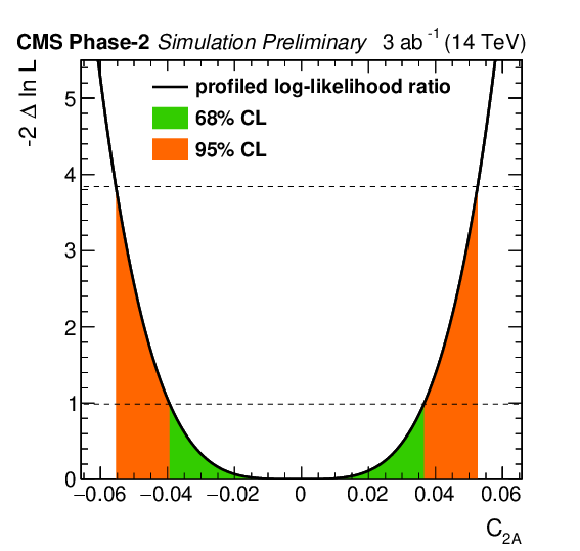
png pdf |
Additional Figure 5:
Profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficient $C_\text {2V}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. |
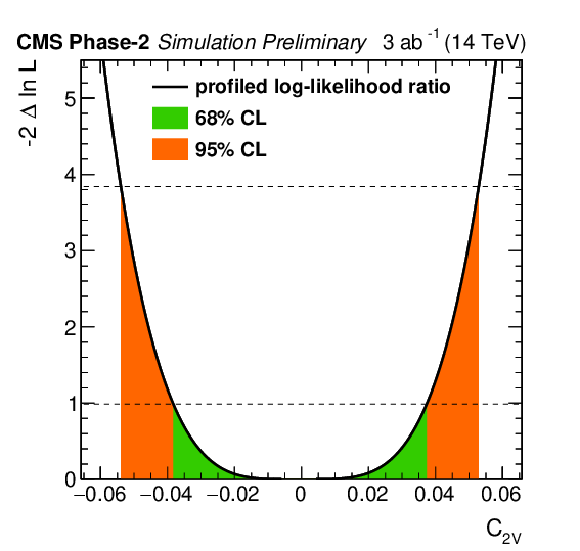
png pdf |
Additional Figure 6:
Profiled likelihood ratio for the Wilson coefficient $C_\text {2A}$ for the ttZ process under the SM hypothesis. The 68% (95%) CL intervals are given in green (red). Parameter definition according to [41,45]. |
| Additional Tables | |
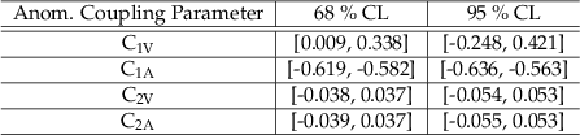
png pdf |
Additional Table 1:
Expected 68 % and 95 % CL intervals for the selected anomalous coupling parameters in a profiled scan over the 2D parameter planes $C_\text {1V}$/$C_\text {1A}$ and $C_\text {2V}$/$C_\text {2A}$. The respective second parameter of the scan is left free. Parameter definition according to [41,45]. The Standard Model values for $C_\text {1V}$ and $C_\text {1A}$ correspond to 0.244 and -0.601 respectively. |
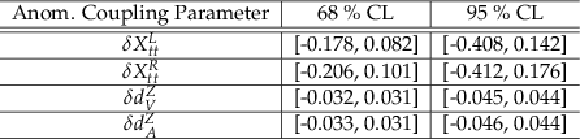
png pdf |
Additional Table 2:
Expected 68 % and 95 % CL intervals for the selected anomalous coupling parameters in a profiled scan over the 2D parameter planes $\delta X_{t t}^{L}$/$\delta X_{t t}^{R}$ and $\delta d_{V}^{Z}$/$\delta d_{A}^{Z}$. The respective second parameter of the scan is left free. Parameter definition according to [45]. |
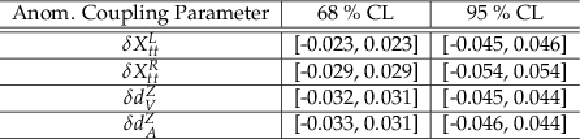
png pdf |
Additional Table 3:
Expected 68 % and 95 % CL intervals, where one anomalous coupling parameter at a time is considered non-zero. Parameter definition according to [45]. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | W. Hollik et al. | Top dipole form-factors and loop induced CP violation in supersymmetry | NPB551 (1999) 3 | hep-ph/9812298 |
| 2 | K. Agashe, G. Perez, and A. Soni | Collider Signals of Top Quark Flavor Violation from a Warped Extra Dimension | PRD75 (2007) 015002 | |
| 3 | A. L. Kagan, G. Perez, T. Volansky, and J. Zupan | General Minimal Flavor Violation | PRD80 (2009) 076002 | |
| 4 | T. Ibrahim and P. Nath | The Top quark electric dipole moment in an MSSM extension with vector like multiplets | PRD82 (2010) 055001 | |
| 5 | T. Ibrahim and P. Nath | The Chromoelectric Dipole Moment of the Top Quark in Models with Vector Like Multiplets | PRD84 (2011) 015003 | |
| 6 | C. Grojean, O. Matsedonskyi, and G. Panico | Light top partners and precision physics | JHEP 10 (2013) 160 | |
| 7 | F. Richard | Can LHC observe an anomaly in ttZ production? | 1304.3594 | |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the cross section for top quark pair production in association with a W or Z boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JHEP 08 (2018) 011 | CMS-TOP-17-005 1711.02547 |
| 9 | M. Schulze and Y. Soreq | Pinning down electroweak dipole operators of the top quark | EPJC76 (2016), no. 8, 466 | 1603.08911 |
| 10 | DELPHES 3 Collaboration | DELPHES 3, A modular framework for fast simulation of a generic collider experiment | JHEP 02 (2014) 057 | 1307.6346 |
| 11 | D. Barducci et al. | Interpreting top-quark LHC measurements in the standard-model effective field theory | 1802.07237 | |
| 12 | B. Grzadkowski, M. Iskrzynski, M. Misiak, and J. Rosiek | Dimension-Six Terms in the Standard Model Lagrangian | JHEP 10 (2010) 085 | 1008.4884 |
| 13 | C. Zhang and S. Willenbrock | Effective-Field-Theory Approach to Top-Quark Production and Decay | PRD83 (2011) 034006 | 1008.3869 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS Experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 15 | G. Apollinari et al. | High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC) : Preliminary Design Report | ||
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Technical Proposal for the Phase-II Upgrade of the CMS Detector | CERN-LHCC-2015-010 | |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Tracker | CERN-LHCC-2017-009 | |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Barrel Calorimeters Technical Design Report | CDS | |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Endcap Calorimeter | CDS | |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Muon Detectors | CDS | |
| 21 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4: A Simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 22 | J. Allison et al. | Geant4 developments and applications | IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53 (2006) 270 | |
| 23 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of $ \mathrm{t\overline{t}} $ differential cross sections in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 TeV using events containing two leptons | CMS-TOP-17-014 1811.06625 |
|
| 24 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the W boson helicity fractions in the decays of top quark pairs to lepton $ + $ jets final states produced in pp collisions at $ \sqrt s= $ 8TeV | PLB762 (2016) 512 | CMS-TOP-13-008 1605.09047 |
| 25 | J. A. Aguilar-Saavedra and J. Bernabeu | W polarisation beyond helicity fractions in top quark decays | NPB840 (2010) 349--378 | 1005.5382 |
| 26 | J. Brehmer, K. Cranmer, F. Kling, and T. Plehn | Better Higgs boson measurements through information geometry | PRD95 (2017), no. 7, 073002 | 1612.05261 |
| 27 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 28 | P. Artoisenet and O. Mattelaer | MadWeight: Automatic event reweighting with matrix elements | PoS CHARGED2008 (2008) 025 | |
| 29 | S. Fichet, A. Tonero, and P. Rebello Teles | Sharpening the shape analysis for higher-dimensional operator searches | PRD96 (2017), no. 3, 036003 | 1611.01165 |
| 30 | P. Artoisenet, R. Frederix, O. Mattelaer, and R. Rietkerk | Automatic spin-entangled decays of heavy resonances in Monte Carlo simulations | JHEP 03 (2013) 015 | 1212.3460 |
| 31 | S. Frixione, E. Laenen, P. Motylinski, and B. R. Webber | Angular correlations of lepton pairs from vector boson and top quark decays in Monte Carlo simulations | JHEP 04 (2007) 081 | hep-ph/0702198 |
| 32 | T. Sjostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Z. Skands | A brief introduction to PYTHIA 8.1 | CPC 178 (2008) 852 | 0710.3820 |
| 33 | T. Sjostrand et al. | An introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | CPC 191 (2015) 159 | 1410.3012 |
| 34 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet User Manual | Eur.Phys.J. C72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 35 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The Anti-k(t) jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 0804 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 36 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the $ t\overline{t}W $ and $ t\overline{t}Z $ production cross sections in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 11 (2015) 172 | 1509.05276 |
| 37 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the $ \mathrm{t\bar{t}}\mathrm{Z} $ and $ \mathrm{t\bar{t}}\mathrm{W} $ production cross sections in multilepton final states using 3.2 fb$ ^{-1} $ of pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC 77 (2017) 40 | 1609.01599 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of associated production of vector bosons and $ \mathrm{t\bar{t}} $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 TeV | PRL 110 (2013) 172002 | CMS-TOP-12-014 1303.3239 |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of top quark-antiquark pair production in association with a W or Z boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | EPJC 74 (2014) 3060 | CMS-TOP-12-036 1406.7830 |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of top quark pairs produced in association with a vector boson in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 8 TeV | JHEP 01 (2016) 096 | CMS-TOP-14-021 1510.01131 |
| 41 | R. Roentsch and M. Schulze | Constraining couplings of top quarks to the Z boson in $ t\overline{t} $ + Z production at the LHC | JHEP 07 (2014) 091 | 1404.1005 |
| 42 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the $ t\bar{t}W $ and $ t\bar{t}Z $ cross sections in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | ATLAS-CONF-2018-047, CERN, Geneva, Sep | |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the cross section for top quark pair production in association with a W or Z boson in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | CMS-TOP-17-005 1711.02547 |
|
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Expected performance of the physics objects with the upgraded CMS detector at the HL-LHC | CDS | |
| 45 | J. A. Aguilar-Saavedra | A Minimal set of top anomalous couplings | NPB812 (2009) 181 | 0811.3842 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|