

Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-HIG-13-035 ; CERN-PH-EP-2015-266 | ||
| Search for a light charged Higgs boson decaying to $ \mathrm{ c \bar{s} } $ in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} =$ 8 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 14 October 2015 | ||
| J. High Energy Phys. 12 (2015) 1 | ||
| Abstract: A search for a light charged Higgs boson, originating from the decay of a top quark and subsequently decaying into a charm quark and a strange antiquark, is presented. The data used in the analysis correspond to an integrated luminosity of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ recorded in proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s}= $ 8 TeV by the CMS experiment at the LHC. The search is performed in the process $ \mathrm{ t \bar{t} \to W^{\pm} b H^{\mp} \bar{b} }$, where the W boson decays to a lepton (electron or muon) and a neutrino. The decays lead to a final state comprising an isolated lepton, at least four jets and large missing transverse energy. No significant deviation is observed in the data with respect to the standard model predictions, and model-independent upper limits are set on the branching fraction ${\cal B} ( \mathrm{ t \to H^{+} b } ) $, ranging from 1.2 to 6.5% for a charged Higgs boson with mass between 90 and 160 GeV, under the assumption that ${\cal B}( \mathrm{ H^{+} \to c \bar{s} } ) =$ 100%. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:1510.04252 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Leading order Feynman diagram for $ {\mathrm {t}\overline {\mathrm {t}}} $ production at the LHC in the $\ell $+jets final state in the SM (a) and additional diagram for the model with a charged Higgs boson (b). |

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
Leading order Feynman diagram for $ {\mathrm {t}\overline {\mathrm {t}}} $ production at the LHC in the $\ell $+jets final state in the SM (a) and additional diagram for the model with a charged Higgs boson (b). |
png pdf |
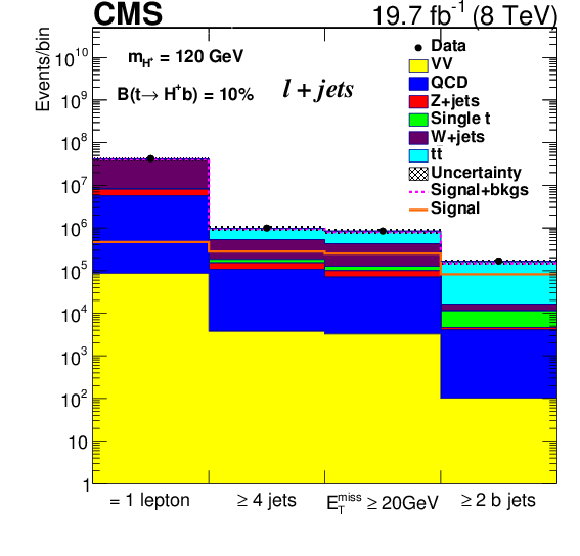
Figure 2:
Number of expected and observed data events after different selection requirements. ``Uncertainty'' in the legend here, and of other plots, includes statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
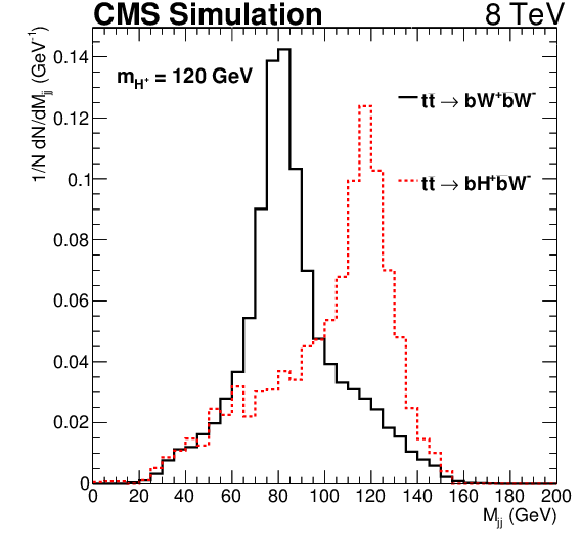
Figure 3:
Invariant mass distributions of the dijet system, assumed to come from $ { {\mathrm {c}} {\overline {\mathrm {s}}}} $ hadronization, obtained with a kinematic fit after all selections. The solid black histogram represents the SM $ {\mathrm {t}\overline {\mathrm {t}}} $ events and the dashed red histogram denotes the same in the presence of a $ {\mathrm {H}} ^{+}$ boson. |
png pdf |
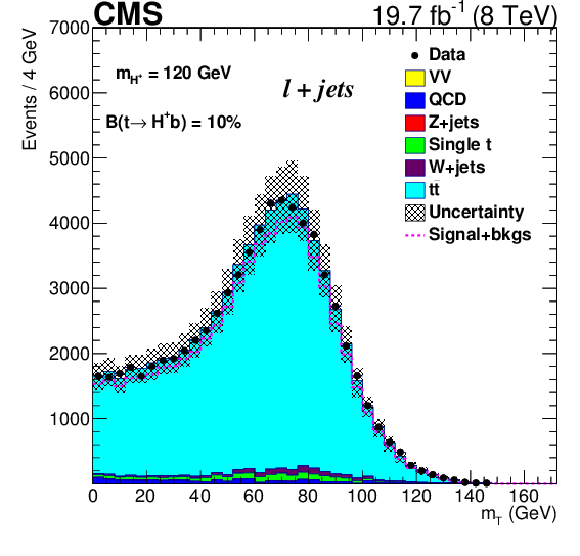
Figure 4:
Transverse mass distribution of the lepton plus $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ system after all selections. |
png pdf |
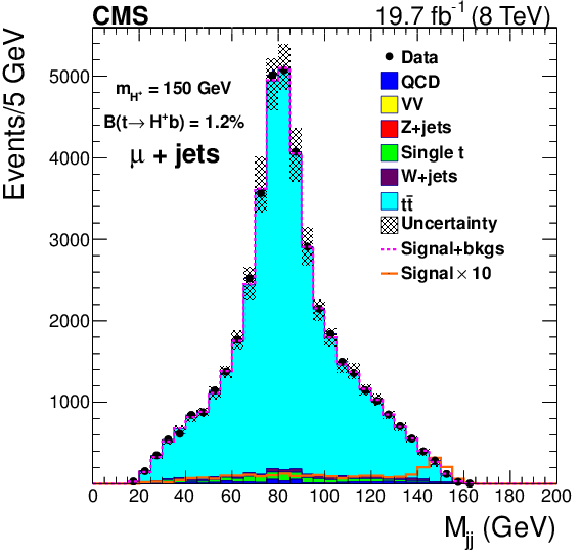
Figure 5-a:
Dijet mass distributions of the hadronically decaying boson after all selections, using background templates and constrained uncertainties obtained from the maximum likelihood fit, for the muon+jets (a) and electron+jets (b) channel. The dotted line represents the expected yield in the presence of signal. |
png pdf |
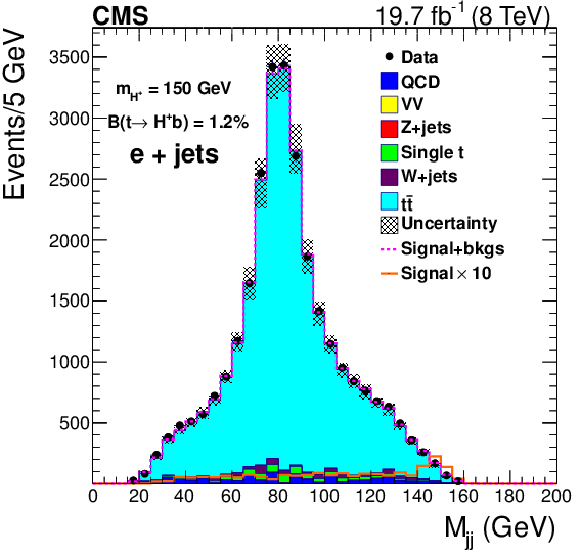
Figure 5-b:
Dijet mass distributions of the hadronically decaying boson after all selections, using background templates and constrained uncertainties obtained from the maximum likelihood fit, for the muon+jets (a) and electron+jets (b) channel. The dotted line represents the expected yield in the presence of signal. |
png pdf |
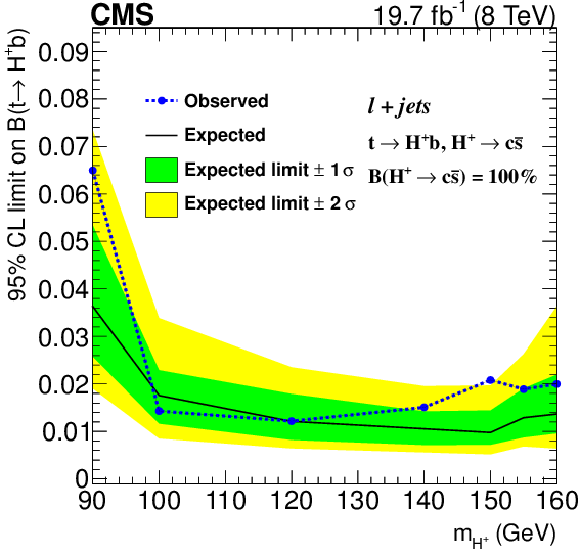
Figure 6:
Exclusion limit on the branching fraction ${\cal B}( { {\mathrm {t}}\to {\mathrm {H}} ^{+} {\mathrm {b}}} )$ as a function of $m_{ {\mathrm {H}} ^+}$ assuming ${\cal B}( { {\mathrm {H}} ^{+}\to {\mathrm {c}} {\overline {\mathrm {s}}}} )=$ 100%. |

png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
An expanded view of the dijet mass distribution of the hadronically decaying boson after all selections, using background templates and constrained uncertainties obtained from the maximum likelihood fit, for the muon+jets (a) and electron+jets (b) channel. The dotted line represents the expected yield in the presence of signal. |
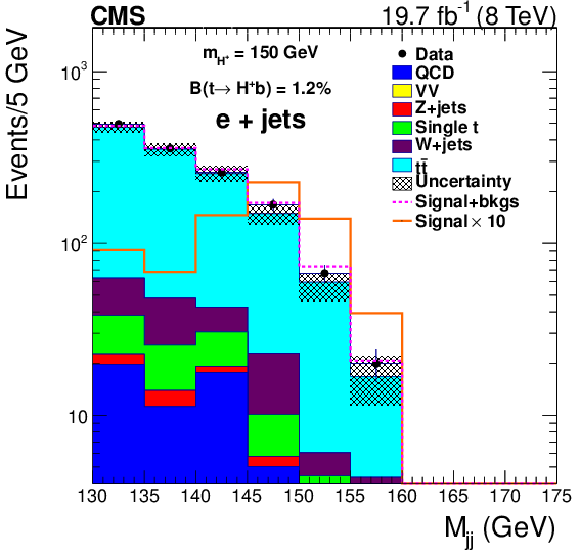
png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
An expanded view of the dijet mass distribution of the hadronically decaying boson after all selections, using background templates and constrained uncertainties obtained from the maximum likelihood fit, for the muon+jets (a) and electron+jets (b) channel. The dotted line represents the expected yield in the presence of signal. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
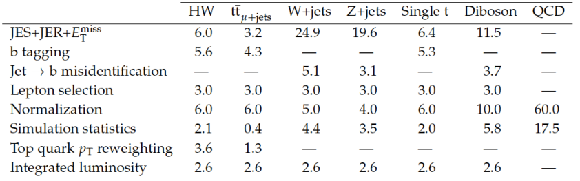
Table 1:
Systematic uncertainties (in percent) for the yield of signal and background processes after all selections in the muon+jets channel. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Systematic uncertainties (in percent) for the yield of signal and background processes after all selections in the electron+jets channel. |
png pdf |
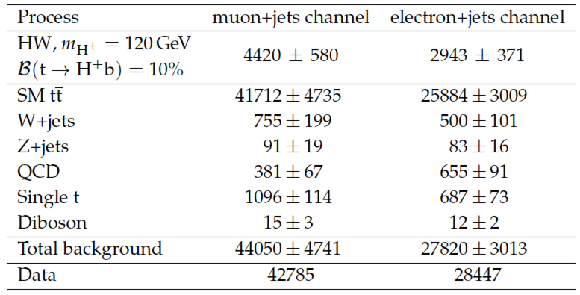
Table 3:
The number of expected signal and background events in 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ of data, along with their combined statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
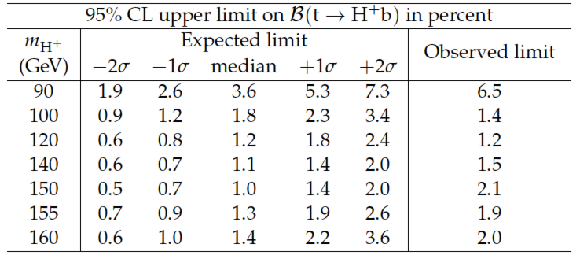
Table 4:
Expected and observed limits on ${\cal B}( { {\mathrm {t}}\to {\mathrm {H}} ^{+} {\mathrm {b}}} )$ (in percent) at 95% CL in the mass range of 90 to 160 GeV . |
| Summary |
| A search has been performed for a light charged Higgs boson produced in the top quark decay, subsequently decaying into a charm quark and a strange antiquark. The data sample used in the analysis corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 19.7 fb$^{-1}$ recorded by the CMS experiment at $\sqrt{s} =$ 8 TeV in pp collisions. After analyzing the dijet mass distribution of the $ \mathrm{ H^+ \to c \bar{s} } $ candidate events that comprise an isolated lepton, at least four hadronic jets, two of which are identified as b jets, and large missing transverse energy, we have set model-independent upper limits on the branching fraction $ {\cal B}( \mathrm{ t \to H^+ b } )$ assuming ${\cal B}( \mathrm{ H^+ \to c \bar{s} }) =$ 100%. The 95% confidence level upper limits are in the range 1.2-6.5% for a charged Higgs boson mass between 90 and 160 GeV. |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|

|

|

|

|

|